Abstract
Purpose
The incidence and time of onset of acute chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (ACIPN) caused by oxaliplatin remain unclarified. Hence, we investigated the prevalence, onset time, and location of ACIPN symptoms in patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) receiving oxaliplatin without cold stimulation.
Methods
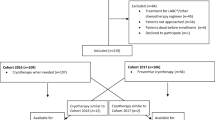
The study cohort comprised patients receiving oxaliplatin for CRC at our hospital between April 2017 and August 2018. Patients were instructed not to touch and/or drink cold things and were monitored for ACIPN symptoms in the hospital for 24 h after chemotherapy. ACIPN symptoms that appeared > 24 h after chemotherapy were recorded at the next visit. Symptom appearance time was defined as the duration from the administration of chemotherapy until the appearance of paresthesia classified as grade 1 using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events.
Results
Forty-five patients received chemotherapy, comprising 23 men and 22 women, aged 67 years (29–88 years). The location of ACIPN was the fingers in 55.6% of cases, pharynx in 26.7%, perioral region in 24.4%, and feet in 6.7%. The average duration from oxaliplatin administration to symptom development was 182 min (range 62–443 min) for the fingers, 291 min (176–432 min) for the pharynx, 311 min (127–494 min) for the perioral region, and 297 min (234–355 min) for the feet. Pharyngeal symptoms were more common in patients older than 65 years than in those younger than 65 years.
Conclusions
The incidence and time of the onset of ACIPN caused by oxaliplatin varies between the body and regions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argyriou AA, Bruna J, Marmiroli P, Cavaletti G (2012) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (CIPN): an update. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 82(1):51–77
Tofthagen C, McAllister RD, McMillan SC (2011) Peripheral neuropathy in patients with colorectal cancer receiving oxaliplatin. Clin J Oncol Nurs 15:2
Pachman DR, Qin R, Seisler DK, Smith EM, Beutler AS, Ta LE, Lafky JM, Wagner-Johnston ND, Ruddy KJ, Dakhil S (2015) Clinical course of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy: results from the randomized phase III trial N08CB (alliance). J Clin Oncol 33(30):3416–3422
Argyriou AA, Polychronopoulos P, Iconomou G, Chroni E, Kalofonos HP (2008) A review on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral nerve damage. Cancer Treat Rev 34(4):368–377
Krishnan AV, Goldstein D, Friedlander M, Kiernan MC (2005) Oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity and the development of neuropathy. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine 32(1):51–60
Miyake T, Nakamura S, Meng Z, Hamano S, Inoue K, Numata T, Takahashi N, Nagayasu K, Shirakawa H, Mori Y (2017) Distinct mechanism of cysteine oxidation-dependent activation and cold sensitization of human transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 channel by high and low oxaliplatin. Front Physiol 8:878
Staff NP, Grisold A, Grisold W, Windebank AJ (2017) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a current review. Ann Neurol 81(6):772–781
Starobova H, Vetter I (2017) Pathophysiology of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Front Mol Neurosci 10:174. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00174
Alejandro LM, Behrendt CE, Chen K, Openshaw H, Shibata S (2013) Predicting acute and persistent neuropathy associated with oxaliplatin. Am J Clin Oncol 36(4):331–337. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0b013e318246b50d
Yoshida Y, Hirata K, Matsuoka H, Iwamoto S, Kotaka M, Fujita H, Aisu N, Hoshino S, Kosaka T, Maeda K, Kiyomi F, Yamashita Y (2015) A single-arm phase II validation study of preventing oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity reactions by dexamethasone: the AVOID trial. Drug design, development and therapy 9:6067–6073. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S94901
Yoshida Y, Hoshino S, Aisu N, Mogi A, Yamada T, Kojima D, Tanimura S, Hirata K, Yamashita Y (2015) Can grade 2 neutropenia predict the risk of grade 3 neutropenia in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with chemotherapy? Supportive care in cancer : official journal of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer 23(6):1623–1627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-014-2518-3
Tan AC, McCrary JM, Park SB, Trinh T, Goldstein D (2019) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy-patient-reported outcomes compared with NCI-CTCAE grade. Supportive care in cancer : official journal of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer 27:4771–4777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-019-04781-6
Argyriou AA, Cavaletti G, Briani C, Velasco R, Bruna J, Campagnolo M, Alberti P, Bergamo F, Cortinovis D, Cazzaniga M (2013) Clinical pattern and associations of oxaliplatin acute neurotoxicity: a prospective study in 170 patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer 119(2):438–444
Park SB, Goldstein D, Lin CS, Krishnan AV, Friedlander ML, Kiernan MC (2009) Acute abnormalities of sensory nerve function associated with oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 27(8):1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2008.19.3425
Alberti P, Canta A, Chiorazzi A, Fumagalli G, Meregalli C, Monza L, Pozzi E, Ballarini E, Rodriguez-Menendez V, Oggioni N, Sancini G, Marmiroli P, Cavaletti G (2020) Topiramate prevents oxaliplatin-related axonal hyperexcitability and oxaliplatin induced peripheral neurotoxicity. Neuropharmacology 164:107905–107905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107905
Davidov DN (2013) Oxaliplatin/5-fluorouracil/leucovorin in the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. International Medical Association Bulgaria 19(3):476–480
Land SR, Kopec JA, Cecchini RS, Ganz PA, Wieand HS, Colangelo LH, Murphy K, Kuebler JP, Seay TE, Needles BM, Bearden JD 3rd, Colman LK, Lanier KS, Pajon ER Jr, Cella D, Smith RE, O'Connell MJ, Costantino JP, Wolmark N (2007) Neurotoxicity from oxaliplatin combined with weekly bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin as surgical adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II and III colon cancer: NSABP C-07. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 25(16):2205–2211. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2006.08.6652
Diaz-Rubio E, Sastre J, Zaniboni A, Labianca R, Cortes-Funes H, de Braud F, Boni C, Benavides M, Dallavalle G, Homerin M (1998) Oxaliplatin as single agent in previously untreated colorectal carcinoma patients: a phase II multicentric study. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology 9(1):105–108. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008200825886
Levi F, Misset JL, Brienza S, Adam R, Metzger G, Itzakhi M, Caussanel JP, Kunstlinger F, Lecouturier S, Descorps-Declere A et al (1992) A chronopharmacologic phase II clinical trial with 5-fluorouracil, folinic acid, and oxaliplatin using an ambulatory multichannel programmable pump. High antitumor effectiveness against metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 69(4):893–900. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19920215)69:4<893::aid-cncr2820690410>3.0.co;2-x
Ravaioli A, Marangolo M, Pasquini E, Rossi A, Amadori D, Cruciani G, Tassinari D, Oliverio G, Giovanis P, Turci D, Zumaglini F, Nicolini M, Panzini I (2002) Bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin with oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 20(10):2545–2550. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2002.08.144
Rothenberg ML, Oza AM, Bigelow RH, Berlin JD, Marshall JL, Ramanathan RK, Hart LL, Gupta S, Garay CA, Burger BG, Le Bail N, Haller DG (2003) Superiority of oxaliplatin and fluorouracil-leucovorin compared with either therapy alone in patients with progressive colorectal cancer after irinotecan and fluorouracil-leucovorin: interim results of a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 21(11):2059–2069. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2003.11.126
Storey DJ, Sakala M, McLean CM, Phillips HA, Dawson LK, Wall LR, Fallon MT, Clive S (2010) Capecitabine combined with oxaliplatin (CapOx) in clinical practice: how significant is peripheral neuropathy? Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology 21(8):1657–1661. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp594
Yoshida Y, Satoh A, Yamada T, Aisu N, Matsuoka T, Koganemaru T, Kajitani R, Munechika T, Matsumoto Y, Nagano H, Komono A, Sakamoto R, Morimoto M, Arima H, Hasegawa S (2019) The relationship between evaluation methods for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Sci Rep 9(1):20361–20361. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56969-9
Altaf R, Brixen AL, Kristensen B, Nielsen SE (2014) Incidence of cold-induced peripheral neuropathy and dose modification of adjuvant oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for patients with colorectal cancer. Oncology 87(3):167–172
Story GM, Peier AM, Reeve AJ, Eid SR, Mosbacher J, Hricik TR, Earley TJ, Hergarden AC, Andersson DA, Hwang SW, McIntyre P, Jegla T, Bevan S, Patapoutian A (2003) ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures. Cell 112(6):819–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00158-2
Zhao M, Isami K, Nakamura S, Shirakawa H, Nakagawa T, Kaneko S (2012) Acute cold hypersensitivity characteristically induced by oxaliplatin is caused by the enhanced responsiveness of TRPA1 in mice. Mol Pain 8:55–55. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-8-55
Miyake T, Nakamura S, Zhao M, So K, Inoue K, Numata T, Takahashi N, Shirakawa H, Mori Y, Nakagawa T, Kaneko S (2016) Cold sensitivity of TRPA1 is unveiled by the prolyl hydroxylation blockade-induced sensitization to ROS. Nat Commun 7:12840–12840. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12840
WHO G Switzerland; 2010.World Health Organization Definition of an older or elderly person. http://www.who.int/healthinfo/survey/ageingdefnolder/en/index.html. Accessed 12 Nov 2013.
Raphael MJ, Fischer HD, Fung K, Austin PC, Anderson GM, Booth CM, Singh S (2017) Neurotoxicity outcomes in a population-based cohort of elderly patients treated with adjuvant oxaliplatin for colorectal Cancer. Clin colorectal Cancer 16(4):397–404.e391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clcc.2017.03.013
Argyriou A, Briani C, Cavaletti G, Bruna J, Alberti P, Velasco R, Lonardi S, Cortinovis D, Cazzaniga M, Campagnolo M (2013) Advanced age and liability to oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: post hoc analysis of a prospective study. Eur J Neurol 20(5):788–794
Acknowledgments
We thank Kelly Zammit, BVSc, from Edanz Editing (www.edanzediting.com/ac), for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Review Board of Fukuoka University Hospital (approval no. 16–8-07) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, Y., Yoshida, Y., Kiba, S. et al. Acute chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy due to oxaliplatin administration without cold stimulation. Support Care Cancer 28, 5405–5410 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05387-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05387-z