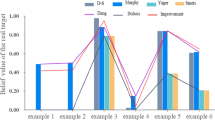
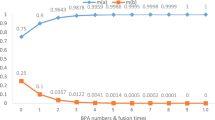
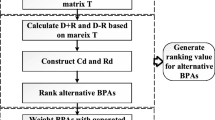
Abstract
How to handle conflict in Dempster-Shafer evidence theory is an open issue. Many approaches have been proposed to solve this problem. The existing approaches can be divided into two kinds. The first is to improve the combination rule, and the second is to modify the data model. A typical method to improve combination rule is to assign the conflict to the total ignorance set \(\varTheta \). However, it does not make full use of conflict information. A novel combination rule is proposed in this paper, which assigns the conflicting mass to the power set (ACTP). Compared with modifying data model, the advantage of the proposed method is the sequential fusion, which greatly decrease computational complexity. To demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed method, some numerical examples are given. Due to the less information loss, the proposed method is better than other methods in terms of identifying the correct evidence, the speed of convergence and computational complexity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials generated or analysed during this study are included in this article.
Code availability
The code of the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abellán J, Moral-García S, Benítez MD (2021) Combination in the theory of evidence via a new measurement of the conflict between evidences. Expert Syst Appl 178:114987
Chang L, Zhang L, Chao F, Chen Y-W (2021) Transparent digital twin for output control using belief rule base. IEEE Trans Cybern 52(10):10364–10378
Chen X, Deng Y (2022) An evidential software risk evaluation model. Mathematics 10(13):2325
Chen X, Deng Y (2023) A new belief entropy and its application in software risk analysis. Int J Comput Commun Control 18(2):5299
Chen L, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2021) Probability transformation of mass function: a weighted network method based on the ordered visibility graph. Eng Appl Artif Intell 105:104438
Chen L, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2023) The distance of random permutation set. Inf Sci 628:226–239
Cuzzolin F (2008) A geometric approach to the theory of evidence. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C 38(4):522–534
Dempster PA (2008) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Classic works of the Dempster-Shafer theory of belief functions. Springer, Cham, pp 57–72
Deng Y (2020) Uncertainty measure in evidence theory. Sci China Inf Sci 63(11):210201
Deng Y (2022) Random permutation set. Int J Comput Commun Control. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2022.1.4542
Deng X, Jiang W (2020) On the negation of a Dempster-Shafer belief structure based on maximum uncertainty allocation. Inf Sci 516:346–352
Deng X, Jiang W (2022) A framework for the fusion of non-exclusive and incomplete information on the basis of d number theory. Appl Intell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03960-z
Deng J, Deng Y, Cheong KH (2021) Combining conflicting evidence based on Pearson correlation coefficient and weighted graph. Int J Intell Syst 36(12):7443–7460
Deng X, Xue S, Jiang W (2023) A novel quantum model of mass function for uncertain information fusion. Inf Fusion 89:619–631
Dong Q, Sheng Q, Martínez L, Zhang Z (2022) An adaptive group decision making framework: Individual and local world opinion based opinion dynamics. Inf Fusion 78:218–231
Dubois D, Prade H (1992) Combination of fuzzy information in the framework of possibility theory. Data Fusion Robot Mach Intell 12:481–505
Fei L, Wang Y (2022) An optimization model for rescuer assignments under an uncertain environment by using dempster-shafer theory. Knowl-Based Syst 255:109680
Fuyuan X (2022) Gejs: a generalized evidential divergence measure for multisource information fusion. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2022.3211498
Gao X, Su X, Qian H, Pan X (2021) Dependence assessment in human reliability analysis under uncertain and dynamic situations. Nucl Eng Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anucene.2017.10.045
Gong Y, Xiaoyan S, Qian H, Yang N (2018) Research on fault diagnosis methods for the reactor coolant system of nuclear power plant based on ds evidence theory. Ann Nucl Energy 112:395–399
Guo K, Li W (2011) Combination rule of d-s evidence theory based on the strategy of cross merging between evidences. Expert Syst Appl 38(10):13360–13366
Han D, Liu W, Dezert J, Yang Y (2016) A novel approach to pre-extracting support vectors based on the theory of belief functions. Knowl-Based Syst 110:210–223
Huang Y, Xiao F (2023) Higher order belief divergence with its application in pattern classification. Inf Sci 635:1–24
Lefevre E, Colot O, Vannoorenberghe P (2002) Belief function combination and conflict management. Inf Fusion 3(2):149–162
Li B, Wang B, Wei J, Huang Y, Guo Z (2001) Efficient combination rule of evidence theory object detection, classification, and tracking technologies. Int Soc Opt Photon 4554:237–240
Li Y, Yang Y, Jiang B (2020) Prediction of coal and gas outbursts by a novel model based on multisource information fusion. Energy Explor Exploit 38(5):1320–1348
Li Y, Herrera-Viedma E, Pérez IJ, Barragán-Guzmán M, Morente-Molinera JA (2023a) Z-number-valued rule-based classification system. Appl Soft Comput 137:110168
Li Z, Zhang Z, Wenyu Yu (2023b) Consensus reaching for ordinal classification-based group decision making with heterogeneous preference information. J Oper Res Soc 0(0):1–22
Liang XR, Yao PY, Liang DL (2008) Improved combination rule of evidence theory and its application in fused target recognition. Electr Opt Control 12:010
Liang Y, Yanbing J, Qin J, Pedrycz W (2021) Multi-granular linguistic distribution evidential reasoning method for renewable energy project risk assessment. Inf Fusion 65:147–164
Liao H, Ren Z, Fang R (2020) A deng-entropy-based evidential reasoning approach for multi-expert multi-criterion decision-making with uncertainty. Int J Comput Intell Syst 13(1):1281–1294
Liu Z-G, Huang L-Q, Zhou K, Denoeux T (2020) Combination of transferable classification with multisource domain adaptation based on evidential reasoning. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(5):2015–2029
Meng D, Xie Tianwen W, Peng ZS-P, Zhengguo H, Yan L (2020) Uncertainty-based design and optimization using first order saddlepoint approximation method for multidisciplinary engineering systems. ASCE-ASME J Risk Uncertain Eng Syst Part A. https://doi.org/10.1061/AJRUA6.0001076
Moral-García S, Abellán J (2021) Required mathematical properties and behaviors of uncertainty measures on belief intervals. Int J Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22432
Murphy CK (2000) Combining belief functions when evidence conflicts. Decis Support Syst 29(1):1–9
Pan L, Gao X (2023) Evidential Markov decision-making model based on belief entropy to predict interference effects. Inf Sci 633:10–26
Qianli Zhou, Ye Cui, Zhen Li, Yong Deng (2023) Marginalization in random permutation set theory: from the cooperative game perspective. Nonlinear Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-023-08506-7
Quan Sun X-Q, Ye W-KG (2000) A new combination rules of evidence theory. Acta Electron Sin 28(8):117–119
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Smets P (1990) The combination of evidence in the transferable belief model. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 12(5):447–458
Solaiman B, Bossé É (2019) Possibility theory for the design of information fusion systems. Springer, Cham
Song Y, Deng Y (2021) Entropic explanation of power set. Int J Comput Commun Control 16(4):4413
Song Y, Wang X, Zhu J, Lei L (2018) Sensor dynamic reliability evaluation based on evidence theory and intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Appl Intell 48(11):3950–3962
Song Y, Fu Q, Wang Y-F, Wang X (2019) Divergence-based cross entropy and uncertainty measures of Atanassovs intuitionistic fuzzy sets with their application in decision making. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105703
Xiao F (2019) Efmcdm: evidential fuzzy multicriteria decision making based on belief entropy. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(7):1477–1491
Xiao F (2020) Generalization of dempster-shafer theory: a complex mass function. Appl Intell 50(10):3266–3275
Xiao F (2021) Ceqd: a complex mass function to predict interference effects. IEEE Trans Cybern. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3040770
Xiao F, Pedrycz W (2022) Negation of the quantum mass function for multisource quantum information fusion with its application to pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 45(2):2054–2070
Xiao F, Junhao W, Witold P (2022a) Generalized divergence-based decision making method with an application to pattern classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2022.3177896
Xiao F, Zehong C, Chin-Teng L (2022b) A complex weighted discounting multisource information fusion with its application in pattern classification. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2022.3206871
Xinyang D, Yebi C, Jiang W (2022) An ecr-pcr rule for fusion of evidences defined on a non-exclusive framework of discernment. Chin J Aeronaut 35(8):179–192
Xiong L, Xiaoyan S, Qian H (2021) Conflicting evidence combination from the perspective of networks. Inf Sci 580:408–418
Yager RR (1987) On the dempster-shafer framework and new combination rules. Inf Sci 41(2):93–137
Yang J-B, Dong-Ling X (2013) Evidential reasoning rule for evidence combination. Artif Intell 205:1–29
Yang X, Xing H, Su X, Ji X (2022) Entropy-based thunderstorm imaging system with real-time prediction and early warning. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3164167
Yang Y, Gai T, Cao M, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Jian W (2023) Application of group decision making in shipping industry 4.0: bibliometric analysis, trends, and future directions. Systems 11(2):69
Zadeh LA (1979) On the validity of Dempster’s rule of combination of evidence. EECS Department, University of California, Berkeley. http://www2.eecs.berkeley.edu/Pubs/TechRpts/1979/28427.html
Zhang W, Deng Y (2019) Combining conflicting evidence using the DEMATEL method. Soft Comput 23:8207–8216
Zhang Z, Li Z (2022) Consensus-based topsis-sort-b for multi-criteria sorting in the context of group decision-making. Ann Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04985-w
Zhou M, Zhu S-S, Chen Y-W, Jian W, Herrera-Viedma E (2021) A generalized belief entropy with nonspecificity and structural conflict. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 52(9):5532–5545
Zhou Q, Huang Y, Deng Y (2022) Belief evolution network-based probability transformation and fusion. Comput Ind Eng 174:108750
Zhun-Ga Liu Yu, Liu JD, Cuzzolin F (2019) Evidence combination based on credal belief redistribution for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28(4):618–631
Acknowledgements
The work is partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61973332), JSPS Invitational Fellowships for Research in Japan (Short-term).
Funding
The work is partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61973332).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. All authors performed material preparation, data collection and analysis. Xingyuan chen wrote the first draft of the paper. All authors contributed to the revisions of the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Author Xingyuan Chen declares that she had no conflict of interest. Author Yong Deng declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The participant has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Deng, Y. A novel combination rule for conflict management in data fusion. Soft Comput 27, 16483–16492 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09112-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09112-w