Abstract
Trial design
Peripheral neuropathy is a commonly reported adverse effect of oxaliplatin treatment, representing a significant limitation which may require discontinuation of effective therapy. The present study investigated the neuroprotective potential of riluzole in patients undergoing oxaliplatin treatment in a randomised-controlled trial comparing riluzole and placebo-control.
Methods
Fifty-two patients (17 females, 58.1 ± 12.7 years) receiving oxaliplatin treatment were randomised into either a treatment (50 mg riluzole) or lactose placebo group. The primary outcome measure was the total neuropathy score-reduced (TNSr). Secondary outcome measures include nerve excitability measures, 9-hole pegboard and FACT-GOG NTX questionnaire. Patients were assessed at baseline, pre-cycle 10 or 12, 4-week and 12-week post-treatment.
Results
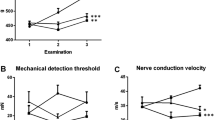
Both the treatment and placebo groups developed objective and patient reported evidence of neurotoxicity over the course of oxaliplatin treatment, although there were no significant differences across any parameters between the two groups. However, across follow-up assessments, the treatment group experienced greater neuropathy, represented by a higher TNSr score at 4-week post-chemotherapy of 8.3 ± 2.7 compared with 4.6 ± 3.6 (p = 0.032) which was sustained at 12-week post-treatment (p = 0.089). Similarly, patients in the treatment group reported worse symptoms with a FACT-GOG NTX score of 37.4 ± 10.2 compared with 43.3 ± 7.4 (p = 0.02) in the placebo group at 4-week post-treatment.
Conclusion
This study is the first to provide an objective clinical investigation of riluzole in oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy employing both functional and neurophysiological measures. Although the recruitment target was not reached, the results do not show any benefit of riluzole in minimising neuropathy and may suggest that riluzole worsens neuropathy associated with oxaliplatin treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKeage MJ, Hsu T, Screnci D, Haddad G, Baguley BC (2001) Nucleolar damage correlates with neurotoxicity induced by different platinum drugs. Br J Cancer 85(8):1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.2001.2024
Amptoulach S, Tsavaris N (2011) Neurotoxicity caused by the treatment with platinum analogues. Chemother Res Pract 2011:843019–843015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/843019
Cassidy J, Misset JL (2002) Oxaliplatin-related side effects: characteristics and management. Semin Oncol 29(5 Suppl 15):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1053/sonc.2002.35524
Argyriou AA, Cavaletti G, Briani C, Velasco R, Bruna J, Campagnolo M, Alberti P, Bergamo F, Cortinovis D, Cazzaniga M, Santos C, Papadimitriou K, Kalofonos HP (2013) Clinical pattern and associations of oxaliplatin acute neurotoxicity: a prospective study in 170 patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer 119(2):438–444. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.27732
Staff NP, Grisold A, Grisold W, Windebank AJ (2017) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a current review. Ann Neurol 81(6):772–781. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24951
Velasco R, Bruna J, Briani C, Argyriou AA, Cavaletti G, Alberti P, Frigeni B, Cacciavillani M, Lonardi S, Cortinovis D, Cazzaniga M, Santos C, Kalofonos HP (2014) Early predictors of oxaliplatin-induced cumulative neuropathy in colorectal cancer patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85(4):392–398. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2013-305334
Krishnan AV, Goldstein D, Friedlander M, Kiernan MC (2005) Oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity and the development of neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 32(1):51–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.20340
Pietrangeli A, Leandri M, Terzoli E, Jandolo B, Garufi C (2006) Persistence of high-dose oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy at long-term follow-up. Eur Neurol 56(1):13–16. https://doi.org/10.1159/000094376
Craner MJ, Hains BC, Lo AC, Black JA, Waxman SG (2004) Co-localization of sodium channel Nav1.6 and the sodium-calcium exchanger at sites of axonal injury in the spinal cord in EAE. Brain 127(Pt 2):294–303. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh032
Kapoor R, Davies M, Blaker PA, Hall SM, Smith KJ (2003) Blockers of sodium and calcium entry protect axons from nitric oxide-mediated degeneration. Ann Neurol 53(2):174–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10443
Adelsberger H, Quasthoff S, Grosskreutz J, Lepier A, Eckel F, Lersch C (2000) The chemotherapeutic oxaliplatin alters voltage-gated Na(+) channel kinetics on rat sensory neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 406(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(00)00667-1
Deuis JR, Zimmermann K, Romanovsky AA, Possani LD, Cabot PJ, Lewis RJ, Vetter I (2013) An animal model of oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia reveals a crucial role for Nav1.6 in peripheral pain pathways. Pain 154(9):1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.05.032
Sittl R, Lampert A, Huth T, Schuy ET, Link AS, Fleckenstein J, Alzheimer C, Grafe P, Carr RW (2012) Anticancer drug oxaliplatin induces acute cooling-aggravated neuropathy via sodium channel subtype Na(V)1.6-resurgent and persistent current. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(17):6704–6709. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118058109
Park SB, Krishnan AV, Lin CS, Goldstein D, Friedlander M, Kiernan MC (2008) Mechanisms underlying chemotherapy-induced neurotoxicity and the potential for neuroprotective strategies. Curr Med Chem 15(29):3081–3094. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986708786848569
Heide R, Bostock H, Ventzel L, Grafe P, Bergmans J, Fuglsang-Frederiksen A, Finnerup NB, Tankisi H (2018) Axonal excitability changes and acute symptoms of oxaliplatin treatment: in vivo evidence for slowed sodium channel inactivation. Clin Neurophysiol 129(3):694–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.11.015
Pachman DR, Qin R, Seisler D, Smith EM, Kaggal S, Novotny P, Ruddy KJ, Lafky JM, Ta LE, Beutler AS, Wagner-Johnston ND, Staff NP, Grothey A, Dougherty PM, Cavaletti G, Loprinzi CL (2016) Comparison of oxaliplatin and paclitaxel-induced neuropathy (Alliance A151505). Support Care Cancer 24(12):5059–5068. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-016-3373-1
Park SB, Lin CS, Krishnan AV, Goldstein D, Friedlander ML, Kiernan MC (2009) Oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity: changes in axonal excitability precede development of neuropathy. Brain 132(Pt 10):2712–2723. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp219
Lacomblez L, Bensimon G, Leigh PN, Guillet P, Meininger V (1996). Dose-ranging study of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/Riluzole Study Group II. Lancet 347 (9013):1425–1431. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(96)91680-3
Cheah BC, Vucic S, Krishnan AV, Kiernan MC (2010) Riluzole, neuroprotection and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr Med Chem 17(18):1942–1199. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710791163939
Bellingham MC (2011) A review of the neural mechanisms of action and clinical efficiency of riluzole in treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: what have we learned in the last decade? CNS Neurosci Ther 17(1):4–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5949.2009.00116.x
Leinster VH, Robson LG, Shortland PJ (2010) Differential effects of riluzole on subpopulations of adult rat dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. Neuroscience 166(3):942–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.058
Yamamoto S, Egashira N, Tsuda M, Masuda S (2018) Riluzole prevents oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia via inhibition of overexpression of transient receptor potential melastatin 8 in rats. J Pharmacol Sci 138(3):214–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2018.10.006
Yamamoto S, Ushio S, Egashira N, Kawashiri T, Mitsuyasu S, Higuchi H, Ozawa N, Masuguchi K, Ono Y, Masuda S (2017) Excessive spinal glutamate transmission is involved in oxaliplatin-induced mechanical allodynia: a possibility for riluzole as a prophylactic drug. Sci Rep 7(1):9661. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08891-1
Poupon L, Lamoine S, Pereira V, Barriere DA, Lolignier S, Giraudet F, Aissouni Y, Meleine M, Prival L, Richard D, Kerckhove N, Authier N, Balayssac D, Eschalier A, Lazdunski M, Busserolles J (2018) Targeting the TREK-1 potassium channel via riluzole to eliminate the neuropathic and depressive-like effects of oxaliplatin. Neuropharmacology 140:43–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.07.026
Cavaletti G, Jann S, Pace A, Plasmati R, Siciliano G, Briani C, Cocito D, Padua L, Ghiglione E, Manicone M, Giussani G (2006) Multi-center assessment of the total neuropathy score for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. J Peripher Nerv Syst 11(2):135–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1085-9489.2006.00078.x
Cornblath DR, Chaudhry V, Carter K, Lee D, Seysedadr M, Miernicki M, Joh T (1999) Total neuropathy score: validation and reliability study. Neurology 53(8):1660–1664. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.53.8.1660
Burke D, Skuse NF, Lethlean AK (1974) Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 37(6):647–652. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.37.6.647
Buschbacher RM (1999) Tibial nerve motor conduction to the abductor hallucis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 78(6 Suppl):S15–S20. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002060-199911001-00004
Krishnan AV, Lin CS, Park SB, Kiernan MC (2009) Axonal ion channels from bench to bedside: a translational neuroscience perspective. 89 (3):288-313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.08.002
Kiernan MC, Lin CS, Andersen KV, Murray NM, Bostock H (2001) Clinical evaluation of excitability measures in sensory nerve. Muscle Nerve 24(7):883–892. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.1085
Bostock H, Cikurel K, Burke D (1998) Threshold tracking techniques in the study of human peripheral nerve. Muscle Nerve 21(2):137–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-4598(199802)21:2<137::aid-mus1>3.0.co;2-c
Calhoun EA, Welshman EE, Chang CH, Lurain JR, Fishman DA, Hunt TL, Cella D (2003). Psychometric evaluation of the functional assessment of cancer therapy/gynecologic oncology group-neurotoxicity (Fact/GOG-Ntx) questionnaire for patients receiving systemic chemotherapy. Int J Gynecol Cancer 13 (6):741–748. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1438.2003.13603.x
Argyriou A, Chroni E, Polychronopoulos P, Iconomou G, Koutras A, Makatsoris T, Gerolymos M, Gourzis P, Assimakopoulos K, Kalofonos HJN (2006) Efficacy of oxcarbazepine for prophylaxis against cumulative oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy. 67 (12):2253-2255. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000249344.99671.d4
Vucic S, Lin CS, Cheah BC, Murray J, Menon P, Krishnan AV, Kiernan MC (2013) Riluzole exerts central and peripheral modulating effects in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 136(Pt 5):1361–1370. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt085
Lazarevic V, Yang Y, Ivanova D, Fejtova A, Svenningsson P (2018) Riluzole attenuates the efficacy of glutamatergic transmission by interfering with the size of the readily releasable neurotransmitter pool. Neuropharmacology 143:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.09.021
Huang CS, Song JH, Nagata K, Yeh JZ, Narahashi T (1997) Effects of the neuroprotective agent riluzole on the high voltage-activated calcium channels of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282(3):1280–1290
Hebert T, Drapeau P, Pradier L, Dunn RJ (1994) Block of the rat brain IIA sodium channel alpha subunit by the neuroprotective drug riluzole. Mol Pharmacol 45(5):1055–1060
Argyriou AA, Chroni E, Polychronopoulos P, Iconomou G, Koutras A, Makatsoris T, Gerolymos MK, Gourzis P, Assimakopoulos K, Kalofonos HP (2006) Efficacy of oxcarbazepine for prophylaxis against cumulative oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy. Neurology 67(12):2253–2255. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000249344.99671.d4
Ichikawa K, Koyama N, Kiguchi S, Kojima M, Yokota T (2001) Inhibitory effect of oxcarbazepine on high-frequency firing in peripheral nerve fibers. Eur J Pharmacol 420(2–3):119–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-2999(01)01007-x
Schmidt D, Elger CE (2004) What is the evidence that oxcarbazepine and carbamazepine are distinctly different antiepileptic drugs? Epilepsy Behav 5(5):627–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2004.07.004
von Delius S, Eckel F, Wagenpfeil S, Mayr M, Stock K, Kullmann F, Obermeier F, Erdmann J, Schmelz R, Quasthoff S, Adelsberger H, Bredenkamp R, Schmid RM, Lersch C (2007) Carbamazepine for prevention of oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: final results of a randomised, controlled, multicenter phase II study. Investig New Drugs 25(2):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-006-9010-y
Gewandter JS, Brell J, Cavaletti G, Dougherty PM, Evans S, Howie L, McDermott MP, O'Mara A, Smith AG, Dastros-Pitei D, Gauthier LR, Haroutounian S, Jarpe M, Katz NP, Loprinzi C, Richardson P, Lavoie-Smith EM, Wen PY, Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Freeman R (2018) Trial designs for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy prevention: ACTTION recommendations. Neurology 91(9):403–413. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000006083
Cassidy J, Paul J, Soukop M, Habeshaw T, Reed NS, Parkin D, Kaye SB (1998) Clinical trials of nimodipine as a potential neuroprotector in ovarian cancer patients treated with cisplatin. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 41(2):161–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050723
Hershman DL, Unger JM, Crew KD, Minasian LM, Awad D, Moinpour CM, Hansen L, Lew DL, Greenlee H, Fehrenbacher L, Wade JL 3rd, Wong SF, Hortobagyi GN, Meyskens FL, Albain KS (2013) Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of acetyl-L-carnitine for the prevention of taxane-induced neuropathy in women undergoing adjuvant breast cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 31(20):2627–2633. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.44.8738
Kerckhove N, Busserolles J, Stanbury T, Pereira B, Plence V, Bonnetain F, Krakowski I, Eschalier A, Pezet D, Balayssac D (2019). Effectiveness assessment of riluzole in the prevention of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: RILUZOX-01: protocol of a randomised, parallel, controlled, double-blind and multicentre study by the UNICANCER-AFSOS Supportive Care intergroup. BMJ Open 9 (6):e027770. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027770
Funding
This study was supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) Project Grant (#1007628) and a Cancer Institute NSW Program Grant (14/TPG/1–05). SBP is supported by a NHMRC Career Development Fellowship (#1148595). MCK is supported by a NHMRC Practitioner Fellowship (#1156093); and by ForeFront, a large collaborative research group dedicated to the study of neurodegenerative diseases and funded by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia Program Grant (#1132524).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 367 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trinh, T., Park, S.B., Murray, J. et al. Neu-horizons: neuroprotection and therapeutic use of riluzole for the prevention of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy—a randomised controlled trial. Support Care Cancer 29, 1103–1110 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05591-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05591-x