Abstract
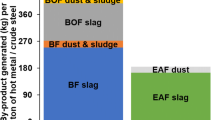
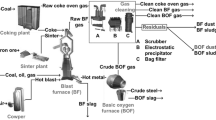
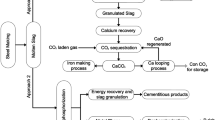
A circular economy is one of the important pillars for a sustainable iron and steel industry. Solid and sludgy residuals from steelmaking processes represent secondary resources with considerable amounts of valuable materials such as metals and minerals. Therefore, several treatment technologies for dusts and sludges target material recovery. Nowadays, European steel producers reach a by-product recycling rate of more than 90% (including onsite recycling and residual utilization performed by external companies). The main benefits are a lower demand for primary resources and a reduced landfill volume as well as economic savings for steel plant operators. The current article gives an overview of the amounts of steelmaking residuals generated in Europe and describes the integrated DK recycling route, which represents one industrial-scale state-of-the-art treatment technology.
Zusammenfassung
Für eine nachhaltige Stahlindustrie braucht es eine effiziente Kreislaufwirtschaft. Stäube und Schlämme aus der Stahlerzeugung stellen Sekundärressourcen mit teils beträchtlichen Anteilen an Wertstoffen, wie z. B. Metalle und mineralische Komponenten, dar. Daher sind zahlreiche Behandlungsmethoden auf eine Materialrückgewinnung fokussiert. Berücksichtigt man die stahlwerksinterne Verwertung sowie die Behandlung und Verwertung durch externe Unternehmen, erreichen europäische Stahlproduzenten heutzutage eine Verwertungsquote von mehr als 90 %. Bedeutende Vorteile dieser hohen Quote sind ein geringerer Bedarf an Deponievolumen sowie finanzielle Einsparungen für Stahlwerksbetreiber durch die Einsparung an Primärrohstoffen. Der gegenständliche Artikel gibt einen Überblick der in Europa anfallenden Mengen an Stahlwerksreststoffen und beschreibt die integrierte DK-Recycling-Route als eine zum Stand der Technik zählende Behandlungsroute.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Steel Association: Statistical steel yearbook 2019, https://www.worldsteel.org/steel-by-topic/statistics/steel-statistical-yearbook.html (20.12.2019)
Remus, R.; Aguado Monsonet, M. A.; Roudier, S.; Delgado Sancho, L. (eds.): Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for iron and steel production, Joint Research Centre reference report, European Commission, Sevilla, 2013
Das, B.; Prakash, S.; Reddy, P. S. R.; Misra, V. N.: An overview of utilization of slag and sludge from steel industries, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 50 (2007), pp. 40–57
Lobato, N. C. C.; Villegas, E. A.; Mansur, M. B.: Management of solid wastes from steelmaking and galvanizing processes: A brief review, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 102 (2015), pp. 49–57
Sadek, D. M.: Effect of cooling technique of blast furnace slag on the thermal behaviour of solid cement bricks, Journal of Cleaner Production, 79 (2014), pp. 134–141
López-Delgado, A.; Pérez, C.; López, V. A.: Sorption of heavy metals on blast furnace sludge. Water Research, 32 (1998), pp. 989–996
Gurtubay, L.; Gallastegui, G.; Elias, A.; Rojo, N.; Barona, A.: Accelerated ageing of an EAF black slag by carbonation and percolation for long-term behaviour assessment, Journal of Environmental Management, 140 (2014), pp. 45–50
voestalpine: environmental declaration 2018, https://www.voestalpine.com/group/static/sites/group/.downloads/de/konzern/2018-umwelterklaerung.pdf (20.12.2019)
voestalpine: environmental declaration 2019, https://www.voestalpine.com/group/static/sites/group/.downloads/de/konzern/2019-umwelterklaerung.pdf (20.12.2019)
Svenskt Stal AB: Annual report 2018—Toward industry leading profitability
Sassen, K. J.; Hillmann, C.: The DK process for recovery of iron and zinc from BOF dusts and sludges, Steel Times International, 04 (2011), pp. 17–20
DK Recycling und Roheisen, https://www.dk-duisburg.de//index_en.html (23.12.2019)
Endemann, G.; Lüngen, H. B.; Wuppermann, C. D.: Dust, scale and sludge generation and utilization in German steelworks, Stahl Eisen, 126 (2009), no. 9, pp. 25–32
Von Billerbeck, E.; Ruh, A.; Kim, D.-S.: Verarbeitung von Filterstäuben aus der Elektrostahlerzeugung im Wälzprozess, in: Thomé-Kozmiensky, K. (Hrsg.): Mineralische Nebenprodukte und Abfälle – Aschen, Schlacken, Stäube und Baurestmassen, Neuruppin: TK Verlag Karl Thomé-Kozmiensky, 2014, S. 387–397
Befesa company presentation, https://www.befesa.com/export/sites/befesa2014/resources/pdf/Befesa-Company-Presentation.pdf (23.12.2019)
Ruetten, J.; Frias, C.; Diaz, G.; Martin, D.; Sanchez, F.: Processing EAF dust through Waelz kiln and ZINCEXTM solvent extraction: the optimum solution, European Metallurgical Conference (EMC), Duesseldorf, Germany, 2011
Wang, C.; Jennes, R.; Mattila, O.; Paananen, T.; Lilja, J.; Larsson, M.: Investigation of applying OxyCup® process for an integrated steel plant from a nordic country, METEC & 2nd European Steel Application Days (ESTAD), Duesseldorf, Germany, 2015
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding support of K1-MET GmbH, metallurgical competence center. The research program of the K1-MET competence center is supported by COMET (Competence Center for Excellent Technologies), the Austrian program for competence centers. K1-MET is funded by the Federal Ministry for Transport, Innovation and Technology, the Federal Ministry for Digital and Economic Affairs, the provinces of Upper Austria, Tyrol and Styria as well as the Styrian Business Promotion Agency (SFG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rieger, J., Schenk, J. State-of-the-art Processing Solutions of Steelmaking Residuals. Berg Huettenmaenn Monatsh 165, 227–231 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-020-00950-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-020-00950-x