Abstract
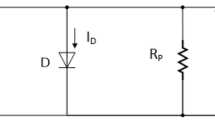
When solar irradiation is uniform along with the array, the P–V curve represents a unique maximum power point (MPP). If the cells undergo shade conditions in the presence of bypass diodes, the solar array’s power is decreased, and the P–V curve of the array represents multiple local MPPs (LMPP) and a global MPP (GMPP). LMPPs might mislead the maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms because their characteristics are identical to the MPP. Various studies have been conducted on partial shading conditions. This study uses parallel distributed maximum power point tracking (DMPPT) due to the advantages of this structure. A high-gain converter is presented to resolve the high conversion gain required by the DC/DC converter in this structure. This study also presents MLP and RBF networks for MPP tracking and compares their efficiencies under the same irradiation and partial shading conditions. Since determining optimal weight coefficients in MLP neural networks and variances, means, and weights in RBF networks play an essential role in their performance, this study uses four optimization algorithms of particle swarm optimization (PSO), gray wolf optimization (GWO), grasshopper optimization algorithm (GOA), and Harris Hawks optimization (HHO). Finally, an adaptive fuzzy-PID controller controls the three-phase grid-connected inverter. A comparison of the results shows that the efficiency of MLP and RBFII is almost the same, about 98–99%. Moreover, the accuracy of MLP networks is higher than RBF, and RBF networks’ only advantage is shorter training time. In addition, RBF networks require much more activation functions for proper performance. The simulation outcomes confirm the superior efficacy of the HHO algorithm in training neural networks when compared to alternative algorithms.























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Abdolazimi O, Esfandarani MS, Shishebori D (2021a) Design of a supply chain network for determining the optimal number of items at the inventory groups based on ABC analysis: a comparison of exact and meta-heuristic methods. Neural Comput Appl 33:6641–6656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-05428-y
Abdolazimi O, Salehi M, Salehi M, Shishebori D (2021b) A Comparison of Solution Methods for the Multi- Objective Closed Loop Supply Chains. Adv Ind Eng 54:75–98. https://doi.org/10.22059/jieng.2021.321634.1758
Achanta SDM, Karthikeyan T, Kanna RV (2021) Wearable sensor based acoustic gait analysis using phase transition-based optimization algorithm on IoT. Int J Speech Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-021-09893-1
Adinolfi G, Femia N, Petrone G, Spagnuolo G, Vitelli M (2009) Energy efficiency effective design of DC/DC converters for DMPPT PV applications. In: 2009 35th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics. IEEE, pp. 4566–4570. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON.2009.5414868
Alirahmi SM, Mousavi SF, Ahmadi P, Arabkoohsar A (2021) Soft computing analysis of a compressed air energy storage and SOFC system via different artificial neural network architecture and tri-objective grey wolf optimization. Energy 236:121412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.121412
Aouchiche N, Aitcheikh MS, Becherif M, Ebrahim MA (2018) AI-based global MPPT for partial shaded grid connected PV plant via MFO approach. Sol Energy 171:593–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2018.06.109
Balato M, Vitelli M (2014) A new control strategy for the optimization of Distributed MPPT in PV applications. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 62:763–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2014.05.032
Balato M, Vitelli M (2015) An algorithm for the fast estimate of the maximum power voltages in PV applications adopting microconverters. COMPEL Int J Comput Math Electr Electron Eng 34:110–131. https://doi.org/10.1108/COMPEL-11-2013-0378
Balato M, Costanzo L, Vitelli M (2018) DMPPT PV system. In: Advances in renewable energies and power technologies. Elsevier, pp. 163–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812959-3.00005-8
Bassi H, Salam Z, Ramli MZ, Sindi H, Rawa M (2019) Hardware Approach to Mitigate the Effects of Module Mismatch in a Grid-connected Photovoltaic System: A Review. Energies 12:4321. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12224321
Biswas J, Kamath AM, Gopi AK, Barai M (2018) Design, Architecture, and Real-Time Distributed Coordination DMPPT Algorithm for PV Systems. IEEE. J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron 6:1418–1433. https://doi.org/10.1109/JESTPE.2017.2756698
Bratcu AI, Munteanu I, Bacha S, Picault D, Raison B (2011) Cascaded DC–DC Converter Photovoltaic Systems: Power Optimization Issues. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 58:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2043041
Chen C-W, Chen K-H, Chen Y-M (2014) Modeling and Controller Design of an Autonomous PV Module for DMPPT PV Systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron 29:4723–4732. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2013.2287752
Coppola M, Guerriero P, Lannuzzi D, Daliento S, Del Pizzo A (2020) Extended operating range of PV module-level CHB inverter. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 119:105892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2020.105892
Dadfar S, Wakil K, Khaksar M, Rezvani A, Miveh MR, Gandomkar M (2019) Enhanced control strategies for a hybrid battery/photovoltaic system using FGS-PID in grid-connected mode. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:14642–14660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.04.174
Dakshina Murthy AS, Karthikeyan T, Lakshmi Jagan BO, Usha Kumari C (2020) Novel deep neural network for individual re recognizing physically disabled individuals. Mater Today Proc 33:4323–4328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.447
Farajdadian S, Hosseini SMH (2019a) Design of an optimal fuzzy controller to obtain maximum power in solar power generation system. Sol Energy 182:161–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2019.02.051
Farajdadian S, Hosseini SMH (2019b) Optimization of fuzzy-based MPPT controller via metaheuristic techniques for stand-alone PV systems. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:25457–25472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.08.037
Farayola AM, Hasan AN, Ali A, Twala B (2018) Distributive MPPT approach using ANFIS and perturb & observe techniques under uniform and partial shading conditions. pp. 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7868-2_3
Femia N, Lisi G, Petrone G, Spagnuolo G, Vitelli M (2008) Distributed maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic arrays: Novel approach and system analysis. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55:2610–2621. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2008.924035
Fouad MM, Shihata LA, Morgan EI (2017) An integrated review of factors influencing the perfomance of photovoltaic panels. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 80:1499–1511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.141
Hassan Hosseini SM, Keymanesh AA (2016) Design and construction of photovoltaic simulator based on dual-diode model. Sol Energy 137:594–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2016.09.001
Heidari AA, Mirjalili S, Faris H, Aljarah I, Mafarja M, Chen H (2019) Harris hawks optimization: algorithm and applications. Futur Gener Comput Syst 97:849–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.02.028
Hosseini S, Taheri S, Pouresmaeil E, Espinoza-Trejo DR (2021) Enhancement of a photovoltaic inverter efficiency using a shade-tolerant MPPT. In: IECON 2021–47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. IEEE, pp. 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/IECON48115.2021.9589280
Huusari J, Suntio T (2012) Dynamic Properties of Current-Fed Quadratic Full-Bridge Buck Converter for Distributed Photovoltaic MPP-Tracking Systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27:4681–4689. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2012.2186318
Huusari J, Suntio T (2013) Origin of cross-coupling effects in distributed DC–DC converters in photovoltaic applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28:4625–4635. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2012.2235860
Khan O, Xiao W (2017) Review and qualitative analysis of submodule-level distributed power electronic solutions in PV power systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:516–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.03.073
Kiani-Moghaddam M, Shivaie M, Weinsier PD (2019) Introduction to meta-heuristic optimization algorithms. pp. 3–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12044-3_1
Liu B, Duan S, Cai T (2011) Photovoltaic DC-building-module-based BIPV system—concept and design considerations. IEEE Trans Power Electron 26:1418–1429. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2010.2085087
Luo H, Wen H, Li X, Jiang L, Hu Y (2016) Synchronous buck converter based low-cost and high-efficiency sub-module DMPPT PV system under partial shading conditions. Energy Convers Manag 126:473–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.08.034
Mahdizadeh Shalmaei AH, Asghari Gorji S (2022) A non-inverting transformerless semi-quadratic buck-boost converter. In: 2022 12th International Conference on Power, Energy and Electrical Engineering (CPEEE). IEEE, pp. 113–119. https://doi.org/10.1109/CPEEE54404.2022.9738662
Mao M, Zhang L, Duan P, Duan Q, Yang M (2018) Grid-connected modular PV-Converter system with shuffled frog leaping algorithm based DMPPT controller. Energy 143:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.10.099
Mashinchi Maheri H, Babaei E, Sabahi M, Hosseini SH (2017) High step-Up DC–DC converter with minimum output voltage ripple. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 64:3568–3575. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2017.2652395
Mirjalili S, Song Dong J, Lewis A (eds) (2020) Nature-inspired optimizers, studies in computational intelligence. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Orduz R, Solórzano J, Egido MÁ, Román E (2013) Analytical study and evaluation results of power optimizers for distributed power conditioning in photovoltaic arrays. Prog Photovoltaics Res Appl 21:359–373. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.1188
Rajabi M, Hosseini SMH (2019) Maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic systems under different operational conditions by using ZA-INC algorithm. SN Appl Sci 1:1535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1536-7
Sajadian S, Ahmadi R (2017) Distributed maximum power point tracking using model predictive control for photovoltaic energy harvesting architectures based on cascaded power optimizers. IEEE J Photovoltaics 7:849–857. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOTOV.2017.2680601
Seo G-S, Shin J-W, Cho B-H, Lee K-C (2014) Digitally Controlled Current Sensorless Photovoltaic Micro-Converter for DC Distribution. IEEE Trans Ind Informatics 10:117–126. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2013.2248015
Solórzano J, Egido MA (2014) Hot-spot mitigation in PV arrays with distributed MPPT (DMPPT). Sol Energy 101:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2013.12.020
Tomar A, Mishra S (2017) Synthesis of a new DLMPPT technique with PLC for enhanced PV energy extraction under varying irradiance and load changing conditions. IEEE J Photovoltaics 7:839–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOTOV.2017.2675979
Wu H, Sun K, Zhou Z, Xing Y (2012) An integrated four-port full-bridge converter with DMPPT for renewable power system. In: 2012 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG). IEEE, pp. 895–900. https://doi.org/10.1109/PEDG.2012.6254107
Yuan J, Zhao Z, Liu Y, He B, Wang L, Xie B, Gao Y (2021) DMPPT control of photovoltaic microgrid based on improved sparrow search algorithm. IEEE Access 9:16623–16629. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3052960
Zhang T, Jiang J, Chen D (2021) An efficient and low-cost DMPPT approach for photovoltaic submodule based on multi-port DC converter. Renew Energy 178:1144–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.06.134
Funding
This study was not funded any institution and organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed to each part of this paper equally. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Research involving human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Ethical approval
The paper and the material are the authors’ own original work, which has not been previously published elsewhere.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Farajdadian, S., Hosseini, S.M.H. DMPPT control of photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions based on optimized neural networks. Soft Comput 28, 4987–5014 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09196-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09196-4