Abstract
Purpose
Hyponatremia is the most common electrolyte disorder in hospitalized patients, and it might be an indicator of poor prognosis and might have negative effects on hospitalization length and quality of life in non-malignant as well as in malignant diseases. The aim of this study is to determine the impact of hyponatremia on the length and on the cost of hospitalization as well as on outcome in cancer patients.
Methods
The present study includes 105 consecutive cancer patients hospitalized at our institution from June 2013 to December 2013. Data regarding age, sex, staging, histology, chemotherapy, and serum sodium levels at admission, during hospitalization, and at discharge were recorded and statistically analyzed. Impact of hyponatremia on length and cost of hospitalization and on outcome was evaluated.
Results
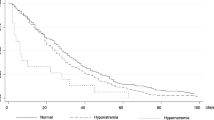
A significant difference in overall survival since the date of admission was observed between eunatremic and hyponatremic patients (p = 0.0255). A statistically significant correlation was also found between the length of stay and the detection of hyponatremia. At multivariate analysis, hyponatremia at admission, severity of hyponatremia, and stage of disease resulted independent prognostic factors. Furthermore, a patient with moderate or severe hyponatremia cost, in rate terms, 128 and 299 % more than a normonatremic patient, respectively.
Conclusions
The occurrence of hyponatremia at the admission or during the hospitalization may represent a significant factor influencing the outcome and the length of hospitalization. Acting effective and timely on the normalization of sodium levels might have a positive effect on prognosis in this setting of patients, as well as on the length of stay in hospital, thus potentially resulting in savings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrogué HJ, Madias NE (2000) Hyponatremia. N Engl J Med 342(21):1581–9
Upadhyay A, Jaber BL, Madias NE (2009) Epidemiology of hyponatremia. Semin Nephrol 29(3):227–38. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2009.03.004
Patel GP, Balk RA (2007) Recognition and treatment of hyponatremia in acutely ill hospitalized patients. Clin Ther 29:211–229
Ghali JK (2008) Mechanisms, risks, and new treatment options for hyponatremia. Cardiology 111:147–157
Palmer BF, Gates JR, Lader M (2003) Causes and management of hyponatremia. Ann Pharmacother 37:1694–1702
Onitilo AA, Kio E, Doi SA (2007) Tumor-related hyponatremia. Clin Med Res 5:228–237
Beukhof CM, Hoorn EJ, Lindemans J, Zietse R (2007) Novel risk factors for hospital-acquired hyponatremia: a matched case–control study. Clin Endocrinol 66:367–72
Hoorn EJ, Lindemans J, Zietse R (2006) Development of severe hyponatraemiain hospitalized patients: treatment-related risk factors and inadequate management. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:70–6
Luca A, Angermayr B, Bertolini G, Koenig F, Vizzini G, Ploner M, Peck- Radosavljevic M, Gridelli B, Bosch J (2007) An integrated MELD model including serum sodium and age improves the prediction of early mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Transpl 13:1174–1180
Rossi J, Bayram M, Udelson JE, Lloyd-Jones D, Adams KF, Oconnor CM, Stough WG, Ouyang J, Shin DD, Orlandi C, Gheorghiade M (2007) Improvement in hyponatremia during hospitalization for worsening heart failure is associated with improved outcomes: insights from the acute and chronic therapeutic impact of a vasopressin antagonist in chronic heart failure (ACTIV in CHF) trial. Acute Card Care 9:82–86
Nair V, Niederman MS, Masani N, Fishbane S (2007) Hyponatremia in community-acquired pneumonia. Am J Nephrol 27:184–190
Bennani SL, Abouqal R, Zeggwagh AA et al (2003) Incidence, causes and prognostic factors of hyponatremia in intensive care. Rev Med Interne 24:224–9
Klein L, O’Connor CM, Leimberger CM et al (2005) Lower serum sodium is associated with increased short-term mortality in hospitalized patients with worsening heart failure: results from the outcomes of a prospective trial of intravenous milrinone for exacerbations of chronic heart failure (OPTIME-CHF) study. Circulation 111:2454–60
Biggins SW, Rodriguez HJ, Bacchetti P, Bass NM, Roberts JP, Terrault NA (2005) Serum sodium predicts mortality in patients listed for liver transplantation. Hepatology 41:32–9
Wald R, Jaber BL, Price LL, Upadhyay A, Madias NE (2010) Impact of hospital-associated hyponatremia on selected outcomes. Arch Intern Med 170(3):294–302
Gill G, Huda B, Boyd A, Skagen K, Wile D et al (2006) Characteristics and mortality of severe hyponatraemia—a hospital-based study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 65:246–49
Berghmans T, Paesmans M, Body JJ (1999) A prospective study on hyponatraemia in medical cancer patients: epidemiology, aetiology and differential diagnosis. Support Care Cancer 8(3):192–7
Keenan AM (1999) Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of anti-diuretic hormone in malignancy. Semin Oncol Nurs 15:160–67
Sørensen JB, Andersen MK, Hansen HH (1995) Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) in malignant disease. J Intern Med 238:97–110
Talmi YP, Hoffman HT, McCabe BF (1992) Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of arginine vasopressin in patients with cancer of the head and neck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 101:946–949
Raftopoulos H (2007) Diagnosis and management of hyponatremia in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 15:1341–1347
Onitilo AA, Ebenezer K, Suhail AR (2007) Tumour related hyponatraemia. Clin Med Res 5:228–23
Comis R, Miller M, Ginsberg S (1980) Abnormalities in water homeostasis in small cell anaplastic lung cancer. Cancer 45(9):2414–242
Kawahara M, Fukuoka M, Saijo N et al (1997) Prognostic factors and prognostic staging system for small cell lung cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 27:158–165
Østerlind K, Andersen PK (1986) Prognostic factors in small cell lung cancer: multivariate model based on 778 patients treated with chemotherapy with or without irradiation. Cancer Res 46:4189–4194
Hansen O, Sørensen P, Hansen KH (2010) The occurrence of hyponatremia in SCLC and the influence on prognosis: a retrospective study of 453 patients treated in a single institution in a 10-year period. Lung Cancer 68(1):111–4
Berardi R, Caramanti M, Fiordoliva I, et al. (2014) Hyponatremia is a predictor of clinical outcome for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Supp Care Cancer, Epub ahead of print
Petereit C, Zaba O, Teber I, Grohé C (2011) Is hyponatraemia a prognostic marker of survivalfor lung cancer? Pneumologie 65:565–71
Mantovani L. (2011) HEALTH TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT Principi, concetti, strumenti operativi. Il Sole 24 ore Spa ISBN: 978-88-324-7918-8 Chap. 3, Pag. 59
Drummond MF, O’Brien B, Stoddart GL, Torrance GW (1997) Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Waikar SS, Mount DB, Curhan GC (2009) Mortality after hospitalization with mild, moderate, and severe hyponatremia. Am J Med 122(9):857–65
Castillo JJ, Vincent M, Justice E (2012) Diagnosis and management of hyponatremia in cancer patients. Oncologist 17(6):756–65
Huo TI, Lin HC, Hsia CY, Huang YH, Wu JC, Chiang JH, Chiou YY, Lui WY, Lee PC, Lee SD (2008) The MELD-Na is an independent short- and long-term prognostic predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective survey. Dig Liver Dis 40:882–889
Kim HS, Yi SY, Jun HJ, Lee J, Park JO, Park YS, Jang J, Kim HJ, Ko Y, Lim HY, Kang WK (2007) Clinical outcome of gastric cancer patients with bone marrow metastases. Oncology 73:192–197
Gandhi L, Johnson BE (2006) Paraneoplastic syndromes associated with small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 4:631–638
Vasudev NS, Brown JE, Brown SR, Rafiq R, Morgan R, Patel PM, O’Donnell D, Harnden P, Rogers M, Cocks K, Anderson K, Paul A, Eardley I, Selby PJ, Banks RE (2008) Prognostic factors in renal cell carcinoma: association of preoperative sodium concentration with survival. Clin Cancer Res 14:1775–1781
Schutz FA, Xie W, Donskov F, Sircar M, McDermott DF, Rini BI, Agarwal N, Pal SK, Srinivas S, Kollmannsberger C, North SA, Wood LA, Vaishampayan U, Tan MH, Mackenzie MJ, Lee JL, Rha SY, Yuasa T, Heng DY, Choueiri TK (2013) The impact of low serum sodium on treatment outcome of targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results from the international metastatic renal cell cancer database consortium. Eur Urol 65(4):723–30
Jeppesen AN, Jensen HK, Donskov F, Marcussen N, von der Maase H (2010) Hyponatremia as a prognostic and predictive factor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 102(5):867–72
Doshi SM, Shah P, Lei X, Lahoti A, Salahudeen AK (2012) Hyponatremia in hospitalized cancer patients and its impact on clinical outcomes. Am J Kidney Dis 59(2):222–8
Nelson M, Palmer JL, Fu J, Williams JL, Yadav R, Guo Y (2014) Hyponatraemia in cancer patients on an inpatient rehabilitation unit. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 23(3):363–9
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sector.
Conflict of interest
All authors disclose no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work or that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported. The authors have full control of all primary data and do agree to allow the journal to review their data if requested.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berardi, R., Caramanti, M., Castagnani, M. et al. Hyponatremia is a predictor of hospital length and cost of stay and outcome in cancer patients. Support Care Cancer 23, 3095–3101 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-015-2683-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-015-2683-z