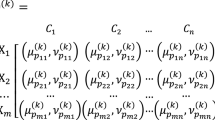Abstract
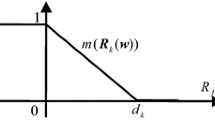
This paper develops a personalized individual semantics (PISs) model for computing with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy information and applies to evaluate different brands of mobile phones. First, considering that a linguistic term means different things to different decision-makers, a consistency-driven optimization model for checking the additive consistent linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations (LIFPRs) is constructed by considering the PISs model. Besides, several optimization models are built to determine the PISs of linguistic terms with LIFPRs and obtain the acceptable additive consistent LIFPRs. Second, a new definition of Hamming distance for measuring linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers (LIFNs) is developed by considering the PISs model, and several desirable properties are discussed. Then, the method of deriving the weight vectors of criteria is calculated based on the proposed distance measure. Subsequently, a framework of group decision-making (GDM) process with LIFPRs is offered, and the application of the proposed method is illustrated by using a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) problem about evaluating different brands of mobile phones. Finally, the comparative analysis is conducted to show the feasibility of proposed method.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Chen Z, Liu P, Pei Z (2015) An approach to multiple attribute group decision making based on linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems 8:747–760
Ding R-X, Palomares I, Wang X, Yang G-R, Liu B, Dong Y, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2020) Large-Scale decision-making: Characterization, taxonomy, challenges and future directions from an Artificial Intelligence and applications perspective. Information Fusion 59:84–102
Dong Y, Herrera-Viedma E (2015) Consistency-driven automatic methodology to set interval numerical scales of 2-tuple linguistic term sets and its use in the linguistic GDM with preference relation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 45:780–792
Dong Y, Herrera-Viedma E (2016) Consistency-driven automatic methodology to set interval numerical scales of 2-tuple linguistic term sets and its use in the linguistic GDM with preference relation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 45:780–792
Dong Y, Xu Y, Yu S (2009) Computing the numerical scale of the linguistic term set for the 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 17:1366–1378
Dong Y, Li C-C, Herrera F (2016) Connecting the linguistic hierarchy and the numerical scale for the 2-tuple linguistic model and its use to deal with hesitant unbalanced linguistic information. Inf Sci 367–368:259–278
Fan S, Liang H, Dong Y, Pedrycz W (2022) A personalized individual semantics-based multi-attribute group decision making approach with flexible linguistic expression. Expert Syst Appl 192:116392
Fan S, Liang H, Dong Y, Pedrycz W, (2021) A Personalized individual semantics-based multi-attribute group decision making approach with flexible linguistic expression, Expert Systems with Applications, 116392.
Fu Z, Liao H (2019) Unbalanced double hierarchy linguistic term set: The TOPSIS method for multi-expert qualitative decision making involving green mine selection. Information Fusion 51:271–286
Giráldez-Cru J, Chica M, Cordón O (2021) A framework of opinion dynamics using fuzzy linguistic 2-tuples. Knowl-Based Syst 233:107559
Herrera-Viedma E, Palomares I, Li CC, Cabrerizo FJ, Dong Y, Chiclana F, Herrera F (2021) Revisiting fuzzy and linguistic decision making: scenarios and challenges for making wiser decisions in a better way. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems 51:191–208
Imanov G, Garibli E, Akbarov R (2017) Analysis of socioeconomic development by intuitionistic linguistic fuzzy numbers. Procedia Computer Science 120:341–348
Jiang L, Liu H, Ma Y, Li Y (2022) Deriving the personalized individual semantics of linguistic information from flexible linguistic preference relations. Information Fusion 81:154–170
Jin F, Ni Z, Pei L, Chen H, Li Y, Zhu X, Ni L (2019) A decision support model for group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy linguistic preferences relations. Neural Comput Appl 31:1103–1124
Kumar K, Chen S-M (2022) Group decision making based on weighted distance measure of linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy sets and the TOPSIS method. Inf Sci 611:660–676
Kumar M, Kaushik M (2020) System failure probability evaluation using fault tree analysis and expert opinions in intuitionistic fuzzy environment. J Loss Prev Process Ind 67:104236
Li C-C, Dong Y, Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E, Martínez L (2017) Personalized individual semantics in computing with words for supporting linguistic group decision making. An Application on Consensus Reaching, Information Fusion 33:29–40
Li C-C, Rodríguez RM, Martínez L, Dong Y, Herrera F (2018) Personalized individual semantics based on consistency in hesitant linguistic group decision making with comparative linguistic expressions. Knowl-Based Syst 145:156–165
C.C. Li, Y. Dong, W. Pedrycz, F. Herrera, Integrating continual personalized individual semantics learning in consensus reaching in linguistic group decision making, IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics, PP (2020) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2020.3031086.
C.C. Li, H. Liang, Y. Dong, F. Chiclana, E. Herrera-Viedma (2021a) Consistency improvement with a feedback recommendation in personalized linguistic group decision making, IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 1–12.
C.C. Li, Y. Dong, F. Chiclana, E. Herrera-Viedma (2021b) Consistency-driven methodology to manage incomplete linguistic preference relation: a perspective based on personalized individual semantics, IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 1–11.
Liang H, Li CC, Dong Y, Herrera F (2021) Linguistic opinions dynamics based on personalized individual semantics. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29:2453–2466
Liang Y, Ju Y, Martínez L, Dong P, Wang A (2022) A multi-granular linguistic distribution-based group decision making method for renewable energy technology selection. Appl Soft Comput 116:108379
Liao H, Wu X, Liang X, Yang J-B, Xu D-L, Herrera F (2018) A continuous interval-valued linguistic ORESTE method for multi-criteria group decision making. Knowl-Based Syst 153:65–77
Lin M, Chen Z, Xu Z, Gou X, Herrera F (2021) Score function based on concentration degree for probabilistic linguistic term sets: An application to TOPSIS and VIKOR. Inf Sci 551:270–290
Liu P, Gao H, Fujita H (2021) The new extension of the MULTIMOORA method for sustainable supplier selection with intuitionistic linguistic rough numbers. Appl Soft Comput 99:106893
Liu J, Mai J, Li H, Huang B, Liu Y (2022) On three perspectives for deriving three-way decision with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy information. Inf Sci 588:350–380
Mahboob A, Rashid T, Sindhu MS (2022) An optimization preference based approach with hesitant intuitionistic linguistic distribution in group decision making. Expert Syst Appl 187:115965
Meng F, Tang J, Xu Z (2017) A 0–1 mixed programming model based method for group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Comput Ind Eng 112:289–304
Meng F, Tang J, Fujita H (2019a) Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations and their application to multi-criteria decision making. Information Fusion 46:77–90
Meng F, Tang J, Zhang Y (2019b) Programming model-based group decision making with multiplicative linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Comput Ind Eng 136:212–224
Mi X, Liao H, Zeng X-J, Xu Z (2021) The two-person and zero-sum matrix game with probabilistic linguistic information. Inf Sci 570:487–499
Muhuri PK, Gupta PK (2020) A novel solution approach for multiobjective linguistic optimization problems based on the 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model. Appl Soft Comput 95:106395
Peng H.-g, Wang J.-q, Cheng P.-f (2018) A linguistic intuitionistic multi-criteria decision-making method based on the Frank Heronian mean operator and its application in evaluating coal mine safety. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 9:1053–1068
Peng H-G, Zhang H-Y, Wang J-Q, Li L (2019) An uncertain Z-number multicriteria group decision-making method with cloud models. Inf Sci 501:136–154
Rabiee M, Aslani B, Rezaei J (2021) A decision support system for detecting and handling biased decision-makers in multi criteria group decision-making problems. Expert Syst Appl 171:114597
Rodríguez RM, Labella Á, Sesma-Sara M, Bustince H, Martínez L (2021) A cohesion-driven consensus reaching process for large scale group decision making under a hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets environment. Comput Ind Eng 155:107158
Tang X, Peng Z, Zhang Q, Pedrycz W, Yang S (2020) Consistency and consensus-driven models to personalize individual semantics of linguistic terms for supporting group decision making with distribution linguistic preference relations. Knowl-Based Syst 189:105078
Wan S-P, Yan J, Dong J-Y (2022a) Personalized individual semantics based consensus reaching process for large-scale group decision making with probabilistic linguistic preference relations and application to COVID-19 surveillance. Expert Syst Appl 191:116328
Wan S-P, Zou W-C, Dong J-Y, Martínez L (2022b) A consensual method for multi-criteria group decision-making with linguistic intuitionistic information. Inf Sci 582:797–832
Wang W, Tian G, Zhang T, Jabarullah NH, Li F, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Wang D, Li Z (2021a) Scheme selection of design for disassembly (DFD) based on sustainability: A novel hybrid of interval 2-tuple linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and regret theory. J Clean Prod 281:124724
Wang X-K, Wang Y-T, Zhang H-Y, Wang J-Q, Li L, Goh M (2021b) An asymmetric trapezoidal cloud-based linguistic group decision-making method under unbalanced linguistic distribution assessments. Comput Ind Eng 160:107457
Wang W, Ding L, Liu X, Liu S (2022) An interval 2-Tuple linguistic Fine-Kinney model for risk analysis based on extended ORESTE method with cumulative prospect theory. Information Fusion 78:40–56
Wu Y, Zhang Z, Kou G, Zhang H, Chao X, Li C-C, Dong Y, Herrera F (2021) Distributed linguistic representations in decision making: Taxonomy, key elements and applications, and challenges in data science and explainable artificial intelligence. Information Fusion 65:165–178
Xiao F, Wang J-Q (2019) Multistage decision support framework for sites selection of solar power plants with probabilistic linguistic information. J Clean Prod 230:1396–1409
Xiao J, Wang X, Zhang H (2020) Managing personalized individual semantics and consensus in linguistic distribution large-scale group decision making. Information Fusion 53:20–34
Xu ZS (2004) EOWA and EOWG operations for aggregation linguistic labels based on linguistic preference relations. Internat J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowledge-Based Systems 12:791–810
Xu ZS, Cai XQ (2010) Recent advances in intuitionistic fuzzy information aggregation. Fuzzy Optimiza and Decision Maming 9:359–381
Zhang H-Y, Peng H-G, Wang J, Wang J-Q (2017) An extended outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Appl Soft Comput 59:462–474
Zhang H, Li CC, Liu Y, Dong Y (2021) Modeling personalized individual semantics and consensus in comparative linguistic expression preference relations with self-confidence: an optimization-based approach. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 29:627–640
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gao L, Dong Y, Pedryczc W (2022a) Consensus reaching with trust evolution in social network group decision making. Expert Syst Appl 188:116022
Zhang Y, Hao Z, Xu Z, Zeng X-J, Xu X (2022b) A process-oriented probabilistic linguistic decision-making model with unknown attribute weights. Knowl-Based Syst 235:107594
Z. Zhang, Z. Li (2021) Personalized individual semantics-based consistency control and consensus reaching in linguistic group decision making, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 1–13.
Zhu H, Zhao J (2022) 2DLIF-PROMETHEE methods for multiple attribute decision making under 2-dimension linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy environments. Software Impacts 13:100312
Zou L, Lin H, Song X, Feng K, Liu X (2021) Rule extraction based on linguistic-valued intuitionistic fuzzy layered concept lattice. Int J Approximate Reasoning 133:1–16
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their insightful and constructive comments and suggestions that have led to an improved version of this paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.72061026), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (Nos. 2020GXNSFAA297239), the Science and Technology Plan of Guangxi (gui ke AD20238006) and Young Teachers’ Basic Scientific Research Ability in Universities of Guangxi (No. 2022KY0387 and 2021KY1563).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Authors, Jian Li, Hongxia Tang, Li–li Niu, Qiongxia Chen, Feilong Li and Zhong-xing Wang, declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Tang, H., Niu, Ll. et al. A personalized individual semantics model for computing with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy information and application in MCDM. Soft Comput 27, 4501–4519 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07698-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07698-1