Abstract
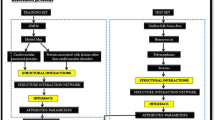
Interactions among various proteins largely govern cellular processes, and this leads to numerous efforts toward extraction of information related to the proteins, their interactions and the function which is determined by these interactions. The main concern of the study is to present interface analysis of age-related-disorder (ARD)-related proteins to shed light on details of the interactions. It also emphasizes on the importance of using structures in network studies. A major goal in the post-genomic era is to identify and characterize disease susceptibility of genes and to apply this knowledge to disease prevention and treatment. Attempts have been made to integrate biological knowledge of Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathways into the genomics field. Many gene set analysis methods have been used to detect disease-related risk pathways. The present study combines the network-centered approach with three-dimensional structures to comprehend the biology behind ARDs. Interface properties of the interacting complexes have been used as descriptors to classify age-related associated proteins and non-age-related associated proteins. Machine learning has been used to generate a classifier which is used to predict potential age-related proteins. The ARD-PRED tool achieved an overall accuracy in terms of precision score 81.5, recall score 81.2, accuracy value 79 and ROC Area score 89.6, F-measure 81.1. The tool has been made online at http://genomeinformatics.dtu.ac.in/ARD-PRED/. The present work would comprehend ongoing research in the field of ARDs and would also significantly improvise the understanding of the molecular mechanism of age-related diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adie EA, Adams RR, Evans KL, Porteous DJ, Pickard BS (2006) SUSPECTS: enabling fast and effective prioritization of positional candidates. Bioinformatics 22(6):773–774. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btk031
Aung Z (2006) Computational analysis of 3D protein structures. Doctoral dissertation, School of Computing, National Institute of Singapore
Basse MJ, Betzi S, Bourgeas R, Bouzidi S, Chetrit B, Hamon V, Morelli X, Roche P (2013) 2P2Idb: a structural database dedicated to orthosteric modulation of protein–protein interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D824–D827. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1002
Bauer-Mehren Anna, Rautschka Michael, Sanz Ferran, Furlong Laura I (2010) DisGeNET: a cytoscape plugin to visualize, integrate, search and analyze gene-disease networks. Bioinformatics 26(22):2924–6. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq538
Calvo S, Jain M, Xie X, Sheth SA, Chang B, Goldberger OA, Spinazzola A, Zeviani M, Carr SA, Mootha VK (2006) Systematic identification of human mitochondrial disease genes through integrative genomics. Nat Genet 38(5):576–582. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1776
Choura M, Rebai A (2011) Structural analysis of hubs in human NRRTK network. Biol Direct 6:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6150-6-49
Chuang HY, Lee E, Liu YT, Lee D, Ideker T (2007) Network-based classification of breast cancer metastasis. Mol Syst Biol 3:140. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb4100180
Davis J, Goadrich M (2006) The relationship between precision-recall and ROC curves. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on machine learning, Pennsylvania, USA, 2006. ACM, New York, NY
Goh KI, Cusick ME, Valle D, Childs B, Vidal M, Baraba’si AL (2007) The human disease network. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(21):8685–8690. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701361104
Gonzalez MW, Kann MG (2012) Protein interactions and disease. PLoS Comput Biol 8(12):e1002819. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002819
Hall M, Frank E, Holmes G, Pfahringer B, Reutemann P, Witten IH (2009) The WEKA data mining software: an update SIGKDD explorations. ACM SIGKDD Explor Newsl. https://doi.org/10.1145/1656274.1656278
Hamon V, Brunel JM, Combes S, Basse MJ, Roche P, Morelli X (2013) 2P2Ichem: focused chemical libraries dedicated to orthosteric modulation of protein–protein interactions. MedChemComm 4(5):797–809. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3MD00018D
Jain P, Thukral N, Gahlot LK, Hasija Y (2015) CARDIO-PRED: an in silico tool for predicting cardiovascular-disorder associated proteins. Syst Synth Biol 9(1–2):55–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11693-015-9164-z
Kann MG (2007) Protein interactions and disease: computational approaches to uncover the etiology of diseases. Brief Bioinf 8(5):333–346. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbm031
Kar G, Gursoy A, Keskin O (2009) Human cancer protein–protein interaction network: a structural perspective. PLoS Comput Biol 5(12):e1000601. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000601
Lopez-Bigas N, Ouzounis CA (2004) Genome-wide identification of genes likely to be involved in human genetic disease. Nucleic Acids Res 32(10):3108–3114. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh605
Magrane M, The UniProt consortium (2011) UniProt knowledgebase: a hub of integrated protein data. Database (Oxford) 2011:bar009. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bar009
Moreira IS, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ (2007) Hot spots—a review of the protein–protein interface determinant amino-acid residues. Proteins 68(4):803–812. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21396
Mosca R, Ce’ol A, Aloy P (2013) Interactome3D: adding structural details to protein networks. Nat Methods 10(1):47–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2289
Srivastava I, Gahlot LK, Khurana P, Hasija Y (2016) dbAARD and AGP: a computational pipeline for the prediction of genes associated with age related disorders. J Biomed Inf 60:153–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2016.01.004
Srivastava I, Khurana P, Yadav M, Hasija Y (2017) An integrative system biology approach to unravel potential drug candidates for multiple age related disorders. Biochimica et Biophys Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteomics 1865(12):1729–1738. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2017.07.016
Stark C, Breitkreutz BJ, Reguly T, Boucher L, Breitkreutz A, Tyers M (2006) BioGRID: a general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 34(suppl 1):D535–D539. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkj109
Wang X, Wei X, Thijssen B, Das J, Lipkin SM, Yu H (2012) Three dimensional reconstruction of protein networks provides insight into human genetic disease. Nat Biotechnol 30(2):159–164. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2106
Zhang KX, Ouellette BF (2011) CAERUS: predicting cancer outcomes using relationship between protein structural information, protein networks, gene expression data, and mutation data. PLoS Comput Biol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001114
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge Pooja Khurana, Nitin Thukral, Lokesh Kumar Gahlot and Isha Srivastava for their scientific contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhadhadhara, K., Hasija, Y. ARD-PRED: an in silico tool for predicting age-related-disorder-associated proteins. Soft Comput 23, 1767–1776 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3154-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3154-5