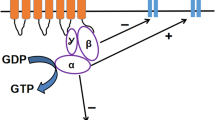
Abstract
Natural and synthetic opioid compounds, either alone or in combination with other drugs, are widely used analgesics for patients with both acute and chronic pain. Decades of extensive pharmacologic investigations have characterized three high-affinity cell-surface neuronal receptors, the activation of which is responsible for both the desirable properties (antinociception) and undesirable properties (respiratory depression, nausea and vomiting, dependence, etc.) of opioid drugs. Recent research in molecular biology and pharmacogenetics in relation to opioids and their receptors has helped clarify previous pharmacologic observations and has laid the groundwork for new analgesic therapies with improved therapeutic outcomes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inturrisi CE (2002) Clinical pharmacology of opioids for pain. Clin J Pain 18:S3–13
Przewlocki R, Przewlocka B (2001) Opioids in chronic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:79–91
Gilbert PE, Martin WR (1976) Sigma effects of nalorphine in the chronic spinal dog. Drug Alcohol Depend 1:373–376
Martin WR, Eades CG, Thompson JA, Huppler RE, Gilbert PE (1976) The effects of morphine- and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:517–532
Lord JA, Waterfield AA, Hughes J, Kosterlitz HW (1977) Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature 267:495–499
Pasternak GW (1980) Multiple opiate receptors: [3H].ethylketocyclazocine receptor binding and ketocyclazocine analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 77:3691–3694
Pasternak GW (1993) Pharmacological mechanisms of opioid analgesics. Clin Neuropharmacol 16:1–18
Knapp RJ, Porreca F, Burks TF, Yamamura HI (1989) Mediation of analgesia by multiple opioid receptors. In: Hill CS, Fields WS (eds) Advances in pain research and therapy. Raven Press, New York, pp 247–289
Freye E (1987) New concepts in opioid activity. Opioid agonists, antagonists, and mixed narcotic analgesics: theoretical background and consideration for practical use. Springer, New York, pp 64–66
Wolozin BL, Pasternak GW (1981) Classification of multiple morphine and enkephalin binding sites in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78:6181–6185
Traynor JR (1996) The u-opioid receptor. Pain Rev 3:221–248
Jiang Q, Takemori AE, Sultana M, Portoghese PS, Bowen WD, Mosberg HI, Porreca F (1991) Differential antagonism of opioid delta antinociception by [D-Ala2, Leu5, Cys6].enkephalin and naltrindole 5′-isothiocyanate: evidence for delta receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:1069–1075
Attali B, Gouarderes C, Mazarguil H, Audigier Y, Cros J (1982) Evidence for multiple “kappa” binding sites by use of opioid peptides in the guinea-pig lumbo-sacral spinal cord. Neuropeptides 3:53–64
Chen Y, Mestek A, Liu J, Hurley JA, Yu L (1993) Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol 44:8–12
Evans CJ, Keith DE Jr, Morrison H, Magendzo K, Edwards RH (1992) Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science 258:1952–1955
Minami M, Toya T, Katao Y, Maekawa K, Nakamura S, Onogi T, Kaneko S, Satoh M (1993) Cloning and expression of a cDNA for the rat kappa-opioid receptor. FEBS Lett 329:291–295
Wei LN, Loh HH (2002) Regulation of opioid receptor expression. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2:69–75
Gourlay GK (2002) Clinical pharmacology of the treatment of chronic non-cancer pain. In: Giamberardino MA (ed) Pain 2002—an updated review (refresher course syllabus). IASP Press, Seattle, pp 381–394
Filizola M, Olmea O, Weinstein H (2002) Prediction of heterodimerization interfaces of G-protein coupled receptors with a new subtractive correlated mutation method. Protein Eng 15:881–885
Jordan BA, Devi LA (1999) G-protein-coupled receptor heterodimerization modulates receptor function. Nature 399:697–700
Gaveriaux-Ruff C, Kieffer BL (1999) Opioid receptors: gene structure and function. In: Stein C (ed) Opioids in pain control: basic and clinical aspects. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 1–20
Gaveriaux-Ruff C, Kieffer BL (2002) Opioid receptor genes inactivated in mice: the highlights. Neuropeptides 36:62–71
Trapaidze N, Gomes I, Cvejic S, Bansinath M, Devi LA (2000) Opioid receptor endocytosis and activation of MAP kinase pathway. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 76:220–228
Chevlen E (2003) Opioids: a review. Curr Pain Headache Rep 7:15–23
Kaufman DL, Keith DE Jr, Anton B, Tian J, Magendzo K, Newman D, Tran TH, Lee DS, Wen C, Xia YR (1995) Characterization of the murine mu opioid receptor gene. J Biol Chem 270:15877–15883
Sora I, Takahashi N, Funada M, Ujike H, Revay RS, Donovan DM, Miner LL, Uhl GR (1997) Opiate receptor knockout mice define mu receptor roles in endogenous nociceptive responses and morphine-induced analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:1544–1549
Zhu Y, King MA, Schuller AG, Nitsche JF, Reidl M, Elde RP, Unterwald E, Pasternak GW, Pintar JE (1999) Retention of supraspinal delta-like analgesia and loss of morphine tolerance in delta opioid receptor knockout mice. Neuron 24:243–252
Simonin F, Valverde O, Smadja C, Slowe S, Kitchen I, Dierich A, Le Meur M, Roques BP, Maldonado R, Kieffer BL (1998) Disruption of the kappa-opioid receptor gene in mice enhances sensitivity to chemical visceral pain, impairs pharmacological actions of the selective kappa-agonist U-50, 488H and attenuates morphine withdrawal. EMBO J 17:886–897
Simonin F, Slowe S, Becker JA, Matthes HW, Filliol D, Chluba J, Kitchen I, Kieffer BL (2001) Analysis of [3H] bremazocine binding in single and combinatorial opioid receptor knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol 414:189–195
Pasternak GW (2001) The pharmacology of mu analgesics: from patients to genes. Neuroscientist 7:220–231
Kieffer BL, Gaveriaux-Ruff C (2002) Exploring the opioid system by gene knockout. Prog Neurobiol 66:285–306
Ma MK, Woo MH, McLeod HL (2002) Genetic basis of drug metabolism. Am J Health Syst Pharm 59:2061–2069
Heiskanen T, Olkkola KT, Kalso E (1998) Effects of blocking CYP2D6 on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oxycodone. Clin Pharmacol Ther 64:603–611
Wright AW, Mather LE, Smith MT (2001) Hydromorphone-3-glucuronide: a more potent neuro-excitant than its structural analogue, morphine-3-glucuronide. Life Sci 69:409–420
Roxane Laboratories (2000) Levorphanol (prescribing information). Roxane Laboratories, Columbus, OH
Foster DJ, Somogyi AA, Bochner F (1999) Methadone N-demethylation in human liver microsomes: lack of stereoselectivity and involvement of CYP3A4. Br J Clin Pharmacol 47:403–412
Barkin RL, Barkin D (2001) Pharmacologic management of acute and chronic pain: focus on drug interactions and patient-specific pharmacotherapeutic selection. South Med J 94:756–770
Penson RT, Joel SP, Bakhshi K, Clark SJ, Langford RM, Slevin ML (2000) Randomized placebo-controlled trial of the activity of the morphine glucuronides. Clin Pharmacol Ther 68:667–676
Smith MT (2000) Neuroexcitatory effects of morphine and hydromorphone: evidence implicating the 3-glucuronide metabolites. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 27:524–528
Bartlett SE, Smith MT (1995) The apparent affinity of morphine-3-glucuronide at mu1-opioid receptors results from morphine contamination: demonstration using HPLC and radioligand binding. Life Sci 57:609–615
Osborne RJ, Joel SP, Slevin ML (1986) Morphine intoxication in renal failure: the role of morphine-6-glucuronide. BMJ 292:1548–1549
Eckhardt K, Li S, Ammon S, Schanzle G, Mikus G, Eichelbaum M (1998) Same incidence of adverse drug events after codeine administration irrespective of the genetically determined differences in morphine formation. Pain 76:27–33
Kaiko RF, Foley KM, Grabinski PY, Heidrich G, Rogers AG, Inturrisi CE, Reidenberg MM (1983) Central nervous system excitatory effects of meperidine in cancer patients. Ann Neurol 13:180–185
Waitman J, McCaffery M (2001) Meperidine—a liability. Am J Nurs 101:57–58
Agency for Healthcare Policy and Research (1994) Management of cancer pain, clinical guideline number 9 (AHCPR publication number 94-0592)
Boden R, Botting R, Coulson P, Spanswick G (1984) Effect of nonselective and selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidases A and B on pethidine toxicity in mice. Br J Pharmacol 82:151–154
Ueda H, Fukushima N, Kitao T, Ge M, Takagi H (1986) Low doses of naloxone produce analgesia in the mouse brain by blocking presynaptic autoinhibition of enkephalin release. Neurosci Lett 65:247–252
Vaughan CW, Christie MJ (1997) Presynaptic inhibitory action of opioids on synaptic transmission in the rat periaqueductal grey in vitro. J Physiol 498 (Pt 2):463–472
Crain SM, Shen KF (2001) Acute thermal hyperalgesia elicited by low-dose morphine in normal mice is blocked by ultra-low-dose naltrexone, unmasking potent opioid analgesia. Brain Res 888:75–82
Crain SM, Shen KF (1995) Ultra-low concentrations of naloxone selectively antagonize excitatory effects of morphine on sensory neurons, thereby increasing its antinociceptive potency and attenuating tolerance/dependence during chronic cotreatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:10540–10544
Wright PM, O’Toole DP, Barron DW (1992) The influence of naloxone infusion on the action of intrathecal diamorphine: low-dose naloxone and neuroendocrine responses. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 36:230–233
Joshi GP, Duffy L, Chehade J, Wesevich J, Gajraj N, Johnson ER (1999) Effects of prophylactic nalmefene on the incidence of morphine-related side effects in patients receiving intravenous patient-controlled analgesia. Anesthesiology 90:1007–1011
Gan TJ, Ginsberg B, Glass PS, Fortney J, Jhaveri R, Perno R (1997) Opioid-sparing effects of a low-dose infusion of naloxone in patient-administered morphine sulfate. Anesthesiology 87:1075–1081
Cepeda MS, Africano JM, Manrique AM, Fragoso W, Carr DB (2002) The combination of low dose of naloxone and morphine in PCA does not decrease opioid requirements in the postoperative period. Pain 96:73–79
Mehlisch DR (2003) The combination of low dose of naloxone and morphine in patient-controlled (PCA) does not decrease opioid requirements in the postoperative period. Pain 101:209–211
Acknowledgements
The preparation of this article was supported by Endo Pharmaceuticals, Chadds Ford, Pennsylvania, with editorial assistance provided by Accel Medical Education, New York, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gourlay, G.K. Advances in opioid pharmacology. Support Care Cancer 13, 153–159 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-004-0690-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-004-0690-6