Abstract
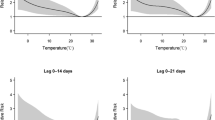
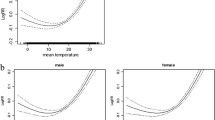
Existing studies suggested that ambient temperature may affect the attack of acute appendicitis. However, the identification of the quantitative effect and vulnerable populations are still unknown. The purposes of this study were to quantify the impact of daily mean temperature on the hospitalization of acute appendicitis and clarify vulnerable groups, further guide targeted prevention of acute appendicitis in Tongling. Daily data of cases and meteorological factors were collected in Tongling, China, during 2015–2019. Time stratified case-crossover design and conditional logistic regression model were used to evaluate the odds ratio (OR) of ambient temperature on hospitalizations for acute appendicitis. Stratified analyses were performed by sex, age, and marital status. The odds ratio (OR) of hospitalizations for acute appendicitis increased by 1.6% for per 1 ℃ rise in mean temperature at lag3[OR = 1.016, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.004–1.028]. In addition, our results suggest it is in the women that increased ambient temperature is more likely to contribute to acute appendicitis hospitalizations; we also found that the married are more susceptible to acute appendicitis hospitalizations due to increased ambient temperature than the unmarried; people in the 21–40 years old are more sensitive to ambient temperature than other age groups. The significant results of the differences between the subgroups indicate that the differences between the groups are all statistically significant. The elevated ambient temperatures increased the risk of hospitalizations for acute appendicitis. The females, married people, and patients aged 21–40 years old were more susceptible to ambient temperature. These findings suggest that more attention should be paid to the impact of high ambient temperature on acute appendicitis in the future.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed W, Akhtar MS, Khan S (2018) Seasonal variation of acute appendicitis. Pak J Med Sci 34(3):564–567. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.343.14793
Al-Omran M, Mamdani M, McLeod RS (2003) Epidemiologic features of acute appendicitis in Ontario. Canada Can J Surg 46(4):263–268
Aroui H, Kalboussi H, El Ghali A et al (2018) The effect of environmental factors on the incidence of perforated appendicitis. Ann Ital Chir. 89:431–437
Bezirtzoglou C, Dekas K, Charvalos E (2011) Climate changes, environment and infection: facts, scenarios and growing awareness from the public health community within Europe. Anaerobe. 17(6):337–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2011.05.016
Bhangu A, Søreide K, Di Saverio S, Assarsson JH, Drake FT. Acute appendicitis: modern understanding of pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management [published correction appears in Lancet. 2017 Oct 14;390(10104):1736]. Lancet. 2015;386(10000):1278-1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00275-5
Chen CC, Yang CY (2018) Effects of ambient air pollution exposure on frequency of hospital admissions for appendicitis in Taipei. Taiwan J Toxicol Environ Health A 81(17):854–860. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2018.1498276
Ditzel M, van Ginhoven TM, van der Wal JB et al (2013) What patients and surgeons should know about the consequences of appendectomy for acute appendicitis after long-term follow-up: factors influencing the incidence of chronic abdominal complaints. J Gastrointest Surg. 17(8):1471–1476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2235-0
Fazzi C, Saunders DH, Linton K, Norman JE, Reynolds RM (2017) Sedentary behaviours during pregnancy: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 14(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12966-017-0485-z
Ferris M, Quan S, Kaplan BS et al (2017) The global incidence of appendicitis: a systematic review of population-based studies. Ann Surg. 266(2):237–241. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000002188
Gaitán HG, Reveiz L, Farquhar C, Elias VM (2014) Laparoscopy for the management of acute lower abdominal pain in women of childbearing age. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5:CD007683. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD007683.pub3
Gallerani M, Boari B, Anania G, Cavallesco G, Manfredini R (2006) Seasonal variation in onset of acute appendicitis. Clin Ter 157(2):123–127
Ilves I, Fagerström A, Herzig KH, Juvonen P, Miettinen P, Paajanen H (2014) Seasonal variations of acute appendicitis and nonspecific abdominal pain in Finland. World J Gastroenterol 20(14):4037–4042. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4037
Jones BA, Demetriades D, Segal I, Burkitt DP (1985) The prevalence of appendiceal fecaliths in patients with and without appendicitis A comparative study from Canada and South Africa. Ann Surg 202(1):80–82. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-198507000-00013
Kaplan GG, Dixon E, Panaccione R et al (2009) Effect of ambient air pollution on the incidence of appendicitis. CMAJ 181(9):591–597. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.082068
Karanikolić A, Karanikolić V, Djordjević L, Pešić I (2016) Correlation between the season, temperature and atmospheric pressure with incidence and pathogenesis of acute appendicitis. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 144(7–8):402–407
Lee M, Paavana T, Mazari F, Wilson TR (2014) The morbidity of negative appendicectomy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 96(7):517–520. https://doi.org/10.1308/003588414X13946184903801
Lu P, Zhang Y, Lin J et al (2020) Multi-city study on air pollution and hospital outpatient visits for asthma in China. Environ Pollut 257:113638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113638
Maclure M (1991) The case-crossover design: a method for studying transient effects on the risk of acute events. Am J Epidemiol 133(2):144–153. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115853
Masoomi H, Nguyen NT, Dolich MO, Mills S, Carmichael JC, Stamos MJ (2014) Laparoscopic appendectomy trends and outcomes in the United States: data from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample (NIS), 2004–2011. Am Surg. 80(10):1074–1077
Moris D, Paulson EK, Pappas TN (2021) Diagnosis and Management of Acute Appendicitis in Adults: A Review. JAMA. 326(22):2299–2311. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.20502
Morral-Puigmal C, Martínez-Solanas È, Villanueva CM, Basagaña X (2018) Weather and gastrointestinal disease in Spain: a retrospective time series regression study. Environ Int 121(Pt 1):649–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.10.003
Nitecki S, Karmeli R, Sarr MG (1990) Appendiceal calculi and fecaliths as indications for appendectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 171(3):185–188
Nshuti R, Kruger D, Luvhengo TE (2014) Clinical presentation of acute appendicitis in adults at the Chris Hani Baragwanath academic hospital. Int J Emerg Med 7(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1865-1380-7-12
Onozuka D, Hagihara A (2015) Nationwide variation in the effects of temperature on infectious gastroenteritis incidence in Japan. Sci Rep 5:12932. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12932
Pande T, Mohanty Z, Nair A, Ranjan P, Kukreja Y (2021) Seasonal variation of acute appendicitis: an armed forces experience of high altitude. Med J Armed Forces India 77(4):479–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mjafi.2020.12.023
Phillips AW, Jones AE, Sargen K (2009) Should the macroscopically normal appendix be removed during laparoscopy for acute right iliac fossa pain when no other explanatory pathology is found? Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 19(5):392–394. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLE.0b013e3181b71957
Reinisch A, Heil J, Woeste G, Bechstein W, Liese J (2017) The meteorological influence on seasonal alterations in the course of acute appendicitis. J Surg Res 217:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2017.05.015
Ren M, Li N, Wang Z et al (2017) The short-term effects of air pollutants on respiratory disease mortality in Wuhan, China: comparison of time-series and case-crossover analyses. Sci Rep 7:40482. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40482
Slotboom T, Hamminga JT, Hofker HS, Heineman E, Haveman JW (2014) Apple study group appendicitis and laparoscopic evaluation Intraoperative motive for performing a laparoscopic appendectomy on a postoperative histological proven normal appendix. Scand J Surg 103(4):245–248. https://doi.org/10.1177/1457496913519771
Song MY, Ullah S, Yang HY, Ahmed MR, Saleh AA, Liu BR (2021) Long-term effects of appendectomy in humans: is it the optimal management of appendicitis? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(6):657–664. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2021.1868298
St George S (2019) The aberrant global synchrony of present-day warming. Nature 571(7766):483–484. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-02179-2
Watts N, Amann M, Arnell N, et al. The 2020 report of the Lancet Countdown on health and climate change: responding to converging crises [published correction appears in Lancet. 2020 Dec 14;:]. Lancet. 2021;397(10269):129-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32290-X
Wei PL, Chen CS, Keller JJ, Lin HC (2012) Monthly variation in acute appendicitis incidence: a 10-year nationwide population-based study. J Surg Res 178(2):670–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.06.034
Wolkomir A, Kornak P, Elsakr M, McGovern P (1987) Seasonal variation of acute appendicitis: a 56-year study. South Med J 80(8):958–960. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007611-198708000-00006
Xu Y, Ramanathan V, Victor DG (2018) Global warming will happen faster than we think. Nature. 564(7734):30–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-07586-5
York TJ. Seasonal and climatic variation in the incidence of adult acute appendicitis: a seven year longitudinal analysis. BMC Emerg Med. 2020;20(1):24. Published 2020 Apr 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12873-020-00321-2
Yoshimoto H, Yamakawa K, Umemura Y et al (2021) Seasonal variation and severity of acute abdomen in Japan: a nine-year retrospective analysis. J Pers Med 11(12):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121346
Zeka A, Zanobetti A, Schwartz J (2006) Individual-level modifiers of the effects of particulate matter on daily mortality. Am J Epidemiol. 163(9):849–859. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwj116
Zhang Y, Lyu FX, Kang Q et al (2018) Association of meteorological factors with pediatric acute appendicitis in China: A 7-year retrospective analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(42):e12913. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000012913
Funding
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 8177120532).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests,
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Luo, X., Wu, Y. et al. Is higher ambient temperature associated with acute appendicitis hospitalizations? A case-crossover study in Tongling, China. Int J Biometeorol 66, 2083–2090 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-022-02342-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-022-02342-x