Abstract
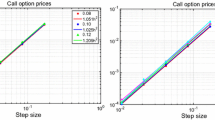
In this paper, we study the existence, uniqueness, and stability of solutions to the pricing problem of European continuous-installment options under the regime-switching model based on a numerical approach. For this, we consider a two-state continuous-time Markov chain for the regime-switching model and a one-dimensional finite element method for the numerical scheme. Under our proposed model and the installment option feature for the option holder to continue paying installments until maturity and receive payoff or to stop installments and terminate the contract, the valuation problem has been formulated as coupled partial differential equations (CPDE) with free boundaries. For this problem, we obtained some appropriate assumptions for the model parameters to prove that the pricing problem has unique solutions under the regime-switching model. We also illustrated some proven theorems to show the stability of solutions with a numerical approach. Finally, some numerical examples are considered to show the performance of the obtained theoretical results through numerical implementations.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Alobaidi G, Mallier R (2006) Installment options close to expiry. J Appl Math Stoch Anal 2006:1–9
Alobaidi G, Mallier R, Deakin A (2004) Laplace transforms and installment options. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 14:1167–1189
Black F, Scholes M (1973) The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. J Polit Econ 81:637–654
Buffington J, Elliott RJ (2002) American options with regime switching. Int J Theor Appl Financ 5:497–514
Chance DM (2011) Essays in derivatives: risk-transfer tools and topics made easy. Wiley
Choi SY, Jeon J, Yoon JH (2020) Analytic valuation of European continuous-installment barrier options. J Comput Appl Math 363:392–412
Ciurlia P (2011) Valuation of European continuous-installment options. Comput Math Appl 62(6):2518–2534
Deng G (2013) Pricing American continuous-installment put option in a jump-diffusion model. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Control Conference. IEEE, pp 8289–8294
Dinçer H, Kou G, Olgu Akdeniz O, Yüksel S (2021) Fintech investments in European banks: a hybrid its fuzzy multidimensional decision-making approach. Financ Innov 7(1):39
Dixit AK, Pindyck RS (1994) Investment under uncertainty. Princeton University Press
François P (2005) Pricing ASX installment warrants under Garch H. Ben-Ameur, M. Breton. Les Cahiers du GERAD ISSN 711:2440
Goard J, AbaOud M (2022) Pricing European and American installment options. Mathematics 10(19):3494
Gong X, Zhang W, Xu W, Li Z (2022) Uncertainty index and stock volatility prediction: evidence from international markets. Financ Innov 8(1):1–44
Griebsch S, Kuhn C, Wystup U (2007) Installment options: a closed-form solution and the limiting case. Mathematical Control Theory and Finance. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Heidari S (2023) Numerical approach for coupled systems resulting from pricing of derivatives: modeling and pricing of installment options. Math Methods Appl Sci 46(4):4663–4675
Heidari S, Azari H (2017a) A front-fixing finite element method for pricing American options under regime-switching jump-diffusion models. Comput Appl Math 37:3691–3707
Heidari S, Azari H (2017b) Pricing American options under multi-states: a radial basis collocation approach. SeMA J 75:365–378
Holmes A, Yang H, Zhang S (2012) A front-fixing finite element method for the valuation of American options with regime switching. Int J Comput Math IJCM 89(1–18):06
Jeon J, Kim G (2019) Pricing European continuous-installment strangle options. N Am J Econ Financ 50:101049
Jeon J, Kim G (2022) Pricing European continuous-installment currency options with mean-reversion. N Am J Econ Financ 59:101605
Kimura T (2010) Valuing continuous-installment options. Eur J Oper Res 201(1):222–230
MacRae CD (2008) The employee stock option: an installment option. Available at SSRN 1286928
Merton RC (1973) Theory of rational option pricing. Bell J Econ Manag Sci 4:141–183
Miglio E, Sgarra C (2011) A finite element discretization method for option pricing with the bates model. SeMA J 55(1):23–40
Oosterlee CW (2003) On multigrid for linear complementarity problems with application to American-style options. Electron Trans Numer Anal 15(1):165–185
Schachermayer W, Davis M, Tompkins R (2000) Pricing no-arbitrage bounds and robust hedging of installment options. Quant Financ 1:597–610
Schachermayer W, Davis M, Tompkins R (2004) The evaluation of venture capital as an instalment option: valuing real options using real options. Real options. Springer, pp 77–96
Tie Li G, Kou Y. Peng, Yu Philip S (2021) An integrated cluster detection, optimization, and interpretation approach for financial data. IEEE Trans Cybern 52(12):13848–13861
Yang H (2010) A numerical analysis of American options with regime switching. J Sci Comput 44(1):69–91
Yang Z, Yi F (2009) Valuation of European installment put option: variational inequality approach. Commun Contemp Math 11(02):279–307
Yi F, Yang Z, Wang X (2008) A variational inequality arising from European installment call options pricing. SIAM J Math Anal 40:306–326
Yüksel S, Kou G, Dinçer H (2022) Inventive problem-solving map of innovative carbon emission strategies for solar energy-based transportation investment projects. Appl Energy 311:118680
Zhang W, Zhou ZQ, Li J, Xiong X (2022) Government intervention model based on behavioral heterogeneity for China’s stock market. Financ Innov 8(1):1–19
Zhu SP, Pasricha P, He XJ (2022) A closed-form pricing formula for European options in an illiquid asset market. Financ Innov 8(1):30
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Shahid Beheshti University.
Funding
There are no funders to report for this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author contributed to all aspects of this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Heidari, S. A finite element method for pricing of continuous-installment options under a Markov-modulated model: existence, uniqueness, and stability of solutions. Soft Comput 28, 3341–3351 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08601-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08601-2