Abstract
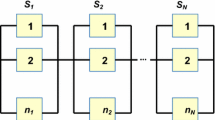
Redundancy allocation is a direct way of enhancing the series-parallel system lifetime and reliability. Since it is difficult to obtain the exact probability distributions about the lifetimes of components, fuzzy random variables are used to characterize them. Under the given system weights and cost constraints, we maximize the equilibrium optimistic system lifetime of redundant elements. This paper proposes an equilibrium optimization model for the standby redundancy system. Since the exact analytical expressions of the equilibrium optimistic system lifetimes are unavailable in general case, the proposed model cannot be analytically solved. Under mild assumptions, the new equilibrium model can be divided into its equivalent stochastic programming subproblems. Moreover, a new approximation method is proposed to solve the general equilibrium model. For the equivalent stochastic programming subproblems, sample average approximation (SAA) is adapted to gain their SAA problems. A hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm with local search is designed to solve the SAA problems. Several numerical experiments are conducted to investigate the effectiveness of proposed model and designed solution method. The comparative studies indicate the randomness, and fuzziness cannot be ignored in the equilibrium standby redundancy optimization problem.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branda M (2014) Sample approximation technique for mixed-integer stochastic programming problems with expected value constraints. Optim Lett 8:861–875
Chen M, Nakagawa T (2013) Optimal redundant systems for works with random processing time. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 116:99–104
Coit DW (2001) Cold-standby redundancy optimization for nonrepairable systems. IIE Trans 33:471–478
Coit DW, Smith AE (1996) Reliability optimization of series-parallel systems using a genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Reliab 45(2):254–260
Coit DW, Smith AE (1998) Redundancy allocation to maximize a lower percentile of the system time-to-failure distribution. IEEE Trans Reliab 47:79–87
Dubois D, Prade H (1988) Possibility theory. Plenum Press, New York
Feizollahi MJ, Soltani R, Feyzollahi H (2015) The robust cold standby redundancy allocation in series-parallel systems with budgeted uncertainty. IEEE Trans Reliab 64(2):799–806
Garg H, Sharma SP (2013) Multi-objective reliability-redundancy allocation problem using particle swarm optimization. Comput Ind Eng 64:247–255
Govindan K, Jafarian A, Azbari ME, Choi TM (2016) Optimal bi-objective redundancy allocation for systems reliability and risk management. IEEE Trans Cybern 46(8):1735–1748
Jeyalakshmi V, Subburaj P (2016) PSO-scaled fuzzy logic to load frequency control in hydrothermal power system. Soft Comput 20(7):2577–2594
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of IEEE international conference on neural networks. Piscataway, NJ, pp 1942–1948
Kumar N, Vidyarthi DP (2016) A model for resource-constrained project scheduling using adaptive PSO. Soft Comput 20(4):1565–1580
Kuo W, Wan R (2007) Recent advances in optimal reliability allocation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A Syst Hum 37(2):143–156
Kwakernaak H (1978) Fuzzy random variables-I. Definitions and theorems. Inf Sci 15:1–29
Li X, Liu B (2009) Chance measure for hybrid events with fuzziness and randomness. Soft Comput 13:105–115
Li ZH, Liu YK, Yang GQ (2015) A new probability model for insuring critical path problem with heuristic algorithm. Neurocomputing 148:129–135
Li B, Zhu M, Xu K (2000) A practical engineering method for fuzzy reliability analysis of mechanical structures. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 67:311–315
Liang YC, Chen YC (2007) Redundancy allocation of series-parallel systems using a variable neighborhood search algorithm. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 92:323–331
Liu YK (2007) The approximation method for two-stage fuzzy random programming with recourse. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 15(6):1197–1208
Liu YK, Liu B (2003) Fuzzy random variable: a scalar expected value operator. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 2(2):143–160
Liu YK, Liu B (2005) Fuzzy random programming with equilibrium chance constraints. Inf Sci 170:363–395
Liu YK, Liu Z, Gao J (2009) The modes of convergence in the approximation of fuzzy random optimization problems. Soft Comput 13(2):117–125
Liu YK, Gao J (2007) The independence of fuzzy variables with applications to fuzzy random optimization. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 15:1–20
Liu YK, Qian W, Yue M (2013) The dominated convergence theorems for sequences of integrable fuzzy random variables. J Uncertain Syst 7(2):118–128
Luedtke J, Ahmed S (2008) A sample approximation approach for optimization with probabilistic constraints. SIAM J Optim 19:674–699
Mahapatra GS, Roy TK (2006) Fuzzy multi-objective mathematical programming on reliability optimization model. Appl Math Comput 174:643–659
Mousavi SM, Alikar N, Niaki STA (2016) An improved fruit fly optimization algorithm to solve the homogeneous fuzzy series–parallel redundancy allocation problem under discount strategies. Soft Comput 20(6):2281–2307
Nahmias S (1978) Fuzzy variables. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1:97–101
Negoita CV, Ralescu D (1987) Simulation, knowledge-based computing, and Fuzzy statistics. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Ni Y (2013) Edge covering problem under hybrid uncertain environments. Appl Math Comput 219:6044–6052
Phelps C, Royset JO, Gong Q (2016) Optimal control of uncertain systems using sample average approximations. SIAM J Control Optim 54(1):1–29
Pedrycz W, Gomide F (2007) Fuzzy systems engineering: toward human-centric computing. Wiley, Hoboken
Qin R, Liu YK (2010) Modeling data envelopment analysis by chance method in hybrid uncertain environments. Math Comput Simul 80(5):922–950
Shi Y, Eberhart RC (1998) Parameter selection in particle swarm optimization. In: International conference on evolutionary programming 1998, pp 591–600
Suman B (2010) Simulated annealing-based multi-objective algorithm and their application for system reliability. Eng Optim 35(4):391–416
Wang Y, Chen Y, Liu YK (2016) Modeling portfolio optimization problem by probability-credibility equilibrium risk criterion. Math Probl Eng 2016: Art ID 9461021, 13
Wang Z, Chen T, Tang K, Yao X (2009) A multi-objective approach to redundancy allocation problem in parallel-series systems. In: IEEE congress on evolutionary computation 2009, pp 582–589
Wu P, Gao L, Zou D, Li S (2011) An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for reliability problems. ISA Trans 50:71–81
Yang K, Liu YK (2015) Developing equilibrium optimization methods for hub location problems. Soft Comput 19(8):2337–2353
Zadeh LA (1978) Fuzzy sets as a basis for a theory of possibility. Fuzzy Sets Syst 1:3–28
Zhai H, Liu YK, Yang K (2016) Modeling two-stage UHL problem with uncertain demands. Appl Math Model 40(4):3029–3048
Zhao P, Chan PS, Li L, Ng HKT (2013) On allocation of redundancies in two-component series systems. Oper Res Lett 41:690–693
Zhao R, Liu B (2003) Stochastic programming models for general redundancy optimization problems. IEEE Trans Reliab 52:181–192
Zhao JH, Liu Z, Dao MT (2007) Reliability optimization using multi-objective ant colony system approaches. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 92:109–120
Zhong S, Chen Y, Zhou J (2015) Fuzzy random programming models for location-allocation problem with applications. Comput Ind Eng 89:194–202
Zoulfaghari H, Hamadani AZ, Ardakan MA (2014) Bi-objective redundancy allocation problem for a system with mixed repairable and non-repairable components. ISA Trans 53:17–24
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61374184), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (NO.A2014201166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Human and animals rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Y. Ni.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Gao, J., Yang, G. et al. Solving equilibrium standby redundancy optimization problem by hybrid PSO algorithm. Soft Comput 22, 5631–5645 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2552-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2552-4