Abstract
Goal of work
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of pro-apoptotic protein p53 and anti-apoptotic proteins BCl-2 and MCl-1, as well as the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) in patients developing mucositis during radiotherapy for head and neck cancer.
Materials and methods
Thirty-five patients receiving radiotherapy for head/neck cancer were included in this study. Patients were examined before radiotherapy. Oral mucositis was recorded weekly during radiotherapy. Cytologic smears from the oral cavity were taken with a brush. Immunocytochemical staining was performed by the use of p53, BCl-2, MCl-1 TNF and IL-1β monoclonal antibodies.
Main results
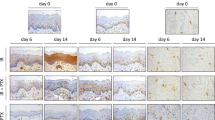
P53 was expressed in 1 of 15 smears before the initiation of radiotherapy (6.5%) compared to 3 of 7 smears from patients with grade III mucositis (43%) during radiotherapy. BCl-2 was expressed in 15 of 15 smears before radiotherapy (100%) and in three of seven patients with grade III mucositis (43%) during radiotherapy. MCl-1 was expressed in 10 of 14 samples before radiotherapy (71.5%) and in two of seven patients with grade III (28.5%) mucositis during radiotherapy. TNF was expressed in 9 of 14 patients before radiotherapy (64%) and in six of seven patients with grade III mucositis during radiotherapy (86%). IL-1β was detected in 7 of 14 patients before radiotherapy (50%) compared to 6 of 7 patients with grade III mucositis during radiotherapy (86%).
Conclusion
Our preliminary results indicate an induction of apoptosis and inflammation in the oral mucosa in patients developing mucositis during radiotherapy for head/neck cancer.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322–1326
Aggarwal B, Kohr W, Hass P (1985) Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, puri®cation and characterization. J Biol Chem 260:2345–2354
Anilkumar T, Sarraf C, Hunt T, Alison M (1992) The nature of cytotoxic drug-induced cell death in murine intestinal crypts. Br J Cancer 65:552–558
Anthony L, Bowen J, Garden A, Hewson I, Sonis S (2006) New thoughts on the pathobiology of regimen-related mucosal injury. Support Care Cancer 14:516–518
Baker S, Markowitz S, Fearon E, Willson J, Vogelstein B (1990) Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science 249:912–915
Bellm L, Epstein J, Rose-Ped A (2000) Patient reports of complications of bone marrow transplantation. Support Care Cancer 8:33–39
Bianco J, Appelbaum F, Nemunaitis J (1991) Phase I–II trial of pentoxifylline for the prevention of transplant-related toxicities following bone marrow transplantation. Blood 78:1205–1211
Bowen J, Gibson R, Keefe D, Cummins A (2005) Cytotoxic chemotherapy upregulates pro-apoptotic Bax and Bak in the small intestine of rats and humans. Pathology 37:56–62
Bowen J, Gibson R, Cummins A, Keefe D (2006) Intestinal mucositis: the role of the Bcl-2 family, p53 and caspases in chemotherapy-induced damage. Support Care Cancer 14:713–731
Bowen J, Gibson R, Cummins A, Tyskin A, Keefe D (2007) Irinotecan changes gene expression in the small intestine of the rat with breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59:337–348
Carswell E, Old L, Kassel R (1975) An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 72:3666–3670
Cox J, Stetz J, Pajak T (1995) Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1341–1346
Dinarello C (1996) Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 87:2095–2147
Dinarello C (2000) Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 118:503–508
Elting L, Cooksley C, Chambers M (2003) The burdens of cancer therapy: clinical and economic outcomes of chemotherapy-induced mucositis. Cancer Nurs 98:153–159
Ferra C, de Sanjose S, Lastra C (1997) Pentoxifylline, ciprofloxacin and prednisone failed to prevent transplantrelated toxicities in bone marrow transplant recipients and were associated with an increased incidence of infectious complications. Bone Marrow Transplant 20:1075–1080
Ferra C, de Sanjose S, Gallardo D (1998) IL-6 and IL-8 levels in plasma during hematopoietic progenitor transplantation. Haematologica 83:1082–1087
Ferra C, de Sanjose S, Gallardo D, Berlanga JJ, Rueda F, Marin D, de la Banda E, Ancin I, Peris J, Garcia J, Granena A (1998) IL-6 and IL-8 levels in plasma during hematopoietic progenitor transplantation. Haematologica 83:1082–1087
Ferrara J, Abhyankar S, Gilliland D (1993) Cytokine stem of graft-versus-host disease: a critical e€ector role for interleukin-1. Transplant Proc 25:1216–1217
Gibson L, Fortney J, Magro G, Ericson S, Lynch J, Landreth K (1999) Regulation of BAX and BCL-2 expression in breast cancer cells by chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 55:107–117
Gross A, McDonnell J, Korsmeyer S (1999) BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:1899–1911
Hall P, Benko H, Hogan K (1995) The influence of serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 concentrations or nonhematologic toxicities and hematologic recovery in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Exp Hematol 23:1256–1260
Hehlgans T, Pfeffer K (2005) The intriguing biology of the tumour necrosis factor/tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily: players, rules and the games. Immunology 115:1–20
Herr I, Debatin K (2001) Cellular stress response and apoptosis in cancer therapy. Blood 98:2603–2614
Hsu S, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin–biotin peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Inomata A, Horii I, Suzuki K (2002) 5-Fluorouracil-induced intestinal toxicity: what determines the severity of damage to murine intestinal crypt epithelia. Toxicol Lett 133:231–240
Keefe D, Brealey J, Goland G, Cummins A (2000) Chemotherapy for cancer causes apoptosis that precedes hypoplasia in crypts of the small intestine in humans. Gut 47:632–637
Khan S, Wingard J (2001) Infection and mucosal injury in cancer treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr:31–36
Kitada S, Krajewski S, Miyashita T, Krajewska M, Reed J (1996) Gamma-radiation induces upregulation of Bax protein and apoptosis in radiosensitive cells in vivo. Oncogene 12:187–192
Krenger W, Ferrara J (1996) Graft-vs-host disease and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. Immunol Res 15:50–73
Leung L, Wang T (1999) Differential effects of chemotherapeutic agents on the Bcl-2/Bax apoptosis pathway in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Breast Cancer Res Treat 55:73–83
Lima V, Brito G, Cunha F (2005) Effects of the tumour necrosis factor-a inhibitors pentoxifylline and thalidomide in short-term experimental oral mucositis in hamsters. Eur J Oral Sci 113:210–217
Logan R, Stringer A, Bowen J, Yeoh A, Gibson R, Sonis S, Keefe D (2007) The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in cancer treatment-induced alimentary tract mucositis: Pathobiology, animal models and cytotoxic drugs. Cancer Treat Rev 33(5):448–460 (May 14)
Lorenz H-M, Kalden J (2002) Perspectives for TNF-a-targeting therapies. Arthritis Res 4:S17–S24
Nicolatou-Galitis O, Dardoufas K, Markoulatos P (2001) Oral pseudomembranous candidiasis, herpes simplex virus-1 infection, and oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients receiving radiotherapy and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) mouthwash. J Oral Pathol Med 30:471–480
Nicolatou-Galitis O, Athanassiadou P, Kouloulias V, Sotiropoulou-Lontou A, Dardoufas K, Polychronopoulou A, Gonidi M, Kyprianou K, Kolitsi G, Skarleas C, Pissakas G, Papanikolaou I, Kouvaris J (2006) Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) infection in radiation-induced oral mucositis. Support Care Cancer 14:753–762
Nicolatou-Galitis O, Velegraki A, Sotiropoulou-Lontou A (2006) Effect of fluconazole antifungal prophylaxis on oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients receiving radiotherapy. Support Care Cancer 14(1):44–51
Nita M, Nagawa H, Tominaga O, Tsuno N, Fujii S, Sasaki S, Fu C, Takenoue T, Tsuruo T, Muto T (1998) 5-Fluorouracil induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cell lines with modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins. Br J Cancer 78:986–992
Peterson DE, Schubert MM (2001) Oral toxicity. In: Perry MC (ed) The chemotherapy source book. 3rd edn. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 404–424
Potten C, Wilson J, Booth C (1997) Regulation and significance of apoptosis in the stem cells of the gastrointestinal epithelium. Stem Cells 15:82–93
Rabinowitz J, Petros W, Stuart A, Peters W (1993) Characterization of endogenous cytokine concentrations after high-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow support. Blood 81:2452–2459
Remberger M, Ringdem O, Markling L (1995) TNF alpha levels are increased during bone marrow transplantation conditioning regimens in patients who develop acute GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant 15:99–104
Rose-Ped A, Bellm L, Epstein J (2002) Complications of radiation therapy for head and neck cancers: the patient’s perspective. Cancer Nurs 25:461–467
Sleijfer S, Vujaskovic Z, Limburg P, Koops H, Mulder N (1998) Induction of tumor necrosis factor-a as a cause of bleomycinrelated toxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 82:970–974
Smith N, Rubenstein J, Eggener S, Kozlowski J (2003) The p53 tumor suppressor gene and nuclear protein: basic science review and relevance in the management of bladder cancer. J Urol 169:1219–1228
Sonis S (1998) Mucositis as a biological process: a new hypothesis for the development of chemotherapy-induced stomatotoxicity. Oral Oncol 34:39–43
Sonis S (2004) A biological approach to mucositis. J Support Oncol 2:21–32
Sonis S, Peterson R, Edwards L (2000) Defining mechanisms of action of interleukin-11 on the progression of radiation-induced mucositis in hamsters. Oral Oncol 36:393–381
Sonis S, Oster G, Fuchs H (2001) Oral mucositis and the clinical and economic outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 19:2201–2205
Stiff P (2001) Mucositis associated with stem cell transplantation: current status and innovative approaches to management. Bone Marrow Transplant 17:S3–S11
Sutherland S, Browman G (2001) Prophylaxis of oral mucositis in irradiated head-and-neck cancer patients: a proposed classification scheme of interventions and metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 49:917–930
Vousden K, Lu X (2002) Live or let die: the cell’s response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2:594–604
Xun C, Thompson J, Jennings C, Brown S, Widmerru B (1994) E€ect of total body irradiation, busulfan-cyclophosphamide or cyclophasphamide conditioning on in¯ammatory cytokine release and development of acute and chronic graft-vs-host disease in H-2-incompatible transplanted ScID mice. Blood 83:2360–2367
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Ms Antonia Sipsa and Ms Amalia Moumouri for their valuable technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xanthinaki, A., Nicolatou-Galitis, O., Athanassiadou, P. et al. Apoptotic and inflammation markers in oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients receiving radiotherapy: preliminary report. Support Care Cancer 16, 1025–1033 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-007-0379-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-007-0379-8