Abstract
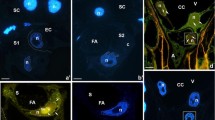
The mechanism by which the sperm activates the egg cell of higher plants is largely unknown. Ca2+—implicated as a second messenger in the response of various plant cells to a wide range of stimuli—is a potential candidate for encoding the information brought by the sperm cell into the angiosperm egg. In higher plant cells the dominant calcium store appears to be the central vacuole; however, in the receptive wheat egg cell few vacuoles can be observed, thus it seems likely that the principal cell organelle performing a pivotal role in regulation of intracellular Ca2+ is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). To examine this hypothesis, microinjection of the ER-specific fluorescent dicarbocyanine dye, 1,1′-dihexadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate [DiIC16(3)], and low-light level CCD technology were used. Following the injection of an oil drop saturated with DiI, structural changes occurring in the ER during the in planta maturation of the female gamete were visualised. The ER was identified by chlorotetracycline labelling to be the main calcium store in the wheat egg cell. Structural changes occurring in the ER during the in planta maturation of the wheat female gamete led to a polarised ER network in the receptive egg cell. Within 3 min of in vitro sperm-egg fusion, a rapid, transient loss of continuity of the ER occurred, which underlines the significance in fertilisation of the ER structure in the female gamete of wheat.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blinks JR, Wier WG, Hess P, Prendergast FG (1982) Measurement of Ca2+ concentratrions in living cells. Progr Biophys Mol Biol 40:10–114
Campanella C, Andreucetti P, Taddei C, Talevi R (1984) The modification of cortical endoplasmic reticulum during in vitro maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes and its involvement in cortical granule exocytosis. J Exp Zool 229:283–293
Caswell A (1979) Methods for measuring intracellular calcium. Int Rev Cytol 56:145–181
Chiba K, Kado RT, Jaffe LA (1990) Development of calcium release mechanisms during starfish oocyte maturation. Dev Biol 140:300–306
Digonnet C, Aldon D, Leduc N, Dumas C, Rougier M (1997) First evidence of a calcium transient in flowering plants at fertilization. Development 124:2867–2874
Dupuis I, Roeckel P, Matthys-Rochon E, Dumas C (1987) Procedure to isolate viable sperm cells from corn (Zea mays L.) pollen grains. Plant Physiol 85:876–878
Eisen A, Reynolds GT (1985) Source and sinks for the calcium released during fertilization of single sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol 127:641–652
Eisen A, Kiehart DP, Wieland SJ, Reynolds GT (1984) Temporal sequence and spatial distribution of early events of fertilization in single sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol 99:1647–1654
Elinson RP (1983) Cytoplasmic phases in the first cell cycle of the activated frog egg. Dev Biol 100:440–451
Faure JE, Digonnet C, Dumas C (1994) An in vitro system for adhesion and fusion of maize gametes. Science 263:1598–1600
Freeman G, Ridgway EB (1993) The role of intracellular calcium and pH during fertilization and egg activation in the hydrozoan Phialidium. Dev Biol 156:176–190
Gao X, Francis D, Ormrod JC, Bennett MD (1992) An electron microscope study of double fertilization in allohexaploid wheat Triticum aestivum L. Ann Bot 70:561–568
Gardiner DM, Grey RD (1983) Membrane junctions in Xenopus eggs: their distribution suggests a role in calcium regulation. J Cell Biol 96:1247–1255
Gilkey JC, Jaffe LJ, Ridgway EB, Reynolds GT (1978) A free calcium wave traverses the activating egg of medaka, Oryzias latipes. J Cell Biol 76:448–466
Heilbrun LV, Wilson WL (1948) Protoplasmic viscosity changes during mitosis in the egg of Chaetopterus. Biol Bull Woods Hole 95:57–68
Henson JH, Begg DA, Beaulieu SM, Fishkind DJ, Bonder EM, Terasaki M, Lebeche D, Kaminer B (1989) A calsequestrin-like protein in the endoplasmic reticulum of the sea urchin: localization and dynamics in the egg and first cell cycle embryo. J Cell Biol 109:149–161
Jaffe LF (1983) Sources of calcium in egg activation: a review and hypothesis. Dev Biol 99:265–276
Jaffe LA (1996) Egg membranes during fertilization. In: Schultz SG (ed) Molecular biology of membrane transport disorders. Plenum Press, New York, pp 367–378
Jaffe LA, Terasaki M (1994) Structural changes in the endoplasmic reticulum of starfish oocytes during meiotic maturation and fertilization. Development 164:579–587
Kline D, Kline JT (1992) Repetitive calcium transients and the role of calcium in exocytosis and cell cycle activation in the mouse egg. Dev Biol 149:80–89
Koch GLE (1990) The endoplasmic reticulum and calcium storage. Bioessays 12:527–531
Kranz E, Lörz H (1990) Micromanipulation and in vitro fertilization with single pollen grains of maize. Sex Plant Reprod 3:160–169
Kranz E, Lörz H (1994) In vitro fertilisation of maize by single egg and sperm cell protoplast fusion mediated by high calcium and high pH. Zygote 2:125–128
Kranz E, Bautor J, Lörz H (1991) In vitro fertilization of single, isolated gametes of maize mediated by electrofusion. Sex Plant Reprod 4:12–16
Kropf DL, Quatrano RS (1987) Localization of membrane-associated calcium during development of fucoid algae using chlorotetracycline. Planta 171:158–170
Kubota HY, Yoshimoto Y, Yoneda M, Hiramoto Y (1987) Free calcium wave upon activation in Xenopus eggs. Dev Biol 119:129–136
Lee C, Chen B (1988) Dynamic behaviour of endoplasmic reticulum in living cells. Cell 54:37–46
Lucero HA, Lebeche D, Kaminer B (1994) Ercalcistorin/protein disulfide isomerase (PDI): sequence determination and expression of a cDNA clone encoding a calcium storage protein with PDI activity from endoplasmic reticulum of the sea urchin egg. J Biol Chem 269:23112–23119
McCauley MM, Hepler PK (1990) Visualization of the endoplasmic reticulum in living buds and branches of the moss Funaria hygrometrica by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Development 109:753–764
Mehlmann LM, Terasaki M, Jaffe LA, Kline D (1995) Reorganization of the endoplasmic reticulum during meiotic maturation of the mouse oocyte. Dev Biol 170:607–615
Miyazaki S, Yuzaki M, Nakada K, Shirakawa H, Nakanishi S, Nakade S, Mikoshiba K (1992) Block of Ca2+ wave and Ca2+ oscillation by antibody to the inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in fertilized hamster eggs. Science 257:251–255
Miyazaki S, Shirakawa H, Nakada K, Honda Y (1993) Essential role of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor/Ca2+ release channel in Ca2+ waves and Ca2+ oscillations at fertilization of mammalian eggs. Dev Biol 158:62–78
Mohri T, Ivonnet PI, Chambers EL (1995) Effect on sperm-induced activation current and increase of cytosolic Ca2+ by agents that modify the mobilization of [Ca2+]i. I. Heparin and pentosan polysulfate. Dev Biol 172:139–157
Naumova TN, Matzk F (1998) Differences in the initiation of the zygotic and parthenogenetic pathway in the Salmon lines of wheat: ultrastructural studies. Sex Plant Reprod 11:121–130
Nuccitelli R (1991) How do sperm activate eggs? Curr Top Dev Biol 25:1–16
Nuccitelli R, Yim DL, Smart T (1993) The sperm-induced Ca2+ wave following fertilization of the Xenopus egg requires the production of Ins[1,4,5)P3. Dev Biol 158:200–212
Pónya Z, Barnabás B (2001) Microinjected fluorescent phalloidin in vivo reveals F-actin dynamics in isolated egg cells of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) developed in situ and fertilised in vitro. J Plant Physiol 158:1527–1539
Pónya Z, Finy P, Fehér A, Mitykó J, Dudits D, Barnabás B (1999a) Optimisation of introducing foreign genes into egg cells and zygotes of wheat (Tritium aestivum L.) via microinjection. Protoplasma 208:163–172
Pónya Z, Tímár I, Szabó L, Kristóf Z, Barnabás B (1999b) Morphological characterisation of wheat (T. aestivum L.) egg cell protoplasts isolated from immature and overaged caryopses. Sex Plant Reprod 11:357–359
Rakow TL, Shen SS (1990) Multiple stores of calcium are released in the sea urchin egg during fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9285–9289
Ridgway EB, Gilkey JC, Jaffe LF (1997) Free calcium increases explosively in activating medaka eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:623–627
Roberts SK, Brownlee C (1995) Calcium influx, fertilisation potential and egg activation in Fucus serratus. Zygote 3:191–197
Roberts SK, Gillot I, Brownlee C (1994) Cytoplasmic calcium and Fucus egg activation. Development 120:155–163
Russell SD (1993) The egg cell: development and role in fertilization and early embryogenesis. Plant Cell 5:1349–1359
Speksnijder JE, Sardet C, Jaffe LF (1990) The activation wave of calcium in the ascidian egg and its role in ooplasmic segregation. J Cell Biol 110:1589–1598
Speksnijder JE, Terasaki M, Hage WJ, Jaffe LF, Sardet C (1993) Polarity and reorganization of the endoplasmic reticulum during fertilization and ooplasmic segregation in the ascidian egg. J Cell Biol 12:1337–1346
Steinhardt R, Zucker R, Schatten G (1977a) Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol 58:185–196
Steinhardt R, Zucker R, Schatten G (1977b) Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the ascidian egg. Dev Biol 135:182–190
Stricker SA (1995) Time-lapse confocal imaging of calcium dynamics in starfish embryos. Dev Biol 170:496–518
Swann K, Ozil JP (1994) Dynamics of the calcium signal that triggers mammalian egg activation. Int Rev Cytol 152:183–222
Terasaki M (1989) Fluorescent labeling of endoplasmic reticulum. Methods Cell Biol 29:125–135
Terasaki M, Jaffe LA (1991) Organization of the sea urchin egg endoplasmic reticulum and its reorganization at fertilization. J Cell Biol 114:1069–1078
Terasaki M, Jaffe LA, Hunnicutt GR, Hammer JA (1996) Structural change of the endoplasmic reticulum during fertilization: evidence for loss of membrane continuity using the green fluorescent protein. Dev Biol 179:320–328
Thomas MV (1982) Techniques in calcium research. Academic Press, New York
Tirlapur UK, Kranz E, Cresti M (1995) Characterization of isolated egg cells, in vitro fusion products and zygotes of Zea mays L. using the technique of image analysis and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Zygote 3:57–64
Tyler A (1932) Changes in volume and surface of Urechis eggs upon fertilization. J Exp Zool 63:155–173
Wagner VT, Song YC, Matthys-Rochon E, Dumas C (1989) Observation on the isolated embryo sac of Zea mays L. Plant Sci 59:127–132
Whitaker MJ, Patel R (1990) Calcium and cell cycle control. Development 108:525–542
Whitaker MJ, Steinhardt RA (1982) Ionic regulation of egg activation. Q Rev Biophys 15:593–666
Whitaker MJ, Steinhardt RA (1985) Ionic signaling in the sea urchin egg at fertilization. In: Metz CB, Monroy A (eds) Biology of fertilization, vol 3. Academic Press, Orlando, Fla., pp 167–221
Whitaker M, Swann K (1993) Lighting the fuse at fertilization. Development 117:1–12
Wolniak SM, Hepler PK, Jackson WT (1980) Detection of the membrane-calcium distribution during mitosis in Haemanthus endosperm with chlorotetracycline. J Cell Biol 87:23–32
You R, Jensen WA (1985) Ultrastructural observations of the mature megagametophyte and the fertilization in wheat (Tritium aestivum). Can J Bot 63:163–178
Acknowledgements
The financial support of the European Commission Research Directorates General under the arrangements of the Marie Curie Individual Fellowship Programme (contract number: QLK5-CT-2002-51591) is hereby acknowledged. The authors are indebted to Prof. J.P. Mascarenas for critically reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pónya, Z., Kristòf, Z., Ciampolini, F. et al. Structural change in the endoplasmic reticulum during the in situ development and in vitro fertilisation of wheat egg cells. Sex Plant Reprod 17, 177–188 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-004-0226-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00497-004-0226-8