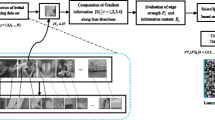
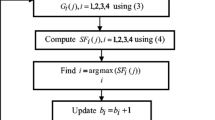
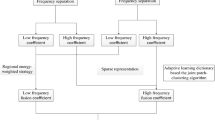
Abstract
Multi-modality image fusion technique is essential for target description. The complementary information can not only compensate the limitations of each image effectively, but also enhance visual effect to human eyes. To preserve structure information and perform detailed information of each source multi-modality image, a novel fusion framework with two-scale image reconstruction is proposed. In the proposal, an improved guided image filtering (GIF)-based weighted average via Gabor energy is put forward for the fusion of base layers contained large scale structure information, and a sparse representation-based separable dictionary learning is recommended to capture small scale detailed information of detail layers. Finally, according to the texture enhancement fusion rule, the fused base and detail layers are integrated to obtain the fusion image. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method exhibits significant performance than the basic GIF algorithm, and also outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of better edge texture clarity. Moreover, the fusion results show abundant information and better visual effect.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon M, Elad M, Bruckstein A (2006) K-SVD: an algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 54(11):4311–4322
Dou W, Ruan S, Chen Y, Bloyet D, Constans J (2007) A framework of fuzzy information fusion for the segmentation of brain tumor tissues on MR images. Image Vis Comput 25(2):164–171
Draper NR, Smith H (1981) Applied regression analysis. Wiley, New York
Engan K, Aase SO, Husoy JH (1999) Method of optimal directions for frame design. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, proceedings, pp 2443–2446
Goshtasby AA, Nikolov S (2007) Guest editorial: image fusion: advances in the state of the art. Inform Fusion 8(2):114–118
Hawe S, Seibert M, Kleinsteuber M (2013) Separable dictionary learning. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 438–445
He C, Zheng YF, Ahalt SC (2002) Object tracking using the Gabor wavelet transform and the golden section algorithm. IEEE Trans Multimed 4(4):528–538
Hermessi H, Mourali O, Zagrouba E (2018) Convolutional neural network based multimodal image fusion via similarity learning in the shearlet domain. Neural Comput Appl 30(7):1–17
Kim M, Han DK, Ko H (2016) Joint patch clustering-based dictionary learning for multimodal image fusion. Inform fusion 27:198–214
Lewis JJ, O’callaghan RJ, Nikolov SG, Bull DR, Canagarajah CN (2004) Region-based image fusion using complex wavelets. Seventh Int Conf Inform 1(555):562
Li S, Yang B (2010) Hybrid multiresolution method for multisensor multimodal image fusion. IEEE Sens J 10(9):1519–1526
Li S, Kwok JT, Wang Y (2002) Using the discrete wavelet frame transform to merge Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic images. Inform Fusion 3(1):17–23
Li S, Kang X, Hu J (2013) Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process 22(7):2864–2875
Li H, Li X, Yu Z, Mao C (2016) Multifocus image fusion by combining with mixed-order structure tensors and multiscale neighbourhood. Inf Sci 349:25–49
Li Y, Sun Y, Huang X, Qi G, Zheng M, Zhu Z (2018) An image fusion method based on sparse representation and sum modified-Laplacian in NSCT domain. Entropy 20(7):522
Liu Y, Wang Z (2014) Simultaneous image fusion and denoising with adaptive sparse representation. IET Image Proc 9(5):347–357
Liu Y, Liu S, Wang Z (2015a) A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inform Fusion 24:147–164
Liu Y, Liu S, Wang Z (2015b) Multi-focus image fusion with dense SIFT. Inform Fusion 23:139–155
Liu Y, Chen X, Ward RK, Wang ZJ (2016) Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process Lett 23(12):1882–1886
Liu Y, Chen X, Cheng J, Peng H (2017) A medical image fusion method based on convolutional neural networks. In: 20th international conference on information fusion, pp 1–7
Liu Y, Chen X, Peng H, Wang Z (2017) Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Inform Fusion 36:191–207
Liu Y, Chen X, Cheng J, Peng H, Wang Z (2018) Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks. Int J Wavel Multiresol Inf Process 16(3):1850018
Liu Y, Chen X, Ward RK, Wang ZJ (2019) Medical image fusion via convolutional sparsity based morphological component analysis. IEEE Signal Process Lett 26(3):485–489
Ma J, Chen C, Li C, Huang J (2016) Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization. Inform Fusion 31:100–109
Ma J, Zhou Z, Wang B, Zong H (2017) Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys Technol 82:8–17
Nejati M, Samavi S, Shirani S (2015) Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Inform Fusion 25:72–84
Nencini F, Garzelli A, Baronti S, Alparone L (2007) Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inform Fusion 8(2):143–156
Pajares G, de la Cruz JM (2004) A wavelet-based image fusion tutorial. Pattern Recogn 37(9):1855–1872
Petrović V (2007) Subjective tests for image fusion evaluation and objective metric validation. Inform Fusion 8(2):208–216
Piella G, Heijmans H (2003) A new quality metric for image fusion. In: Proceedings 2003 international conference on image processing (Cat. No. 03CH37429) 3:III–173
Seibert M, Wörmann J, Gribonval R, Kleinsteuber M (2014) Separable cosparse analysis operator learning. In: 22nd European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO), pp 770–774
Toet A, Franken EM (2003) Perceptual evaluation of different image fusion schemes. Displays 24(1):25–37
Wang Z, Bovik AC (2002) A universal image quality index. IEEE Signal Process Lett 9(3):81–84
Yang B, Li S (2009) Multifocus image fusion and restoration with sparse representation. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 59(4):884–892
Yang B, Li S (2012) Pixel-level image fusion with simultaneous orthogonal matching pursuit. Inform Fusion 13(1):10–19
Yin M, Liu X, Liu Y, Chen X (2018) Medical image fusion with parameter-adaptive pulse coupled-neural network in nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 68(1):49–64
Zhang Z, Blum RS (1999) A categorization of multiscale-decomposition-based image fusion schemes with a performance study for a digital camera application. Proc IEEE 87(8):1315–1326
Zhang F, Cen Y, Zhao R, Wang H, Cen Y, Cui L, Hu S (2017) Analytic separable dictionary learning based on oblique manifold. Neurocomputing 236(C):32–38
Zhou Z, Li S, Wang B (2014) Multi-scale weighted gradient-based fusion for multi-focus images. Inform Fusion 20:60–72
Zhu Z, Yin H, Chai Y, Li Y, Qi G (2018) A novel multi-modality image fusion method based on image decomposition and sparse representation. Inf Sci 432:516–529
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 61572063]; Youth Science Foundation Project of China [Grant No. 61902371]; Youth Science Foundation Project of China [Grant No. 62002208].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
This paper does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Hu, S. & Zhang, F. Multi-modality image fusion combining sparse representation with guidance filtering. Soft Comput 25, 4393–4407 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05448-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05448-9