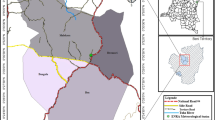
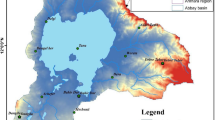
Abstract
Hydro-climatic extremes, such as floods and droughts, are influenced by climate change and climate variability, significantly affecting natural ecosystems, human lives, and livelihood. It is crucial to advance the understanding of long-term trends of hydro-climatic extremes for effective water resource planning and management. We analyzed 25 climatic extremes-related indices and 33 hydrologic extremes-related indices in a medium-range river basin in western Nepal, the Babai River Basin. We used RClimDex and Indicators for Hydrologic Alterations to analyze extreme climatic and hydrologic parameters. We computed monotonic trends to evaluate temporal changes in extreme events. The results show a positive trend of total precipitation at Kusum (+ 2.2 mm/year) and Bargadaha (+ 17.7 mm/year) stations and a negative trend at Gulariya (− 5.7 mm/year), Nayabasti (− 7.0 mm/year), Luwamjula (− 5.9 mm/year), and Ghorai (− 18.5 mm/year) stations. Similarly, we observe that almost all temperature extreme indices have a rising trend except the percentage of the days when the maximum temperature is less than the 10th percentile index at Rani Jaruwa station, located at a low elevation. Notably, the cold day temperature index falls at 0.13 days per year. Overall, the hydrologic alteration value shows moderate variability and reduction in the median flow for the second half. The findings of this study indicate that the study area is subjected to a reduced flow regime with a medium degree of variability.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghakouchak A, Chiang F, Huning LS et al (2020) Climate extremes and compound hazards in a warming world. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 48:519–567. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-071719
Arnell NW, Lowe JA, Challinor AJ, Osborn TJ (2019) Global and regional impacts of climate change at different levels of global temperature increase. Clim Change 155:377–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10584-019-02464-Z/FIGURES/4
Bates BC, Kundzewicz Z, Wu S, Palitikof JP (2008) Climate Change and Water, Climate change and water. Techical Papper Intergovermental Panel Climate Chang IPCC
Bhandari D, Uprety M, Ghimire G, et al (2018) Nepal flood 2017: Wake up call for effective preparedness and response. Rugby
Boretti A, Rosa L (2019) Reassessing the projections of the world water development report. Clean Water. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-019-0039-9
Clarvis MH, Fatichi S, Allan A et al (2014) Governing and managing water resources under changing hydro-climatic contexts: The case of the upper Rhone basin. Environ Sci Policy 43:56–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVSCI.2013.11.005
Collins M, Knutti R, Arblaster J, et al (2013) Long-term Climate Change: Projections, Commitments and Irreversibility. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K, et al. (eds) Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
Conway D, Mould C, Bewket W (2004) Over one century of rainfall and temperature observations in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 24:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/JOC.989
Dewan TH (2015) Societal impacts and vulnerability to floods in Bangladesh and Nepal. Weather Clim ExtremE 7:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WACE.2014.11.001
Fischer EM, Knutti R (2015) Anthropogenic contribution to global occurrence of heavy-precipitation and high-temperature extremes. Nat Clim Chang 5:560–564. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2617
Gaál L, Beranová R, Hlavčová K, Meteorology JK (2014) Climate change scenarios of precipitation extremes in the carpathian region based on an ensemble of regional climate models. Adv Meteorol 2014:1–14
Gariano SL, Guzzetti F (2016) Landslides in a changing climate. Earth-Sci Rev 162:227–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EARSCIREV.2016.08.011
Gu H, Yu Z, Wang G et al (2015) Impact of climate change on hydrological extremes in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29:693–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-0957-5
Haqiqi I, Grogan DS, Hertel TW, Schlenker W (2021) Quantifying the impacts of compound extremes on agriculture. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 25:551–564. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-25-551-2021
Hasan MA, Mouw C, Jutla A, Akanda AS (2018) Quantification of rotavirus diarrheal risk due to hydroclimatic extremes over South Asia: prospects of satellite-based observations in detecting outbreaks. GeoHealth 2:70–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GH000101
Huang J, Liu F, Xue Y et al (2015) The spatial and temporal analysis of precipitation concentration and dry spell in Qinghai, northwest China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29:1403–1411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1051-3
IPCC (2007) Climate Change 2007: Synthesis report. contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Geneva, Switzerland
Jiang L, Ban X, Wang X, Cai X (2014) Assessment of hydrologic alterations caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River, China. Water 6(5):1419–1434
Joshi GR (2018) Agricultural economy of Nepal: development challenges & opportunities. Sustainable Research & Development Center
Kalkuhl M, Wenz L (2020) The impact of climate conditions on economic production. Evidence from a global panel of regions. J Environ Econ Manag 103:102360. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEEM.2020.102360
Karki R, Ul Hasson S, Schickhoff U et al (2017) Rising precipitation extremes across Nepal. Climate. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli5010004
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation methods, 5th edn. Griffin, Oxford, England
Khatiwada KR, Panthi J, Lall Shrestha M et al (2016) Hydro-climatic variability in the Karnali river basin of Nepal himalaya. Climate 4:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/CLI4020017
Kim J-B, Bae D-H (2020) Intensification characteristics of hydroclimatic extremes in the Asian monsoon region under 1.5 and 2.0 °C of global warming. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 24:5799–5820. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-24-5799-2020
Kim YH, Min SK, Zhang X et al (2020) Evaluation of the CMIP6 multi-model ensemble for climate extreme indices. Weather Clim Extrem 29:100269. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WACE.2020.100269
Kourgialas NN (2021) Hydroclimatic impact on mediterranean tree crops area – mapping hydrological extremes (drought/flood) prone parcels. J Hydrol 596:125684. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHYDROL.2020.125684
McLeod AI (2015) Kendall rank correlation and Mann-Kendall trend test
Muhamad Y, Usha H (2015) Regional observed trends in daily rainfall indices of extremes over the Indochina Peninsula from 1960 to 2007. Climate 3:168–192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli3010168
Ngo NS, Horton RM (2016) Climate change and fetal health: the impacts of exposure to extreme temperatures in New York City. Environ Res 144:158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2015.11.016
Nie H, Qin T, Yang H et al (2019) Trend analysis of temperature and precipitation extremes during winter wheat growth period in the major winter wheat planting area of China. Atmosphere. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10050240
Ouarda TBMJ (2019) Charron C (2019) Changes in the distribution of hydro-climatic extremes in a non-stationary framework. Sci Rep 91(9):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44603-7
Pandey VP, Shrestha D, Adhikari M (2021) Characterizing natural drivers of water-induced disasters in a rain-fed watershed: hydro-climatic extremes in the extended East Rapti watershed Nepal. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126383
Pathak H, Ladha JK, Aggarwal PK et al (2003) Trends of climatic potential and on-farm yields of rice and wheat in the Indo-Gangetic plains. Food Crop Res 80:223–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(02)00194-6
Radinger J, Alcaraz-Hernández JD, García-Berthou E (2018) Environmental and spatial correlates of hydrologic alteration in a large mediterranean river catchment. Sci Total Environ 639:1138–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.227
Rahman MATMT, Hoque S, Saadat · A H M, (2017) Selection of minimum indicators of hydrologic alteration of the Gorai river, Bangladesh using principal component analysis. Sustain Water Resour Manag 3:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0079-6
Richter BD, Baumgartner JV, Powell J, Braun DP (1996) A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv Biol 10:1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1523-1739.1996.10041163.X
Richter BD, Baumgartner JV, Wigington R, Braun DP (1997) How much water does a river need? Freshw Biol 37:231–249. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1365-2427.1997.00153.X
Richter BD, Baumgartner JV, Braun DP, Powell J (1998) A spatial assessment of hydrologic alteration within a river network. Regul Res Mgmt 14:329–340. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1646(199807/08)14:4
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1968.10480934
Sharma T, Vittal H, Karmakar S, Ghosh S (2020) Increasing agricultural risk to hydro-climatic extremes in India. Environ Res Lett 15:034010. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/AB63E1
Shiau JT, Wu FC (2007) Pareto-optimal solutions for environmental flow schemes incorporating the intra-annual and interannual variability of the natural flow regime. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005523
Shrestha AB, Bajracharya SR, Sharma AR et al (2017) Observed trends and changes in daily temperature and precipitation extremes over the Koshi river basin 1975–2010. Int J Climatol 37:1066–1083. https://doi.org/10.1002/JOC.4761
Sillmann J, Kharin VV, Zhang X et al (2013a) Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: part 1. Model evaluation in the present climate. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:1716–1733. https://doi.org/10.1002/JGRD.50203
Sillmann J, Kharin VV, Zwiers FW et al (2013b) Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: part 2. Future climate projections. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:2473–2493. https://doi.org/10.1002/JGRD.50188
Singh R, Pandey VP, Kayastha SP (2021) Hydro-climatic extremes in the Himalayan watersheds: a case of the Marshyangdi Watershed, Nepal. Theor Appl Climatol 143:131–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00704-020-03401-2/FIGURES/9
Stefanidis K, Panagopoulos Y, Psomas A, Mimikou M (2016) Assessment of the natural flow regime in a Mediterranean river impacted from irrigated agriculture. Sci Total Environ 573:1492–1502. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2016.08.046
Stern PC, Ebi KL, Leichenko R et al (2013) Managing risk with climate vulnerability science. Nat Clim Chang 3:607–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate1929
Talchabhadel R, Karki R, Yadav M et al (2019) Spatial distribution of soil moisture index across Nepal: a step towards sharing climatic information for agricultural sector. Theor Appl Climatol 137:3089–3102. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00704-019-02801-3/FIGURES/8
Talchabhadel R, Aryal A, Kawaike K et al (2021a) A comprehensive analysis of projected changes of extreme precipitation indices in West Rapti River basin, Nepal under changing climate. Int J Climatol 41:E2581–E2599. https://doi.org/10.1002/JOC.6866
Talchabhadel R, Aryal A, Kawaike K et al (2021b) Evaluation of precipitation elasticity using precipitation data from ground and satellite-based estimates and watershed modeling in Western Nepal. J Hydrol Reg Stud 33:100768. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJRH.2020.100768
Talchabhadel R, Panthi J, Sharma S et al (2021c) Insights on the impacts of hydroclimatic extremes and anthropogenic activities on sediment yield of a river Basin. Earth 2:32–50. https://doi.org/10.3390/EARTH2010003
Tan ML, Gassman PW, Yang X, Haywood J (2020) A review of SWAT applications, performance and future needs for simulation of hydro-climatic extremes. Adv Water Resour 143:103662. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADVWATRES.2020.103662
The Nature Conservancy (2009) Indicators of Hydrologic Alteration Version 7.1. User's Manual. http://www.conservationgateway.org/ConservationPractices/Freshwater/EnvironmentalFlows/MethodsandTools/IndicatorsofHydrologicAlteration/Pages/IHASoftware-Download.aspx
Trenberth KE (2008) The impact of climate change and variability on heavy precipitation, floods, and droughts. Encycl Hydrol Sci 17:1–11
Vittal H, Karmakar S, Ghosh S, Murtugudde R (2020) A comprehensive India-wide social vulnerability analysis: highlighting its influence on hydro-climatic risk. Environ Res Lett 15:014005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/AB6499
Vogel E, Donat MG, Alexander LV et al (2019) The effects of climate extremes on global agricultural yields. Environ Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab154b
Wang J, Hong Y, Gourley J, Adhikari P, Li L, Su F (2010) Quantitative assessment of climate change and human impacts on long-term hydrologic response: a case study in a sub-basin of the Yellow River, China. Int J Climatol 30(14):2130–2137
Wijngaard RR, Lutz AF, Nepal S et al (2017) Future changes in hydro-climatic extremes in the Upper Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra River basins. PLoS ONE 12:e0190224. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0190224
Xu J, Grumbine RE, Shrestha A et al (2009) The melting himalayas: cascading effects of climate change on water, biodiversity, and livelihoods. Conserv Biol 23:520–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1523-1739.2009.01237.X
Xue L, Zhang H, Yang C et al (2017) Quantitative assessment of hydrological alteration caused by irrigation projects in the Tarim river basin, China. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04583-y
Zhang X, Yang F (2004) RClimDex (1.0) User Manual. Clim Res Branch 22:13–14
Zhang H, Huang G, Wang D, Zhang X (2011) Uncertainty assessment of climate change impacts on the hydrology of small prairie wetlands. J Hydrol 396:94–103
Zheng X, Yang T, Cui T, Xu C, Zhou X, Li Z, Shi P, Qin Y (2021) A revised range of variability approach considering the morphological alteration of hydrological indicators. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 35(9):1783–1803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01926-6
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express sincere gratitude towards the Department of Hydrology and Meteorology (DHM), Nepal, for providing the necessary data to complete this research work.
Funding
The first author received research funding from Center of Research for Environment, Energy, and Water (CREEW), Kathmandu, Nepal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(i) AA: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data Curation, Software, Formal Analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing—Original Draft. (ii) VPP: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Visualization, Writing—Review and Editing. (iii) RT: Visualization, Writing—Review and Editing. (iv) BRT: Visualization, Writing—Review and Editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aryal, A., Pandey, V.P., Talchabhadel, R. et al. Hydro-climatic extremes in a medium range River Basin in western Nepal: Learning from analysis of observed data. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 38, 85–105 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02552-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02552-8