Abstract
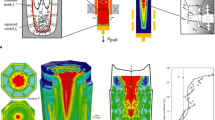
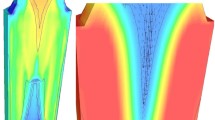
In order to demonstrate how advanced process simulation can help to understand metallurgical process details and thus to improve industrial productivity, a number of examples are shown and discussed. The paper covers recent simulation results gained at the Chair of Simulation and Modeling of Metallurgical Processes, namely (i) the flow and shell formation in thin slap casting of steel, (ii) multiphase flow and magneto-hydrodynamic during Electro-Slag-Remelting, (iii) mold filling, surface wave dissipation and solidification during horizontal centrifugal casting of rolls, and (iv) forced and natural convection during electro-refining of copper in an industrial-size tankhouse cell.
Zusammenfassung
In dieser Arbeit wird anhand von vier Beispielen gezeigt, wie fortschrittliche Prozesssimulationen helfen können, metallurgische Prozessdetails zu verstehen und somit die industrielle Produktivität zu erhöhen. Die Beispiele stammen aus laufenden Forschungsarbeiten des Lehrstuhls für Simulation und Modellierung metallurgischer Prozesse. Es werden i) Strömungen und Erstarrung beim Dünnbrammengießen von Stahl, ii) Mehrphasenströmung und Magnetohydrodynamik beim Elektroschlackeumschmelzen, iii) Formfüllung, Bewegung von Oberflächenwellen und Erstarrung beim horizontalen Schleuderguss von Großwalzen, und iv) erzwungene und natürliche Strömung in industriellen Aggregaten bei der Elektroraffinationselektrolyse von Kupfer behandelt.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tang, Y.; Krobath, M.; Nitzl, G.; Eglsaeer, C.; Morales, R.: SEN Design Optimization Using Transient Flow Simulations and Modelling at High-Speed Thin Slab Casting, J. Iron & Steel Res., 16 (2009), Supplement 1, pp. 173–179
Thomas, B.G.: Brimacombe Lecture, 59th Electric Furnace Conf., Iron & Steel Soc., 2001, pp. 3–30
Camporredondo, J.E.; Castillejos, A.H.; Acosta F.A.; Gutierrez E.P.; Herrera M.A.: Analysis of thin-slab casting by the compact-strip process: Part I. Heat extraction and solidification Metall. Mater. Trans. B, vol. 35 (2004), pp. 541–560
Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Gan, Y.: Numerical Simulation of Fluid Flow and Thermal Characteristics of Thin Slab in the Funnel-Type Molds of Two Casters, ISIJ Int., 51 (2011), pp. 392–401
Pfeiler, C.; Thomas, B.G.; Wu, M.; Ludwig, A.; Kharicha, A.: Solidification and Particle Entrapment during Continuous Casting of Steel. Steel Res. Int., 79 (2008), pp. 599–607
Thomas, B.G.; O’Malley, R.O.; Stone, D.: Measurement of Temperature, Solidification, and Microstructure in a Continuous Cast Thin Slab, in: Thomas, B.G.; Beckermann, C. (eds), Proc. MCWASP VIII TMS Publications, USA, (1998), pp. 1185–1199
Wu, M.; Vakhrushev, A.; Nunner, G.; Pfeiler, C.; Kharicha, A.; Ludwig, A.: Importance of Melt Flow in Solidifying Mushy Zone, Open Transport Phenomena J.—Bentham Open, 2 (2010), pp. 16–23
Vakhrushev, A.; Ludwig, A.; Wu, M.; Tang, Y.; Nitzl, G.; Hackl, G.: Modeling of Turbulent Melt Flow and Solidification Processes in Steel Continuous Caster with the Open Source Software Package OpenFOAM, Proc. OSCIC’10. Germany, Munich, Nov. 4–5, 2010
Vakhrushev, A.; Ludwig, A.; Wu, M.; Tang, Y.; Nitzl, G.; Hackl, G.: Modeling of nonmetallic inclusions and gas bubbles motion in continuous caster, Proc. ECCC Germany, Düsseldorf, June 27–July 01, 2011
Vakhrushev, A.; Ludwig, A.; Wu, M.; Tang, Y.; Nitzl, G.; Hackl, G.: Coupling the turbulent flow with the solidification processes in OpenFOAM, Proc. OSCIC’11. France, Paris Chantilly, Nov. 3–4, 2011
Vakhrushev, A.; Wu, M.; Ludwig, A.; Tang, Y.; Hackl, G.; Nitzl, G.: Proc. MCWASP XIII, in: Ludwig, A.; Wu, M.; Kharicha, A. (eds.), IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng., 33 (2012), 012014
Melgaard, D.K.; Williamson, R.L.; Beaman, J.J.: Controlling Remelting Processes for Superalloys and Aerospace Ti Alloystitle, JOM, 1998 March, pp. 13–17
Hernandez-Morales, B.; Mitchell, A.: Review of mathematical models of fluid flow, heat transfer, and mass transfer in electroslag remelting process, Ironmaking & Steelmaking, Vol. 26 (1999), pp. 423–438
Werber, V.; Jardy, A.; Dussoubs, B.; Ablitzer, D.; Ryberon, S.; Schmitt, V.; Hans, S.; Poisson, H.: A Comprehensive Model of the Electroslag Remelting Process: Description and Validation, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 40B (2009), pp. 271–280
Kharicha, A.; Schützenhöfer, W.; Ludwig, A.; Tanzer, R.; Wu M.: Reformulation of the Joule heating in presence of turbulent fluctuation, in: Int. J. Cast Metals Research, vol 22 (2009) pp. 155–159
Kharicha, A.; Schützenhöfer, W.; Ludwig, A.; Tanzer, R.: On the Importance of Electric Currents Flowing directly into the Mould during an ESR Process, Steel Research Int. vol. 79 (2008), 8, pp. 632–636
Kharicha, A.; Ludwig, A.; Wu M.: Int. Symp. on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting in: Lee, P. D. et al. (eds.), LMPC-11, France, Nancy, 2011, pp. 41–48
Kaschnitz, E.: Numerical simulation of centrifugal casting of pipes, in: Ludwig, A.; M. Wu, M.; A. Kharicha, A. (eds.), Proc. MCWASP XIII, IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng., 33 (2012), 012031.
Leveque, R. J.: Finite volume Methods for hyperbolic problems, Cambridge texts in applied mathematics, New York, Cambridge University Press, 2002.
Kharicha, A.; Bohacek, J.; Ludwig, A.; Wu, M.: Vibration induced flow in a horizontal centrifugal casting, in: Nastac, L. et al. (eds.) CFD Modeling and Simulation in Materials Processing, Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2012, pp. 227–234.
Boháček, J.; Kharicha, A.; Ludwig, A.; Wu, M.: Liquid metal inside a horizontally rotating cylinder under vibrations, in: Experimental Fluid Mechanics (EFM 2011), Czech Republic, Jičín, Nov. 22–25. 2011, vol. 2, pp. 564–73.
Kharicha, A.; Bohacek, J.; Ludwig, A.; Wu, M.: Simulation of Horizontal Centrifugal Casting, to be published.
Dantzig, J. A.; Rappaz, M.: Solidification, Lausanne, EPFL Press (etc): Taylor & Francis, 2009.
Martinez, G.; Garnier, M.; Durand, F.: Stirring phenomena in centrifugal casting of pipes, J Appl. Sci. Res., vol. 44 (1987), pp. 225–39
Davenport, W. G.; King, M.; Schlesinger, M.; Biswas, A. K.: Extractive Metallurgy of Copper, 4th edition, Pergamon Publishing, 2002, pp. 265–288.
Filzwieser, A.: Modellierung der kathodennahen Vorgänge in der Kupferelektrolyse, Diss., Montanuniv. Leoben, Lehrstuhl Nichteisenmetallurgie, 2000
Leahy, M. J.; Schwartz, P.: Experimental Validation of a Computational Fluid Dynamics Model of Copper Electrowinning, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B 41 (2010), No. 6, pp. 1247–1260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ludwig, A., Wu, M., Kharicha, A. et al. Process Simulation for the Metallurgical Industry: New Insights into Invisible Phenomena. Berg Huettenmaenn Monatsh 158, 184–188 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-013-0135-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00501-013-0135-y
Keywords
- Process simulation
- Continuous casting
- Electro-slag-remelting
- Centrifugal casting
- Copper-electro-refining