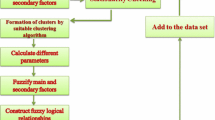
Abstract
Fuzzy time series, based on type-1 fuzzy sets, continue to have a wide range of use in the literature. These methods use only membership values to determine the fuzzy relations. However, intuitionistic fuzzy time series models use both membership values and non-membership values. So it can be considered that the use of intuitionistic fuzzy time forecasting models will be able to increase the forecasting performance because the intuitionistic fuzzy sets have more information than fuzzy sets. Therefore, intuitionistic fuzzy time series models have started to employ for forecasting the real-life series in the fuzzy time series literature. A novel, explainable, robust high-order intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting method is proposed based on a newly defined model. In the proposed method, the intuitionistic fuzzy c-means algorithm is used for the fuzzification of observations, and a robust regression method employed for determining fuzzy relations. With the use of robust regression in determining the fuzzy relationships, all inputs of the proposed method can be explainable and they can be tested and commented on statistically. Applications of this study are made by using energy data of Primary Energy Consumption between the years 1965 and 2016 for 23 countries in the region of Europe-Eurasia. The forecasting performance of the proposed method is compared with the performance of some selected benchmarks, and the obtained results are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhishekh Gautam SS, Singh SR (2018) A score function-based method of forecasting using intuitionistic fuzzy time series. New Math Nat Comput 14(1):91–111
Aladag CH (2013) Using multiplicative neuron model to establish fuzzy logic relationships. Expert Syst Appl 40(3):850–853
Aladag CH, Basaran MA, Egrioglu E, Yolcu U, Uslu VR (2009) Forecasting in high order fuzzy time series by using neural networks to define fuzzy relations. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):4228–4231
Aladag CH, Yolcu U, Egrioglu E (2010) A high order fuzzy time series forecasting model based on adaptive expectation and artificial neural networks. Math Comput Simul 81(4):875–882
Aladag CH, Yolcu U, Egrioglu E, Dalar AZ (2012) A new time invariant fuzzy time series forecasting method based on particle swarm optimization. Appl Soft Comput 12(10):3291–3299
Aladag CH, Yolcu U, Egrioglu E (2014) Robust multilayer neural network based on median neuron model. Neural Comput Appl 24(3–4):945–956
Bas E, Egrioglu E, Aladag CH, Yolcu U (2015) Fuzzy-time-series network used to forecast linear and nonlinear time series. Appl Intell 43(2):343–355
Bas E, Grosan C, Egrioglu E, Yolcu U (2018) High order fuzzy time series method based on pi-sigma neural network. Eng Appl Artif Intell 72:350–356
Box GEP, Jenkins GM (1976) Time series analysis: forecasting and control. Holden Day Press, San Francisco
Cagcag Yolcu O, Alpaslan F (2018) Prediction of TAIEX based on hybrid fuzzy time series model with single optimization process. Appl Soft Comput 66:18–33
Cagcag Yolcu O, Lam HK (2017) A combined robust fuzzy time series method for prediction of time series. Neurocomputing 247:87–101
Chaira T (2011) A novel intuitionistic fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm and its application to medical images. Appl Soft Comput 11(2):1711–1717
Chen SM (1996) Forecasting enrollments based on fuzzy time-series. Fuzzy Sets Syst 81(3):311–319
Chen SM (2002) Forecasting enrollments based on high order fuzzy time series. Cybern Syst 33(1):1–16
Chen SM, Chen CD (2011) Handling forecasting problems based on high-order fuzzy logical relationships. Expert Syst Appl 38(4):3857–3864
Chen SM, Kao PY (2013) TAIEX forecasting based on fuzzy time series particle swarm optimization techniques and support vector machines. Appl Inf Sci 247:62–71
Chen SM, Tanuwijaya K (2011) Fuzzy forecasting on high-order relationships and automatic clustering techniques. Expert Syst Appl 38(12):15425–15437
Cheng SH, Chen SM, Jian WS (2016) Fuzzy time series forecasting based on fuzzy logical relationships and similarity measures. Inf Sci 327:272–287
Edgeworth FY (1887) On observations relating to several quantities. Hermathena 6(13):278–285
Egrioglu E, Aladag CH, Yolcu U, Uslu VR, Basaran MA (2009a) A new approach based on artificial neural networks for high order multivariate fuzzy time series. Expert Syst Appl 36(7):10589–10594
Egrioglu E, Uslu VR, Yolcu U, Basaran MA, Aladag CH (2009b) A new approach based on artificial neural networks for high order bivariate fuzzy time series. Applications of Soft Computing. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 265–273
Egrioglu E, Aladag CH, Yolcu U, Uslu VR, Basaran MA (2010) Finding an optimal interval length in high order fuzzy time series. Expert Syst Appl 37(7):5052–5055
Egrioglu E, Aladag CH, Basaran MA, Uslu VR, Yolcu U (2011) A new approach based on the optimization of the length of intervals in fuzzy time series. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 22(1):15–19
Egrioglu E, Aladag CH, Yolcu U (2013) Fuzzy time series forecasting with a novel hybrid approach combining fuzzy c-means and neural networks. Expert Syst Appl 40(3):854–857
Egrioglu E, Yolcu U, Bas E (2019a) Intuitionistic high-order fuzzy time series forecasting method based on pi-sigma artificial neural networks trained by artificial bee colony. Granular Comput 4(4):639–654
Egrioglu E, Yolcu U, Bas E, Dalar AZ (2019b) Median-Pi artificial neural network for forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 31(1):307–316
Fan XS, Lei YJ, Lu YL, Wang YN (2016) Long-term intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting model based on DTW. J Commun 37(8):95–104
Fan X, Lei Y, Wang Y (2017) Adaptive partition intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting model. J Syst Eng Electron 28(3):585–596
Hsu LY, Horng SJ, Kao TW, Chen YH, Run RS, Chen RJ, Lai JL, Kuo IH (2010) Temperature prediction and TAIFEX forecasting based on fuzzy relationships and MTPSO techniques. Expert Syst Appl 37(4):2756–2770
Hu D, Zan L, Chen X, Jie W (2017) Prediction of satellite clock errors based on deterministic intuitionistic fuzzy time series. In: International conference on signal processing (ICSP) proceedings, Art. no. 7877981, pp 1006–1009
Huang YL, Horng SJ, He M, Fan P, Kuo IH (2011) A hybrid forecasting model for enrollments based on aggregated fuzzy time series and particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 38(7):8014–8023
Huarng K (2001) Effective length of intervals to improve forecasting in fuzzy time-series. Fuzzy Sets Syst 123(3):387–394
Huarng K, Yu TKK (2006) Ratio-based lengths of intervals to improve fuzyy time series forecasting. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern-Part B: Cybern 36(2):328–340
James JO, Raymond LC, Ruppert D (1988) A note on computing robust regression estimates via iteratively reweighted least squares. Am Stat 42(2):152–1154
Joshi BP, Pandey M, Kumar S (2016) Use of intuitionistic fuzzy time series in forecasting enrollments to an academic institution. Adv Intell Syst Comput 436:843–852
Kadılar C (2005) Introduction to time series analysis with SPSS applications. Bizim Press, Istanbul
Kocak C (2013) First-order ARMA type fuzzy time series method based on fuzzy logic relation tables. Math Probl Eng, Article ID 769125, 12
Kocak C (2015) A new high order fuzzy ARMA time series forecasting method by using neural networks to define fuzzy relations. Math Probl Eng, Article ID 128097, pp 1–14
Kocak C (2017) ARMA(p, q) type high order fuzzy time series forecast method based on fuzzy logic relations. Appl Soft Comput 58:92–103
Kumar S, Gangwar SS (2016) Intuitionistic fuzzy time series: an approach for handling nondeterminism in time series forecasting. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 24(6):1270–1281
Kuo IH, Horng SJ, Kao TW, Lin TL, Lee CL, Pan Y (2009) An improved method for forecasting enrollments based on fuzzy time series and particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 36(3):6108–6117
Kuo IH, Horng SJ, Chen YH, Run RS, Lin TL (2010) Forecasting TAIFEX based on fuzzy time series and particle swarm optimization. Expert Syst Appl 37(2):1494–1502
Lei Y, Lei Y, Fan X (2016) Multi-factor high-order intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting model. J Syst Eng Electron 27(5):1054–1062
Mallows C (1975) On some topics in robustness. Technical Memorandum. Bell Telephone Laboratories, Murray Hill, NJ
Park JI, Lee DJ, Song CK, Chun MG (2010) TAIFEX and KOSPI 200 forecasting based on two-factors high-order fuzzy time series and particle swarm optimizations. Expert Syst Appl 37(2):959–967
Rousseeuw PJ (1984) Least median of squares regression. J Am Stat Assoc 79(388):871–880
Singh P, Borah B (2014) Forecasting stock index price based on M-Factors fuzzy time series and particle swarm optimization. Int J Approx Reason 55(3):812–833
Song Q, Chissom BS (1993a) Fuzzy time series and its models. Fuzzy Sets Syst 54(3):269–277
Song Q, Chissom BS (1993b) Forecasting enrollments with fuzzy time series—part I. Fuzzy Sets Syst 54(1):1–9
Tak N (2018) Meta fuzzy functions: application of recurrent type-1 fuzzy functions. Appl Soft Comput 73:1–13
Tak N (2020a) Type-1 possibilistic fuzzy forecasting functions. J Comput Appl Math 370:112653
Tak N (2020b) Type-1 recurrent intuitionistic fuzzy functions for forecasting. Expert Syst Appl 140:112913
Tak N (2021) Meta fuzzy functions-based feed-forward neural networks with a single hidden layer for forecasting. J Stat Comput Simul:1–17
Tak N, Evren AA, Tez M, Egrioglu E (2018) Recurrent type-1 fuzzy functions approach for time series forecasting. Appl Intell 48(1):68–77
Wang L, Liu X, Pedrycz W, Shao Y (2014) Determination of temporal information granules to improve forecasting in fuzzy time series. Expert Syst Appl 41(6):3134–3142
Yapar G (2016) Modified simple exponential smoothing. Hacettepe J Math Stat 47(143):1–16
Yapar G, Capar S, Selamlar HT, Yavuz I (2017a) Modified Holt’s linear trend method. Hacettepe J Math Stat 47(2):1–10
Yapar G, Yavuz I, Selamlar HT (2017b) Why and how does exponential smoothing fail? An in-depth comparison of ATA-simple and simple exponential smoothing. Turk J Forecast 1(1):30–39
Yolcu U, Egrioglu E, Uslu VR, Basaran MA, Aladag CH (2009) A new approach for determining the length of intervals for fuzzy time series. Appl Soft Comput 9(2):647–651
Yolcu U, Egrioglu E, Aladag CH (2013) A new linear & nonlinear artificial neural network model for time series forecasting. Decis Support Syst 54(3):1340–1347
Yu THK, Huarng KHA (2010) A neural network-based fuzzy time series model to improve forecasting. Expert Syst Appl 37(4):3366–3372
Zadeh LA (1965) Information and control. Fuzzy Sets 8(3):338–353
Zheng KQ, Lei YJ, Wang R, Wang Y (2013a) Prediction of IFTS based on deterministic transition. J Appl Sci Electron Inf Eng 31(2):204–211
Zheng KQ, Lei YJ, Wang R, Wang YF (2013b) Modeling and application of IFTS. Control Decis 28(10):1525–1530
Zheng KQ, Lei YJ, Wang R, Xing YQ (2014) Method of long-term IFTS forecasting based on parameter adaptation. Syst Eng Electron 36(1):99–104
Zhou T, Gao S, Wang J, Chu C, Todo Z (2016) Financial time series prediction using a dendritic neuron model. Knowl-Based Syst 105:214–224
Egrioğlu E, Yolcu U, Bas E, Dalar AZ (2017) Median-Pi artificial neural network for forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 31(1):307-316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest toward the publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Communicated by Mu-Yen Chen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocak, C., Egrioglu, E. & Bas, E. A new explainable robust high-order intuitionistic fuzzy time-series method. Soft Comput 27, 1783–1796 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06079-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06079-4