Abstract
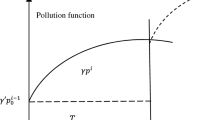
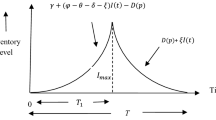
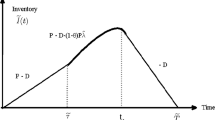
This article deals with a cost minimization objective function of an economic production quantity (EPQ) inventory model with production breakdown and deterioration. The process reliability and the environmental pollution due to over production have also been considered. The model has been split into two different scenarios according to the breaking time before and after the production period. In scenario 1, no machinery failure occurs during production run time and that of scenario 2 the failure occurs during production run time. We develop a deterministic cost minimization problem first then we fuzzify the model by considering the production rate, the demand rate and all the cost components as lock fuzzy numbers. We convert the fuzzy model into equivalent game problem by considering Gaussian normal strategic probabilities. The model has been solved with the help of different key vectors employed by the decision maker. We have shown that the value of the game might be changed with the change of different key vectors. A comparative study has been made with the numerical results of the general fuzzy and crisp models. Finally, graphical illustrations and sensitivity analysis have been done followed by a conclusion.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Aarthi HT (2017) Review on mitigation of air pollution in sponge iron industries. Int J Civil Eng Technol 8(8):1353–1356
Abdel-Aleem A, El-Sharief M, Hassan MA, El-Sebaie MG (2017) Optimization of reliability-based model for production inventory system. Int J Manage Sci Eng Manage 13(2):1–11
Ahmed I, Sultana I (2014) A literature review on inventory modelling with reliability consideration. Int J Ind Eng Comput 5:169–178
Ahmed AA, Mahmoud AES, Mohsen AH, Mohamed GES (2017) Optimization of reliability-based model for production inventory system. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/17509653.2017.1292156
Akten M, Akyol A (2018) Determination of environmental perceptions and awareness towards reducing carbon footprint. Appl Ecol Environ Res 16(4):5249–5267
Aljazzar SM, Gurtu A, Jaber MY (2018) Delay-in-payments-A strategy to reduce carbon emissions from supply chains. J Clean Prod 170:636–644
Arfi B (2006) Linguistic fuzzy-logic game theory. J Conflict Resolut 50(1):28–57
Bag S, Chakraborty D, Roy AR (2009) A production inventory model with fuzzy random demand and with flexibility and reliability considerations. Comput Ind Eng 56:411–416
Benjaafar S, Li Y, Daskin M (2010) Carbon footprint and the management of supply chains: insights from simple models. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2012.2203304
Bhattacharya K, De SK (2020) A robust two layer green supply chain modelling under performance based fuzzy game theoretic approach. Comput Ind Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.107005
Chakraborty T, Giri BC, Chaudhuri KS (2008) Production lot sizing with process deterioration and machine breakdown. Eur J Oper Res 185:606–618
Chen X, Benjaafar S, Elomri A (2013) The carbon-constrained EOQ. Oper Res Lett 41(2):172–179
Cheng T (1989) An economic production quantity model with flexibility and reliability consideration. Eur J Oper Res 39:174–179
Cheng T (1991) EPQ with process reliability and quality assurance considerations. J Oper Res Soc 42:713–720
Chung CJ, Widyadana GA, Wee HM (2011) Economic production quantity model for deteriorating inventory with random machine unavailability and shortage. Int J Prod Res 49:883–902
Chunhai Y, Zebin Q, Thomas WA, Zhaoning L (2020) An inventory model of a deteriorating product considering carbon emissions. Comput Ind Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106694
Ciardiello F, Genovese A, Simpson A (2018) Pollution responsibility allocation in supply networks: a game-theoretic approach and a case study. Int J Prod Econ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2018.10.006
De SK (2017) Triangular dense fuzzy lock sets. Soft Comput 5:6–9
De SK, Beg I (2016) Triangular dense fuzzy sets and new defuzzification methods. Int J Intell Fuzzy Syst 31(1):469–477
De SK, Mahata GC (2019) A production inventory supply chain model with partial backordering and disruption under triangular linguistic dense fuzzy lock set approach. Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04254-2
De S, Nayak PK, Khan A, Bhattacharya K, Smarandache F (2020) Solution of an EPQ model for imperfect production process under game and neutrosophic fuzzy approach. Appl Soft Comput. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106397
De SK, Bhattacharya K, Roy B (2021) Solution of a pollution sensitive supply chain model under fuzzy approximate reasoning. Int J Intell Syst. https://doi.org/10.1002/int2.20210424
Doust MHR, Gholizade S (2014) An analysis of the modified Lotka-Volterra predator-prey model. Gen Meth Notes 25(2):1–5
Glock CH (2013) The machine breakdown paradox: how random shifts in the production rate may increase company profits. Comput Ind Eng 66:1171–1176
He Y, He J (2010) A production model for deteriorating inventory items with production disruptions. Discret Dyn Nat Soc 2010:1–14
Huang H, He Y, Li D (2017) EPQ for an unreliable production system with endogenous reliability and product deterioration. Int Trans Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12311
Huang H, He Y, Li D (2018) Coordination of pricing, inventory and production reliability decisions in deteriorating product supply chains. Int J Prod Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1480070
Jeang A (2012) Simultaneous determination of production lot size and process parameters under process deterioration and process breakdown. Omega 40:774–781
Karmakar S, De SK, Goswami A (2017) A pollution sensitive dense fuzzy economic production quantity model with cycle time dependent production rate. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.080
Krishnaveni G, Ganesan K (2018) A new approach for the solution of fuzzy games. J Phys Conf Ser. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1000/1/0120174
Leung KNF (2007) A generalized geometric programming solution to an economic production quantity model with flexibility and reliability considerations. Eur J Oper Res 176:240–251
Lin YK, Chang PC (2012) System reliability of a manufacturing network with reworking action and different failure rates. Int J Prod Res 50(23):6930–6944
Louit D, Pascual R, Banjevic D, Jardine KS (2011) Optimization models for critical spare parts inventories-A reliability Approach. J Oper Res Soc 62(6):992–1004
Lücker F, Seifert RW, Bicer I (2018) Roles of inventory and reserve capacity in mitigating supply chain disruption risk. Int J Prod Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1504173
Mahapatra GS, Mandal TK, Samanta GP (2012) Fuzzy parametric geometric programming with application in fuzzy EPQ model under flexibility and reliability consideration. J Inf CompuT Sci 7(3):223–234
Metzger LP, Rieger MO (2019) Non-cooperative games with prospect theory players and dominated strategies. Games Econ Behav 115:396–409
Meyer RR, Rothkopf MH, Smith SA (1979) Reliability and inventory in a production-storage system. Manag Sci 25(8):799–807
Mirzahosseinian M, Piplani R (2011) A study of repairable parts inventory system operating under performance-based contract. Eur J Oper Res 214:256–261
Panda D, Maiti M (2009) Multi-item inventory models with price dependent demand under flexibility and reliability consideration and imprecise space constraint: a geometric programming approach. Math Comput Model 49:1733–1749
Paul SK, Azeem A, Sarker R, Essam D (2013) Development of a production inventory model with uncertainty and reliability considerations. Optim Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-013-9218-6
Posner MJM, Berg M (1989) Analysis of a production-inventory system with unreliable production facility. Oper Res Lett 8:339–345
Preda V (1989) Convex optimization with nested maxima and matrix game equivalence. Ann Bucharest Univ 3:57–60
Prekopa A (1965) Reliability equation for an inventory problem and its asymptotic solutions. Colloq Appl Math Econ 1:317–327
Prekopa A, Kelly P (1978) Reliability type inventory modelling based on stochastic programming. Math Program Study 9:43–58
Rao NV, Rajasekhar M, Rao GC (2014) Detrimental effect of air pollution, corrosion on building materials and historical structures. Am J Eng Res 3(3):359–364
Sana SS (2010) An economic production lot size model in an imperfect production system. Eur J Oper Res 201:158–170
Song H, Gao X (2018) Green supply chain game model and analysis under revenue-sharing contract. J Clean Prod 170:183–192
Tariqul-Islam M, Azeem A, Jabir M, Paul A, Paul SK (2020) An inventory model for a three-stage supply chain with random capacities considering disruptions and supplier reliability. Ann Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-020-03639-z
Thirucheran M, Meena-kumari ER, Lavanya S (2017) A new approach for solving fuzzy game problem. Int J Pure Appl Math 114(6):67–75
Tripathy PK, Pattnaik M (2011) Optimal inventory policy with reliability consideration and instantaneous receipt under imperfect production process. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag 6(6):413–420
Tripathy P, Wee W, Majhi P (2003) An EOQ model with process reliability consideration. J Oper Res Soc 54:549–554
Wee HM, Widyadana GA (2012) Economic production quantity models for deteriorating items with rework and stochastic preventive maintenance time. Int J Prod Res 50:2940–2952
Widyadana GA, Wee HM (2012) An economic production quantity model for deteriorating items with preventive maintenance policy and random machine breakdown. Int J Syst Sci 43:1870–1882
Wiedmann T, Minx J (2008) A Definition of ‘Carbon Footprint.’ In: Pertsova CC (ed) Ecological Economics Research Trends. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge NY, pp 1–11
Xu X, Xu X, He P (2016) Joint production and pricing decisions for multiple products with cap-and trade and carbon tax regulations. J Clean Prod 112:4093–4106
Yager RR (1981) A procedure for ordering fuzzy subsets of the unit interval. Inf Sci 24:143–161
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–356
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the honourable Editor-in-Chief, Associate Editors and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions to improve the quality of this article.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, K., De, S.K. A pollution sensitive fuzzy EPQ model with endogenous reliability and product deterioration based on lock fuzzy game theoretic approach. Soft Comput 27, 3065–3081 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07485-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-07485-y