Abstract
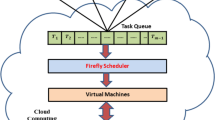
Cloud is an important smart platform for digital applications to enrich communication services. However, massive data has made sharing resources and scheduling tasks a complex score. Also, any fault in one connected VM has degraded the entire cloud system. Considering these issues, the load balancing objective was taken into consideration. Moreover, the current study has implemented a novel Fruitfly-based transfer learning for sharing the required resources to each Virtual Machine (VM) for the task execution. Initially, the Virtual Machines (VMs) were created with different user tasks then the load was balanced by equally sharing the burden with other connected VMs. Consequently, the task ordering function was performed based on priority, and the required resources were assigned. Moreover, the planned model was tested in the python platform, and the metrics were measured. Also, the improved score for enhancing cloud services is validated by performing a comparative analysis. The shortest duration for the job scheduling process is 180 s, execution time 700 s and response time 15 s. These outcomes are better than the compared conventional models. Hence, this model efficiently balances the data load in the cloud computing environment, improving the cloud services.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Alouffi B, Hasnain M, Alharbi A, Alosaimi W et al (2021) A systematic literature review on cloud computing security: threats and mitigation strategies. IEEE Access 9:57792–57807. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3073203
Ansari MD, Gunjan VK, Rashid E (2021) On security and data integrity framework for cloud computing using tamper-proofing. ICCCE 2020, Springer, Singapore, pp 1419–1427. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7961-5_129
Asghari A, Sohrabi MK, Yaghmaee F (2021) Task scheduling, resource provisioning, and load balancing on scientific workflows using parallel SARSA reinforcement learning agents and genetic algorithm. J Supercomput 77(3):2800–2828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03364-1
Balaji K, Kiran PS, Kumar MS (2021) An energy efficient load balancing on cloud computing using adaptive cat swarm optimization. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.11.106
Baucas MJ, Spachos P (2020) Using cloud and fog computing for large scale IoT-based urban sound classification. Simulat Model Pract Theor 101:102013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.simpat.2019.102013
Bello SA, Oyedele LO, Akinade OO et al (2021) Cloud computing in construction industry: Use cases, benefits and challenges. Autom Constr 122:103441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103441
Dalal S, Seth B, Jaglan V et al (2022) An adaptive traffic routing approach toward load balancing and congestion control in Cloud–MANET ad hoc networks. Soft Comput 26:5377–5388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07099-4
de Carvalho PS, Siluk JCM, Schaefer JL, Pinheiro JR, Schneider PS (2021) Proposal for a new layer for energy cloud management: the regulatory layer. Int J Energy Res 45(7):9780–9799. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.6507
Deng S, Zhang C, Li C, Yin J, Dustdar S, Zomaya AY (2021) Burst load evacuation based on dispatching and scheduling in distributed edge networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 32(8):1918–1932. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2021.3052236
Ebadifard F, Babamir SM (2021) Autonomic task scheduling algorithm for dynamic workloads through a load balancing technique for the cloud-computing environment. Clust Comput 24(2):1075–1101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-020-03177-0
Fathalla A, Li K, Salah A (2022) Best-KFF: a multi-objective preemptive resource allocation policy for cloud computing systems. Cluster Comput 25(1):321–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03407-z
Gabhane JP, Pathak S, Thakare NM (2021) Metaheuristics algorithms for virtual machine placement in cloud computing environments—a review. Comput Netw Big Data IoT. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0965-7_28
Haseeb-Ur-Rehman RMA, Liaqat M et al (2021) Sensor cloud frameworks: state-of-the-art, taxonomy, and research issues. IEEE Sens J 21(20):22347–22370. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3090967
Helali L, Omri MN (2021) A survey of data center consolidation in cloud computing systems. Comput Sci Rev 39:100366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cosrev.2021.100366
Houssein EH, Gad AG, Wazery YM et al (2021) Task scheduling in cloud computing based on meta-heuristics: review, taxonomy, open challenges, and future trends. Swarm Evol Comput 62:100841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2021.100841
Hu G, Xu Z, Wang G, Zeng B, Liu Y, Lei Y (2021) Forecasting energy consumption of long-distance oil products pipeline based on improved fruitfly optimization algorithm and support vector regression. Energy 224:120153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120153
Karthick G, Mapp G, Kammueller F, Aiash M (2021) Modeling and verifying a resource allocation algorithm for secure service migration for commercial cloud systems. Comput Intell. https://doi.org/10.1111/coin.12421
Karthiban K, Raj JS (2020) An efficient green computing fair resource allocation in cloud computing using modified deep reinforcement learning algorithm. Soft Comput 24:14933–14942. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04846-3
Kodli S, Terda S (2021) Hybrid max-min genetic algorithm for load balancing and task scheduling in cloud environment. Int J Intell Eng Syst 14(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.22266/ijies2021.0228.07
Kouatli I (2018) Emotions in the cloud: a framework architecture for managing emotions with an example of emotional intelligence management for cloud computing organizations. Int J Work Organ Emot 9(2):187–208. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJWOE.2018.093317
Kouatli I (2019) People-process-performance benchmarking technique in cloud computing environment: an AHP approach. Int J Product Perform Manag 69(9):1955–1972. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-04-2017-0083
Li W, Cao J, Hu K, Xu J, Buyya R (2019) A trust-based agent learning model for service composition in mobile cloud computing environments. IEEE Access 7:34207–34226. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904081
Liu L, Zhu H, Chen S, Huang Z (2022) Privacy regulation aware service selection for multi-provision cloud service composition. Futu Gen Comput Syst 126:263–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2021.08.010
Liu Y, Zeng Z, Liu X, Zhu X, Bhuiyan MZA (2019) A novel load balancing and low response delay framework for edge-cloud network based on SDN. IEEE Internet Things J 7(7):5922–5933. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2951857
Malik MK, Singh A, Swaroop A (2022) A planned scheduling process of cloud computing by an effective job allocation and fault-tolerant mechanism. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 13(2):1153–1171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03537-7
Mireslami S, Rakai L, Wang M et al (2019) Dynamic cloud resource allocation considering demand uncertainty. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput 9(3):981–994. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2019.2897304
Pourghaffari A, Barari M, Kashi SS (2019) An efficient method for allocating resources in a cloud computing environment with a load balancing approach. Concurr Comput Pract Exp 31(17):e5285. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.5285
Pradhan A, Bisoy SK (2020) A novel load balancing technique for cloud computing platform based on PSO. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci 34(7):3988–3995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.10.016
Priya V, Kumar CS, Kannan R (2019) Resource scheduling algorithm with load balancing for cloud service provisioning. Appl Soft Comput 76:416–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.12.021
Rajput DS, Basha SM, Xin Q, Gadekallu TR et al (2022) Providing diagnosis on diabetes using cloud computing environment to the people living in rural areas of India. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13(5):2829–2840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03154-4
Ranapana R, Jayasena KPN (2021) Novel approach for load balancing in mobile cloud computing. In: 2021 6th international conference on information technology research (ICITR), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITR54349.2021.9657441
Reshmi R, Saravanan DS (2020) Load prediction using (DoG–ALMS) for resource allocation based on IFP soft computing approach in cloud computing. Soft Comput 24:15307–15315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04864-1
Sabireen H, Neelanarayanan V (2021) A review on fog computing: architecture, fog with IoT, algorithms and research challenges. Ict Express 7(2):162–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icte.2021.05.004
Saldamli G, Doshatti A, Kapadia D, Nyati D, Bodiwala M, Ertaul L (2021) Enterprise backend as a service (EBaaS). Advances in parallel & distributed processing, and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 1077–1099. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-69984-0_78
Sefati S, Navimipour NJ (2021) A qos-aware service composition mechanism in the internet of things using a hidden-markov-model-based optimization algorithm. IEEE Internet Things J 8(20):15620–15627. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2021.3074499
Seth B, Dalal S, Kumar R (2019) Hybrid homomorphic encryption scheme for secure cloud data storage. Recent advances in computational intelligence. Springer, Cham, pp 71–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12500-4_5
Siddesha K, Jayaramaiah GV, Singh C (2022) A novel deep reinforcement learning scheme for task scheduling in cloud computing. Cluster Comput 25(6):4171–4188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-022-03630-2
Swarna Priya RM, Bhattacharya S, Maddikunta PKR et al (2020) Load balancing of energy cloud using wind driven and firefly algorithms in internet of everything. J Parallel Distrib Comput 142:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2020.02.010
Therese MJ, Dharanyadevi P, Harshithaa K (2021) Integrating IoT and cloud computing for wireless sensor network applications. Cloud IoT-Based Veh Ad Hoc Netw. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119761846.ch7
Tong Z, Deng X, Chen H, Mei J (2021) DDMTS: a novel dynamic load balancing scheduling scheme under SLA constraints in cloud computing. J Parallel Distrib Comput 149:138–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpdc.2020.11.007
Wei W, Yang R, Gu H, Zhao W et al (2021) Multi-objective optimization for resource allocation in vehicular cloud computing networks. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 23(12):25536–25545. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2021.3091321
Yu C, Wang J, Chen Y, Huang M (2019) Transfer learning with dynamic adversarial adaptation network. In: 2019 IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM), IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2019.00088
Zanbouri K, Jafari Navimipour N (2020) A cloud service composition method using a trust-based clustering algorithm and honeybee mating optimization algorithm. Int J Commun Syst 33(5):e4259. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.4259
Ziyath S, Senthilkumar S (2021) MHO: meta heuristic optimization applied task scheduling with load balancing technique for cloud infrastructure services. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 12(6):6629–6638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02282-7
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional and/or national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
For this type of analysis formal consent is not needed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Edward Gerald, B., Geetha, P. & Ramaraj, E. A fruitfly-based optimal resource sharing and load balancing for the better cloud services. Soft Comput 27, 6507–6520 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07873-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-07873-y