Abstract
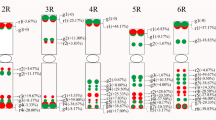
Gametophytic self-incompatibility (GSI) in sweet cherry (Prunus avium, Rosaceae) is controlled by the multi-allelic S-locus. This complex locus contains two linked genes, an S-RNase that controls pistil specificity, and an F-box gene named SFB (S-haplotype-specific F-box protein gene) that is the putative determinant of pollen specificity in Prunus species. The S-locus is considered to be a region of repressed recombination, as recombination has not been observed. Recombination between the pistil-S and pollen-S determinant genes would result in non-functional S-haplotypes and loss of self-incompatibility. With the recent identification of multiple SFB alleles in sweet cherry, along with the existing S-RNase alleles, it is now possible to estimate the linkage distance and quantify the physical distance between the two GSI specificity genes in multiple sweet cherry S-haplotypes. A recombinational analysis between S-RNase and SFB was performed for four sweet cherry S-haplotypes (S2, S3, S4, S6) using F1 progeny from reciprocal crosses between ‘Emperor Francis’ (S3 S4) and ‘NY 54’ (S2 S6). For SFB genotyping, allele-specific primer sets were designed from the sequence of the SFB coding region. The S-RNase and SFB genotypes of 511 progeny, representing the outcomes of 1,022 meioses, were determined. All four S-haplotypes individually segregated according to the expected Mendelian ratio of 1:1. The S-RNase and SFB loci were completely linked as no recombinant individuals were identified, thus maintaining the co-evolved allele specificities for the pistil and putative pollen determinant. The physical distance between S-RNase and SFB in six sweet cherry S-haplotypes (S1–S6) was determined using PCR with genomic clones as the template. The relative order and transcriptional orientation of S-RNase and SFB were conserved across the six S-haplotypes. However, the physical distance between these two genes varied widely, ranging from 380 bp to approximately 40 kb. This study represents the first large-scale recombinational analysis of the S-locus region in the Rosaceae, serving as the starting point for future comparative analyses of physical distances, linkage distances, and sequence diversity among Prunus S-haplotypes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MA, Cornish EC, Mau S-L, Williams, EG, Hoggart R, Atkinson A, Boning I, Grego B, Simpson R, Roche PJ, Haley JD, Penschow JD, Niall HD, Tregear GW, Coghlan JP, Crawford RJ, Clarke AE (1986) Cloning of cDNA for a stylar glycoprotein associated with expression of self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata. Nature 321:38–44
Boyes DC, Nasrallah ME, Vrebalov J, Nasrallah JB (1997) The self-incompatility (S) haplotypes of Brassica contain highly divergent and rearranged sequences of ancient origin. Plant Cell 9:237–247
Broothaerts W, Janssens GA, Proost P, Broekaert WF (1995) cDNA cloning and molecular analysis of two self-incompatible alleles from apple. Plant Mol Biol 27:499–511
Coleman CE, Kao T-h (1992) The flanking regions of two Petunia inflate S-alleles are heterogeneous and contain repetitive sequences. Plant Mol Biol 18:725–737
Cui Y, Brugiere N, Jackman L, Bi Y-M, Rothstein SJ (1999) Structural and transcriptional comparative analysis of the S locus regions in two self-incompatible Brassica napus lines. Plant Cell 11:2217–2231
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Caldere F, Cosson P, Howad W, Arús P (2004) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9891–9896
Dodds PN, Fergusen C, Clarke AE, Newbigin E (1999) Pollen-expressed S-RNases are not involved in self-incompatibility in Lycopersicon peruvianum. Sex Plant Reprod 12:76–87
Entani T, Iwono M, Shiba H, Takayama S, Fukui K, Isogai A (1999) Centromeric localization of an S-RNase gene in Petunia hybrida Vilm. Theor Appl Genet 99:391–397
Entani T, Iwano M, Shiba H, Che FS, Isogai A, Takayama S (2003) Comparative analysis of the self-incompatibility (S-) locus region of Prunus mume: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with allelic diversity. Genes Cells 8:203–213
Golz JF, Clarke AE, Newbigin E (2000) Mutational approaches to the study of self-incompatibility: revising the pollen part mutants. Ann Bot 85[Suppl A]:95–103
Hauck NR, Yamane H, Tao R, Iezzoni AF (2002) Self-compatibility and incompatibility in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.). Sex Plant Reprod 15:39–46
Igic B, Kohn JR (2001) Evolutionary relationships among self-incompatibility RNases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13167–13171
Ikeda K, Igic B, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Hauck NR, Nakano R, Sassa H, Iezzoni AF, Kohn JR, Tao R (2004) Primary structure futures of the S haplotype-specific F-box protein, SFB, in Prunus. Sex Plant Reprod 16:235–243
Kao T-h, Tsukamoto T (2004) The molecular and genetic basis of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant Cell 16[Suppl]:S72–S83
Lai Z, Ma W, Han B, Liang L, Zhang Y, Hong G, XueY (2002) An F-box gene linked to the self-incompatibility (S) locus of Antirrhinum is expressed specifically in pollen and tapetum. Plant Mol Biol 50:29–42
Lee H-S, Huang S, Kao T-h (1994) S proteins control rejection of incompatible pollen in Petunia inflata. Nature 367:560–563
Lewis D (1949) Structure of the incompatibility gene II. Induced mutation rate. Heredity 3:339–355
Ma W-S, Zhou J-L, Lai Z, Zhang, Y-S, Xue Y-B (2003) The self-incompatibility S locus of Antirrhinum resides in a pericentromeric region. Acta Bot Sin 45:47–52
Matton DP, Mau SL, Okamoto S, Clarke AE, Newbigin E (1995) The S-locus of Nicotiana alata: genomic organization and sequence analysis of 2 S-RNase alleles. Plant Mol Biol 28:847–858
McClure BA, Haring V, Ebert PR, Anderson MA, Simpson RJ, Sakiyama,F, Clarke AE (1989) Style self-compatibility gene products of Nicotiana alata are ribonucleases. Nature 342:757–760
McCubbin AG, Kao T-h (2000) Molecular recognition and response in pollen and pistil interactions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:333–364
McCubbin AG, Chung YY, Kao T-h (1997) A mutant S3 RNase of Petunia inflate lacking RNase activity has an allele-specific dominant negative effect on self incompatibility interactions. Plant Cell 9:85–95
Murfett J, Atherton TL, Mou B, Gasser CS, McClure BA (1994) S-RNase expressed in transgenic Nicotiana causes S-allele-specific pollen rejection. Nature 367:563–566
Nasrallah JB, Nasrallah NE (1993) Pollen stigma signaling in the sporophytic self-incompatibility response. Plant Cell 5:1325–1335
Nettancourt D de (2001) Incompatibility and incongruity in wild and cultivated plants. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Nishio T, Kusaba M, Sakamoto K, Ockendon DJ (1997) Polymorphism of the kinase domain of the S-locus receptor kinase gene (SRK) in Brassica oleraceae. Theor Appl Genet 95:335–342
Qiao H, Wang F, Zhao L, Zhou J, Lai Z, Zhang Y, Robbins TP, Xue Y (2004) The F-box protein AhSLF-S2 controls the pollen function of S-RNase-based self-incompatibility. Plant Cell 16:2307–2322
Roalson EH, McCubbin AG (2003) S-RNases and sexual incompatibility: structure, functions, and evolutionary perspectives. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29:490–506
Romero C, Vilanova S, Burgos L, Martinez-Calvo J, Vicente M, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2004) Analysis of the S-locus structure in Prunus armeniaca L. Identification of S-haplotype specific S-RNase and F-box genes. Plant Mol Biol 56:145–157
Sassa H, Hirano H, Ikehashi H (1992) Self-incompatibility-related RNase in style of Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina Rehd.). Plant Cell Physiol 33:811–814
Sassa H, Nishio T, Kowyama Y, Hirano H, Koba T, Ikehashi H (1996) Self-incompatibility (S) alleles of the Rosaceae encode members of a distinct class of the T2/S ribonuclease superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 250:547–557
Sassa H, Hirano H, Nishio T, Koba M (1997) Style-specific self-compatible mutation caused by deletion of the S-RNase gene in Japanese pear (Pyrus serotina). Plant J 12:223–227
Sato K, Nishio T, Kimura R, Kusaba M, Suzuki T, Hatakeyama K, Ockendon DJ, Satta Y (2002) Coevolution of the S-locus genes SRK, SLG and SP11/SCR in Brassica oleracea and B. rapa. Genetics 162:931–940
Shiba H, Kenmochi M, Sugihara M, Iwano M, Kawasaki S, Suzuki G, Watanabe W, Isogai A, Takayama S (2003) Genomic organization of the S-locus region of Brassica. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:622–626
Sijacic P, Wang X, Skirpan AL, Wang Y, Dowd PE, McCubbin AG, Huang S, Kao T-h (2004) Identification of the pollen determinant of S-RNase-mediated self-incompatibility. Nature 429:302–305
Sonneveld T, Robbins TP, Boskovic R, Tobutt KR (2001) Cloning of six cherry self-incompatibility alleles and development of allele-specific PCR detection. Theor Appl Genet 102:1046–1055
Steinbachs JE, Holsinger KE (2002) S-RNase-mediated gametophytic self-incompatibility is ancestral in eudicots. Mol Biol Evol 19:825–829
Stockinger EJ, Mulinix CA, Long CM, Brettin TS, Iezzoni AF (1996) A linkage map of sweet cherry based on RAPD analysis of a microspore-derived callus culture population. J Hered 87:214–218
Tao R, Yamane H, Sugiura A, Murayama H, Sassa H, Mori H (1999) Molecular typing of S-alleles through identification, characterization and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in sweet cherry. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 124:224–233
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Kusaba M, Tao R, Tamura M, Gradziel TM, Dandekar AM, Hirano H (2001) Characterization of the S-locus region of almond (Prunus dulcis): analysis of a somaclonal mutant and a cosmid contig for an S haplotype. Genetics 158:379–386
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Tao R, Hirano H (2003) Structural and transcriptional analysis of the self-incompatibility locus of almond: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with haplotype-specific polymorphism. Plant Cell 15:771–781
Ushijima K, Yamane H, Watari A, Kakehi E, Ikeda K, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AI, Tao R (2004) The S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, is defective in self-compatible haplotypes of Prunus avium and P. mume. Plant J 39:573–586
Wang Y, Wang X, McCubbin AG, Kao T-h (2003). Genetic mapping and molecular characterization of the self-incompatibility (S) locus in Petunia inflata. Plant Mol Biol 53:565–580
Wang Y, Tsukamoto Y, Yi K-W, Wang X, Huang S, McCubbin AG, Kao T-h (2004) Chromosome walking in the Petunia inflate self-incompatibility (S-) locus and gene identification in an 881-kb contig containing S2-RNase. Plant Mol Biol 54:727–742
Xue Y, Carpenter R, Dickinson HG, Coen ES (1996) Origin of allelic diversity in Antirrhinum S locus RNases. Plant Cell 8:805–814
Yamane H, Tao R, Sugiura A, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AF (2001) Identification and characterization of S-RNases in tetraploid sour cherry (Prunus cerasus L.). J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126:661–667
Yamane H, Ikeda K, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AF, Tao R (2003a) Self-incompatibility (S) locus region of the mutated S6-haplotypes of sour cherry (Prunus cerasus) contains a functional pollen S-allele and a non-functional pistil S allele. J Exp Bot 54:2431–2434
Yamane H, Ikeda K, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003b) A pollen-expressed gene for a novel protein with an F-box motif that is very tightly linked to a gene for S-RNase in two species of cherry, Prunus cerasus and P. avium. Plant Cell Physiol 44:764–769
Yamane H, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003c) The use of S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, as a molecular marker for S-haplotype and self-compatibility in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume). Theor Appl Genet 107:1357–1361
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Sassa for his critical review of this manuscript. This work was supported by a grant-in-aid (no. 13460014) for Scientific Research (B) and Japan-US Cooperative Science Program to R.T. from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, K., Ushijima, K., Yamane, H. et al. Linkage and physical distances between the S-haplotype S-RNase and SFB genes in sweet cherry. Sex Plant Reprod 17, 289–296 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-004-0240-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-004-0240-x