Abstract
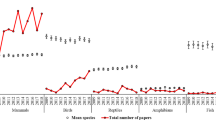
Animal biometeorology (insects excluded) has been part of the International Journal of Biometeorology since its inception in 1958. Over the first 60 years of the journal, 480 animal biometeorology papers were published. Thus, approximately 14% of published papers dealt with animals. Over the first 60 years, data from more than 50 animal species was presented, with the lead authors coming from 48 countries. The two most common species used in animal papers between 1957 and 2016 were cattle (109 papers: 22.7% of all animal papers) and rats (96 papers: 20.0% of all animal papers). Although cattle and rats dominated, the species in the most cited paper (240 citations) was chickens, followed by bird migration (155 citations), and general livestock (118 citations). Overall, five papers exceeded 100 citations, and a further two exceeded 200 citations. In the last decade, 126 animal papers were published (26% of all animal papers). Many of these papers had a focus on livestock production in developing countries especially Brazil.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeni F, Calamari L, Stefanini L (2007) Metabolic conditions of lactating Friesian cows during the hot season in the Po valley. 1. Blood indicators of heat stress. Int J Biometeorol 52:87–96
Altland PD, Highman B, Sellner RG (1973) Tolerance of cold-acclimated and unacclimated rats to hypoxia at 1.7° C. Int J Biometeorol 17:59–71
Amakiri SF, Hill DH (1975) Hair follicle measurements in some tropical and temperate breeds of cattle in Nigeria. Int J Biometeorol 19:115–121
Bachman CH, McDonald RD, Lorenz PJ (1966) Some effects of air ions on the activity of rats. Int J Biometeorol 10:39–46
Banerjee MR (1972) Rat lungs as affected by an acute exposure to an increased level of carbon dioxide in the ambient air. Int J Biometeorol 16:259–267
Battini M, Barbieri S, Fioni L, Mattiello S (2016) Feasibility and validity of animal-based indicators for on-farm welfare assessment of thermal stress in dairy goats. Int J Biometeorol 60:289–296
Bauer Z, Trnka M, Bauerová J, Možný M, Štěpánek P, Bartošová L, Žalud Z (2010) Changing climate and the phenological response of great tit and collared flycatcher populations in floodplain forest ecosystems in Central Europe. Int J Biometeorol 54:99–111
Becker BA, Johnson HD, Li R, Collier RJ (1990) Effect of farm and simulated laboratory cold environmental conditions on the performance and physiological responses of lactating dairy cows supplemented with bovine somatotropin (BST). Int J Biometeorol 34:151–156
Bhatia B, Thomas S, Purkayastha SS (1966) Seasonal variations in the survival index of rats at simulated high altitudes. Int J Biometeorol 10:63–69
Bianca W (1961) Heat tolerance in cattle—its concept, measurement and dependence on modifying factors. Int J Biometeorol 5:5–30
Bianca W, Hays FL (1975) Responses of calves to a simulated altitude of 5000 m. Int J Biometeorol 19:155–165
Blatteis CM (1967) Survival of newborn rats at 4,350 m simulated altitude. Int J Biometeorol 11:51–57
Brouček J, Letkovičovfă M, Kovalčuj K (1991) Estimation of cold stress effect on dairy cows. Int J Biometeorol 35:29–32
Bureau YRJ, Persinger MA, Parker GH (1996) Effect of enhanced geomagnetic activity on hypothermia and mortality in rats. Int J Biometeorol 39:197–200
Correa-Calderon A, Armstrong D, Ray D, DeNise S, Enns M, Howison C (2004) Thermoregulatory responses of Holstein and Brown Swiss heat-stressed dairy cows to two different cooling systems. Int J Biometeorol 48:142–148
Dikmen S, Ustuner H, Orman A (2012) The effect of body weight on some welfare indicators in feedlot cattle in a hot environment. Int J Biometeorol 56:297–303
Donkoh A (1989) Ambient temperature: a factor affecting performance and physiological response of broiler chickens. Int J Biometeorol 33:259–265
Donkoh A, Atuahene CC (1988) Management of environmental temperature and rations for poultry production in the hot and humid tropics. Int J Biometeorol 32:247–253
Dutt RH (1964) Detrimental effects of high ambient temperature on fertility and early embryo survival in sheep. Int J Biometeorol 8:47–56
Entwistle KW (1973) Ram fertility and fertilization rates in the ewe in a semi-arid tropical environment. Int J Biometeorol 17:109–113
Findlay JD (1958) The physiological effects of climate stress on the bovine animal. IJBB 2: part III, section C
Fuquay JW, Chapin LT, Brown WH (1980) Short term post-partum heat stress in dairy cows. Int J Biometeorol 24:141–148
Gaughan JB, Mader TL, Holt SM, Sullivan ML, Hahn GL (2010) Assessing the heat tolerance of 17 beef cattle genotypes. Int J Biometeorol 54:617–627
Ghazi S, Amjadian T, Norouzi S (2015) Single and combined effects of vitamin C and oregano essential oil in diet, on growth performance, and blood parameters of broiler chicks reared under heat stress condition. Int J Biometeorol 59:1019–1024
Glądalski M, Bańbura M, Kaliński A, Markowski M, Skwarska J, Wawrzyniak J, Zieliński P, Bańbura J (2016) Effects of extreme thermal conditions on plasticity in breeding phenology and double-broodedness of Great Tits and Blue Tits in central Poland in 2013 and 2014. Int J Biometeorol 60:1795–1800
Heldmaier G, Steinlechner S, Rafael J, Latteier B (1982) Photoperiod and ambient temperature as environmental cues for seasonal thermogenic adaptation in the Djungarian hamster, Phodopus sungorus. Int J Biometeorol 26:339–345
Honda K, Inoué S (1988) Sleep-enhancing effects of far-infrared radiation in rats. Int J Biometeorol 32:92–94
Igono M, Bjotvedt G, Sanford-Crane H (1992) Environmental profile and critical temperature effects on milk production of Holstein cows in desert climate. Int J Biometeorol 36:77–87
Igono MO, Molokwu ECI, Aliu YO (1982) Body temperature responses of Savanna Brown goat to the harmattan and hot-dry season. Int J Biometeorol 26:225–230
Jöchle W (1972) Seasonal fluctuations of reproductive functions in Zebu cattle. Int J Biometeorol 16:131–144
Johnson HD (1965) Environmental temperature and lactation (with special reference to cattle). Int J Biometeorol 9:105–116
Kabuga J (1992) The influence of thermal conditions on rectal temperature, respiration rate and pulse rate of lactating Holstein-Friesian cows in the humid tropics. Int J Biometeorol 36:146–150
Kabuga JD, Sarpong K (1991) Influence of weather conditions on milk production and rectal temperature of Holsteins fed two levels of concentrate. Int J Biometeorol 34:226–230
Kali J, Morag M, Amir S (1968) Seasonal changes in milk production and fertility in high yielding dairy cows in a desert climate. Int J Biometeorol 12:271–275
Kamal TH, Ibrahim II (1969) The effect of the natural climate of the Sahara and controlled climate on the rectal temperature and cardiorespiratory activities of Friesian cattle and water buffaloes. Int J Biometeorol 13:275–285
Kashimura O, Sakai A (1991) Effects of physical training on pulmonary arterial pressure during exercise under hypobaric hypoxia in rats. Int J Biometeorol 35:214–221
Kikuchi M, Chiba M, Yoshida A (1973) Light-dark cycle and the response of liver temperature to cold in the rat. Int J Biometeorol 17:41–49
Kment A (1958) Die nahrungsaufnahme bei verschiedenen temperature im tierversuch. IJBB 2: Part III, Section A
Krueger AP, Kotaka S (1969) The effects of air ions on brain levels of serotonin in mice. Int J Biometeorol 13:25–38
Kuroshima A, Doi K, Itoh S (1971) Effects of a high fat diet on thyroid activity, with special reference to thyroidal responses to cold. Int J Biometeorol 15:55–64
Lynch H, Ozaki Y, Shakal D, Wurtman R (1975) Melatonin excretion of man and rats: effect of time of day, sleep, pinealectomy and food consumption. Int J Biometeorol 19:267–279
Lincoln B, Bonkovsky HL, Ou L-C (1987) Effects of chronic normobaric hypoxic and hypercapnic exposure in rats: prevention of experimental chronic mountain sickness by hypercapnia. Int J Biometeorol 31:201–210
Mader TL, Gaughan JB, Johnson LJ, Hahn GL (2010) Tympanic temperature in confined beef cattle exposed to excessive heat load. Int J Biometeorol 54:629–635
Maia A, da Silva RG, Loureiro CB (2005) Sensible and latent heat loss from the body surface of Holstein cows in a tropical environment. Int J Biometeorol 50:17–22
Mayer L, Lustick S, Battersby B (1982) The importance of cavity roosting and hypothermia to the energy balance of the winter acclimatized Carolina chickadee. Int J Biometeorol 26:231–238
McNitt J, First N (1970) Effects of 72—hour heat stress on semen quality in boars. Int J Biometeorol 14:373–380
Morrison PR, Kerst K, Reynafarje C, Ramos J (1963a) Hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in some Peruvian rodents from high and low altitude. Int J Biometeorol 7:51–58
Morrison PR, Kerst K, Rosenrnann M (1963b) Hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in some Chilean rodents from high and low altitude. Int J Biometeorol 7:45–50
Nienaber JA, Hahn GL (2007) Livestock production system management responses to thermal challenges. Int J Biometeorol 52:149–157
Pereira AM, Baccari F, Titto EA, Almeida JA (2008) Effect of thermal stress on physiological parameters, feed intake and plasma thyroid hormones concentration in Alentejana, Mertolenga, Frisian and Limousine cattle breeds. Int J Biometeorol 52:199–208
Reid K, Falter H, Persinger MA (1991) Humoral (immunological) responses in female albino rats during rotating magnetic field exposures. Int J Biometeorol 34:239–241
Saxena D (1995) Effect of hypoxia by intermittent altitude exposure on semen characteristics and testicular morphology of male rhesus monkeys. Int J Biometeorol 38:137–140
Scott IM, Johnson HD, Hahn GL (1983) Effect of programmed diurnal temperature cycles on plasma thyroxine level, body temperature, and feed intake of Holstein dairy cows. Int J Biometeorol 27:47–62
Seo SN (2015) Adapting to extreme climates: raising animals in hot and arid ecosystems in Australia. Int J Biometeorol 59:541–550
Siebert BD (1973) The effects of temporal variation in the water climate on beef cattle reproduction in the seasonally dry tropics of Australia. Int J Biometeorol 17:123–129
Singh SB, Selvamurthy W (1993) Effect of intermittent chronic exposure to hypoxia on feeding behaviour of rats. Int J Biometeorol 37:200–202
Sheridan SC, Allen MJ (2017) Sixty years of the International Journal of Biometeorology. Int J Biometeorol 61: In Press https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-017-1366-5
Shkolnik A (1971) Diurnal activity in a small desert rodent. Int J Biometeorol 15:115–120
Somparn P, Gibb MJ, Markvichitr K, Chaiyabutr N, Thummabood S, Vajrabukka C (2004) Analysis of climatic risk for cattle and buffalo production in northeast Thailand. Int J Biometeorol 49:59–64
Sparks TH (1999) Phenology and the changing pattern of bird migration in Britain. Int J Biometeorol 42:134–138
Steinbach J (1973) Bioclimatic influences on the reproductive processes in swine in a humid tropical environment. Int J Biometeorol 17:141–145
Steinlechner S, Heldmaier G (1982) Role of photoperiod and melatonin in seasonal acclimatization of the Djungarian hamster, Phodopus Sungorus. Int J Biometeorol 26:329–337
Tryjanowski P, Sparks T (2001) Is the detection of the first arrival date of migrating birds influenced by population size? A case study of the red-backed shrike Lanius collurio. Int J Biometeorol 45:217–219
Vajrabukka C, Thwaites CJ (1984) The relative influences of exercise and coat-type on the thermoregulatory responses of cattle. Int J Biometeorol 28:9–15
Valtorta S, Leva PE, Gallardo MR (1997) Evaluation of different shades to improve dairy cattle well-being in Argentina. Int J Biometeorol 41:65–67
van Albada M (1958) Seasonal and lighting influences on the laying rhythm of the fowl. IJBB 2: part III, section A
Weihe WH (1965) Influence of altitude and cold on pregnancy and lactation of rats fed on two different diets. Int J Biometeorol 9:45–52
Weihe WH, Brezowsky H (1962) A method to estimate the effect of weather changes on the growing rat. Int J Biometeorol 5:31–36
Weihe WH, Schidlow J, Strittmatter J (1969) The effect of light intensity on the breeding and development of rats and golden hamsters. Int J Biometeorol 13:69–79
Wright GL, Lindsey WD, Johnson HL, Krzywicki HJ (1972) The effect of high temperatures on tissue lactate, pyruvate and venous blood properties in the rat. Int J Biometeorol 16:71–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaughan, J.B., Lees, A.M. & Sejian, V. Sixty years of animal biometeorology. Int J Biometeorol 64, 157–163 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-017-1459-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-017-1459-1