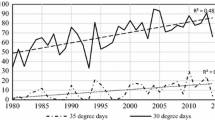
Abstract
Heat waves are natural disasters that can result in large numbers of casualties. The frequency and damage caused by heat waves have been increasing in Korea due to climate change. The regional impacts of heat waves can vary according to environmental and socioeconomic factors regardless of duration and intensity. This study assessed the risks posed by heat waves for administrative districts in Korea according to climate change scenarios and the risk assessment framework of Fifth Assessment Report presented by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. The risk of heat waves is usually based on a combination of hazard, exposure, and vulnerability. Unlike previous studies using subjective weights, this study employed partial least squares—structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) and entropy weighting, which are more objective methods of determining the indicators and weights, to estimate the exposure and vulnerability of heat waves. The results showed that at least 40% and 46% of administrative districts are expected to experience a high level of risk according to the representative concentration pathway scenarios, i.e., RCP 4.5 and 8.5, respectively. In addition, significant differences were observed in the heat wave risks calculated in this study for the upper and lower regions, with respect to cumulative heat-related morbidity rates, whereas the heat wave risk reported by the Korean Ministry of Environment was found to be insignificant. The results of this study can be used to prepare for heat waves and minimize damage caused by them.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon a reasonable request.
References
Abadie LM, Chiabai A, Neumann MB (2019) Stochastic diffusion models to describe the evolution of annual heatwave statistics: a three-factor model with risk calculations. Sci Total Environ 646:670–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.158
Anbalagan R, Kumar R, Lakshmanan K, Parida S, Neethu S (2015) Landslide hazard zonation mapping using frequency ratio and fuzzy logic approach, a case study of Lachung Valley, Sikkim. Geoenviron Disasters 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-014-0009-y
Balica S (2012) Approaches of understanding developments of vulnerability indices for natural disasters. Environ Eng Manag J 11:963–974. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2012.120
Bao J, Li X, Yu C (2015) The construction and validation of the heat vulnerability index, a review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:7220–7234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120707220
Cha Y, Choi JW, Kim ES, Ahn JB (2022) Occurrence of heatwave in Korea by the displacement of South Asian high. Clim Dyn 58:1699–1718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05987-3
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, New Jersey
Ding X, Chong X, Bao Z, Xue Y, Zhang S (2017) Fuzzy comprehensive assessment nethod based on the entropy weight method and its application in the water environmental safety evaluation of the Heshangshan drinking water source area, three gorges reservoir area, China. Water 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050329
Dong J, Peng J, He X et al (2020) Heatwave-induced human health risk assessment in megacities based on heat stress-social vulnerability-human exposure framework. Landsc Urban Plan 203:103907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2020.103907
Dong Z, Wang L, Sun Y et al (2021) Heatwaves in Southeast Asia and their changes in a warmer world. Earth’s Future 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021EF001992
Fariza A, Abhimata NP, NurHasim JA (2017) Earthquake disaster risk map in Rast Java, Indonesia, using analytical hierarchy process – Natural break classification. Int Conf Knowl Creat Intell Comput KCIC 2016:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1109/KCIC.2016.7883638
Ha Anh H, Da Hanh TM, ThiTuong Vi N, Shunbo Y (2018) Examining the interaction of flood vulnerability determinants in Cambodia and Vietnam using partial least squares structural equation modeling. Water Policy 20:1256–1278. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2018.198
Hair JF Jr, Hult GTM, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M (2017) A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd edn. Sage Publications
Henseler J, Ringle CM, Sarstedt M (2015) A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J Acad Mark Sci 43:115–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Imran M, Sumra K, Mahmood SA, Sajjad SF (2019) Mapping flood vulnerability from socioeconomic classes and GI data: Linking socially resilient policies to geographically sustainable neighborhoods using PLS-SEM. Int J Disaster Risk Reduc 41:101288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101288
IPCC (2014a) Climate change 2014: synthesis report. In: Core Writing Team, Pachauri RK, Meyer LA (eds) Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC, Geneva, p 151
IPCC (2014b) Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part A: global and sectoral aspects. In: Field CB, Barros VR, Dokken DJ, Mach KJ, Mastrandrea MD, Bilir TE, Chatterjee M, Ebi KL, Estrada YO, Genova RC, Girma B, Kissel ES, Levy AN, MacCracken S, Mastrandrea PR, White LL (eds) Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 1132
Jenks GF (1967) The data model concept in statistical mapping. Int Yearb Cartogr 7:186–190
Johnson DP, Stanforth A, Lulla V, Luber G (2012) Developing an applied extreme heat vulnerability index utilizing socioeconomic and environmental data. Appl Geogr 35:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2012.04.006
Keramitsoglou I, Kiranoudis CT, Maiheu B et al (2013) Heat wave hazard classification and risk assessment using artificial intelligence fuzzy logic. Environ Monit Assess 185:8239–8258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3170-y
Kim DW, Deo RC, Lee JS, Yeom JM (2017) Mapping heatwave vulnerability in Korea. Nat Hazards 89:35–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-2951-y
Lee S, Kang JE, Park CS, Yoon DK, Yoon S (2020) Multi-risk assessment of heat waves under intensifying climate change using Bayesian networks. Int J Disaster Risk Reduc 50:101704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101704
Li B, Sain S, Mearns LO et al (2012) The impact of extreme heat on morbidity in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Clim Change 110:959–976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0120-y
Lianxiao MT, Morimoto T (2019) Spatial analysis of social vulnerability to floods based on the MOVE framework and information entropy method: Case study of Katsushika Ward, Tokyo. Sustainability 11 https://doi.org/10.3390/su11020529
Liu Y, Feng G, Xue Y, Zhang H, Wang R (2015) Small-scale natural disaster risk scenario analysis: A case study from the town of Shuitou, Pingyang County, Wenzhou, China. Nat Hazards 75:2167–2183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1420-0
Lu Y, He T, Xu X, Qiao Z (2021) Investigation the robustness of standard classification methods for defining urban heat islands. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 14:11386–11394. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3124558
Macnee RGD, Tokai A (2016) Heat wave vulnerability and exposure mapping for Osaka City, Japan. Environ Syst Decis 36:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-016-9607-4
Menteş EN, Kaya Ş, Tanık A, Gazioğlu C (2019) Calculation of flood risk index for Yeşilırmak basin- Turkey. Int J Environ Geoinf 6:288–299. https://doi.org/10.30897/ijegeo.661533
Moon JH, Park SY, Lee SH (2022) Comparative study of spatiotemporal variation in the urban heat island core in coastal and inland basin cities. Air Qual Atmos Health 15:1439–1451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-022-01173-4
Mora C, Dousset B, Caldwell IR et al (2017) Global risk of deadly heat. Nat Clim Change 7:501–506. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3322
Naumann G, Barbosa P, Garrote L, Iglesias A, Vogt J (2014) Exploring drought vulnerability in Africa: An indicator based analysis to be used in early warning systems. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 18:1591–1604. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-18-1591-2014
Nayak SG, Shrestha S, Kinney PL et al (2018) Development of a heat vulnerability index for New York State. Public Health 161:127–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2017.09.006
Niu Y, Li Z, Gao Y et al (2021) A systematic review of the development and validation of the heat vulnerability index: Major factors, methods, and spatial units. Curr Clim Change Rep 7:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40641-021-00173-3
Philip SY, Kew SF, Van OGJ et al (2021) Rapid attribution analysis of the extraordinary heatwave on the Pacific Coast of the US and Canada June 2021. Earth Syst Dyn Discuss 2021:1–34
Reid CE, O’Neill MS, Gronlund CJ et al (2009) Mapping community determinants of heat vulnerability. Environ Health Perspect 117:1730–1736. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0900683
Robine JM, Cheung SLK, Le Roy S et al (2008) Death toll exceeded 70,000 in Europe during the summer of 2003. C R Biol 331:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2007.12.001
Tapsell S, McCarthy S, Faulkner H, Alexander M (2010) Social vulnerability and natural hazards. CapHaz-Net WP4 Report, Flood Hazard Research Centre – FHRC, Middlesex University, London
Tebaldi C, Lobell D (2018) Estimated impacts of emission reductions on wheat and maize crops. Clim Change 146:533–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1537-5
Tran DN, Doan VQ, Nguyen VT et al (2020) Spatial patterns of health vulnerability to heatwaves in Vietnam. Int J Biometeorol 64:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-020-01876-2
Waseem M, Ajmal M, Kim TW (2015) Development of a new composite drought index for multivariate drought assessment. J Hydrol 527:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.04.044
Wolf T, McGregor G (2013) The development of a heat wave vulnerability index for London, United Kingdom. Weather Clim Extrem 1:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2013.07.004
Wu J, Chen X, Lu J (2022) Assessment of long and short-term flood risk using the multi-criteria analysis model with the AHP-Entropy method in Poyang Lake basin. Int J Disaster Risk Reduc 75:102968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.102968
Xia Y, Li Y, Guan D et al (2018) Assessment of the economic impacts of heat waves: A case study of Nanjing, China. J Clean Prod 171:811–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.069
Yoon DK (2012) Assessment of social vulnerability to natural disasters: A comparative study. Nat Hazards 63:823–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0189-2
Yoon D, Kim K, Cha DH et al (2022) Development of model output statistics based on the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression for forecasting next-day maximum temperature in South Korea. Q J R Meteorol Soc 148:1929–1944. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.4286
Zhang M, Wang H, Jin W, Van Dijk MPV (2019) Assessing heat wave vulnerability in Beijing and its districts, using a three dimensional model. Int J Glob Warm 17:297–314. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJGW.2019.098524
Zhu Y, Tian D, Yan F (2020) Effectiveness of entropy weight method in decision-making. Math Probl Eng 2020:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3564835
Ziarh GF, Asaduzzaman M, Dewan A et al (2021) Integration of catastrophe and entropy theories for flood risk mapping in peninsular Malaysia. J Flood Risk Manag 14:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfr3.12686
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the editors and reviewers for their helpful comments.
Funding
This research was supported by grants (2022-MOIS63-001(RS-2022-ND641011), 2020-MOIS33-006) funded by Ministry of the Interior and Safety, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Dongwook Kim and Tae-Woong Kim; data preparation: Ji Eun Kim; methodology and analysis: Dongwook Kim; validation and investigation: Juil Song and Sang Won Lee; visualization: Ji Eun Kim and Jae-Hyun Ahn; writing—original draft: Dongwook Kim; writing—review and editing: Tae-Woong Kim; supervision: Jae-Hyun Ahn.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D., Kim, J.E., Song, J. et al. Risks of heat waves in South Korea using structural equation modeling and entropy weighting. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-024-02725-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-024-02725-z