Abstract
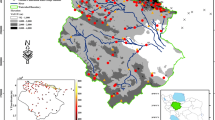
Precipitation is a key constituent of the water cycle and its accurate measurement is essential for a wide range of hydroclimatic studies. Although advances in technology have provided new sources of precipitation data (e.g., satellite data), gauge measurements are still considered as the most reliable source of information. Accuracy of ground measurements highly depends on the network density and positions of the rain gauges and thus, many studies have attempted to re-design the rain gauge networks around the globe. This is while, a limited number of researches have investigated the potential of utilizing global gridded precipitation products in network optimization context. In this study, a two-step framework was proposed to remove redundant rain gauge stations of the Central Plateau watershed of Iran. In the first step, number of excess rain gauges was detected based on transinformation–distance (T–D) analysis. In the second step, exact location of the extra rain gauges was determined through high degree of freedom and low degree of freedom (LDF) scenarios by a combination of harmony search optimization algorithm and a geostatistical model. According to the results, 58 out of 580 rain gauges were detected to be removed. Results of the proposed scenarios differed in detecting 13 out of 58 gauges. While LDF scenario required less computational time, network re-designed by this scenario was about 32% less accurate than the other scenario. Performance of the both optimized networks was equally similar to the initial network in terms of developing precipitation rasters.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemohammad SH, McColl KA, Konings AG, Entekhabi D, Stoffelen A (2015) Characterization of precipitation product errors across the United States using multiplicative triple collocation. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 19:3489–3503. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-3489-2015
Alsafadi K, Mohammed S, Mokhtar A, Sharaf M, He H (2021) Fine-resolution precipitation mapping over Syria using local regression and spatial interpolation. Atmos Res 256:105524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105524
Ayvaz MT (2007) Simultaneous determination of aquifer parameters and zone structures with fuzzy c-means clustering and meta-heuristic harmony search algorithm. Adv Water Resour 30:2326–2338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2007.05.009
Bakhtar A, Rahmati A, Shayeghi A, Teymoori J, Ghajarnia N, Saemian P (2022) Spatio-temporal evaluation of GPM-IMERGV6.0 final run precipitation product in capturing extreme precipitation events across Iran. Water 14:1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14101650
Bayat B, Nasseri M, Hosseini K, Karami H (2018) Revisited rainfall network design: evaluation of heuristic versus entropy theory methods. Arab J Geosci 11:561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3915-6
Bayat B, Hosseini K, Nasseri M, Karami H (2019) Challenge of rainfall network design considering spatial versus spatiotemporal variations. J Hydrol 574:990–1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.091
Bayat B, Nasseri M, Hosseini K, Karami H (2021) Nested augmentation of rainfall monitoring network: proposing a hybrid implementation of block kriging and entropy theory. Water Resour Manag 35:4665–4680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02976-3
Beck HE, Zimmermann NE, McVicar TR, Vergopolan N, Berg A, Wood EF (2018) Present and future Köppen–Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci Data 5:180214. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.214
Behboudian M, Kerachian R, Hosseini M (2021) Application of information fusion techniques and satellite products in the optimal redesign of rain gauge networks. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 35:1665–1680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-01990-6
Bertini C, Ridolfi E, de Padua LHR, Russo F, Napolitano F, Alfonso L (2021) An entropy-based approach for the optimization of rain gauge network using satellite and ground-based data. Hydrol Res 52:620–635. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2021.113
Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) An analysis of transformations. J R Stat Soc Ser B 26:211–252
Chang CH, Wu SJ, Hsu CT, Shen JC, Lien HC (2017) An evaluation framework for identifying the optimal raingauge network based on spatiotemporal variation in quantitative precipitation estimation. Hydrol Res 48:77–98. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2016.169
Chebbi A, Bargaoui ZK, Cunha MC (2011) Optimal extension of rain gauge monitoring network for rainfall intensity and erosivity index interpolation. J Hydrol Eng 16:665–676. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000353
Chen A, Chen D, Azorin-Molina C (2018) Assessing reliability of precipitation data over the Mekong River Basin: a comparison of ground-based, satellite, and reanalysis datasets. Int J Climatol 38:4314–4334. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5670
Cheng K, Lin Y, Liou J (2008) Rain-gauge network evaluation and augmentation using geostatistics. Hydrol Process 22:2554–2564. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6851
Contreras J, Ballari D, de Bruin S, Samaniego E (2019) Rainfall monitoring network design using conditioned Latin hypercube sampling and satellite precipitation estimates: an application in the ungauged Ecuadorian Amazon. Int J Climatol 39:2209–2226. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5946
Dai Q, Bray M, Zhuo L, Islam T, Han D (2017) A scheme for rain gauge network design based on remotely sensed rainfall measurements. J Hydrometeorol 18:363–379. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-16-0136.1
Dodangeh E, Panahi M, Rezaie F, Lee S, Tien Bui D, Lee CW, Pradhan B (2020) Novel hybrid intelligence models for flood-susceptibility prediction: meta optimization of the GMDH and SVR models with the genetic algorithm and harmony search. J Hydrol 590:125423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125423
Ekeu-wei IT (2018) Evaluation of hydrological data collection challenges and flood estimation uncertainties in Nigeria. Environ Nat Resour Res 8:44–54. https://doi.org/10.5539/enrr.v8n2p44
Geem ZW, Kim JH, Loganathan GV (2001) A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search. SIMULATION 76:60–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/003754970107600201
Ghomlaghi A, Nasseri M, Bayat B (2022a) Comparing and contrasting the performance of high-resolution precipitation products via error decomposition and triple collocation: an application to different climate classes of the central Iran. J Hydrol 612:128298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128298
Ghomlaghi A, Nasseri M, Bayat B (2022b) How to enhance the inverse distance weighting method to detect precipitation pattern on a large-scale watershed. Hydrol Sci J 67:2014–2028. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2022.2124874
Ghozi M, Budiati A (2018) Comparison of genetic algorithm and harmony search method for 2D geometry optimization. MATEC Web Conf 159:01009. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201815901009
Goovaerts P (1997) Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Goovaerts P (2000) Geostatistical approaches for incorporating elevation into the spatial interpolation of rainfall. J Hydrol 228:113–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00144-X
Gray RM (2013) Entropy and Information Theory. Springer-Verlag
Gyasi-Agyei Y (2020) Identification of the optimum rain gauge network density for hydrological modelling based on radar rainfall analysis. Water 12:1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12071906
Hengl T (2009) A practical guide to geostatistical mapping. University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam
Hosseini-Moghari SM, Tang Q (2020) Validation of GPM IMERG V05 and V06 precipitation products over Iran. J Hydrometeorol 21:1011–1037. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-19-0269.1
Hou AY, Kakar RK, Neeck S, Azarbarzin AA, Kummerow CD, Kojima M, Oki R, Nakamura K, Iguchi T (2014) The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 95:701–722. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-13-00164.1
Huang Y, Zhao H, Jiang Y, Lu X (2020) A method for the optimized design of a rain gauge network combined with satellite remote sensing data. Remote Sens 12:194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010194
Isaaks EH, Srivastava RM (1989) Applied geostatistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Karahan H, Gurarslan G, Geem ZW (2013) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum flood-routing model using a hybrid harmony search algorithm. J Hydrol Eng 18:352–360. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000608
Khan L, Mumtaz S, Khattak A (2012) Comparison of genetic algorithm and harmony search for generator maintenance scheduling. Mehran Univ Res J Eng Technol 31:587–598
Kim JH, Geem ZW, Kim ES (2001) Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using harmony search. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37:1131–1138. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2001.tb03627.x
Kim YH, Yoon Y, Geem ZW (2019) A comparison study of harmony search and genetic algorithm for the max-cut problem. Swarm Evol Comput 44:130–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.01.004
Liu Z, Wang H, Huang J, Zhuo L (2021) Data mining of remotely-sensed rainfall for a large-scale rain gauge network design. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 14:12300–12311. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3131157
Ma Q, Li Y, Feng H, Yu Q, Zou Y, Liu F, Pulatov B (2021) Performance evaluation and correction of precipitation data using the 20-year IMERG and TMPA precipitation products in diverse subregions of China. Atmos Res 249:105304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105304
Mahmoudi-Meimand H, Nazif S, Ali Abbaspour R, Faraji Sabokbar H (2016) An algorithm for optimisation of a rain gauge network based on geostatistics and entropy concepts using GIS. J Spat Sci 61:233–252. https://doi.org/10.1080/14498596.2015.1030789
Miri M, Masoudi R, Raziei T (2019) Performance evaluation of three satellites-based precipitation data sets over Iran. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 47:2073–2084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01053-y
Mogheir Y, Singh VP, de Lima JLMP (2006) Spatial assessment and redesign of a groundwater quality monitoring network using entropy theory, Gaza Strip. Palestine Hydrogeol J 14:700–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-005-0464-3
Morsy M, Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi R, Michaelides S, Scholten T, Dietrich P, Schmidt K (2021) Optimization of rain gauge networks for arid regions based on remote sensing data. Remote Sens 13:4243. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214243
Nasseri M, Schoups G, Taheri M (2022) A spatiotemporal framework to calibrate high-resolution global monthly precipitation products: an application to the Urmia Lake Watershed in Iran. Int J Climatol 42:2169–2194. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.7358
Rossiter DG (2018) Technical Note: co-kriging with the gstat package of the R environment for statistical computing
Shannon CE (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27:623–656. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x
Sreeparvathy V, Srinivas VV (2022) A Bayesian fuzzy clustering approach for design of precipitation gauge network using merged remote sensing and ground-based precipitation products. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2021WR030612
Tanim AH, Mullick MRA, Sikdar MS (2021) Evaluation of spatial rainfall products in sparsely gauged region using copula uncertainty modeling with triple collocation. J Hydrol Eng 26:04021004. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0002071
Tiwari S, Kumar Jha S, Sivakumar B (2019) Reconstruction of daily rainfall data using the concepts of networks: accounting for spatial connections in neighborhood selection. J Hydrol 579:124185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124185
Vivekanandan N, Jagtap RS (2012) Evaluation and selection of rain gauge network using entropy. J Inst Eng Ser A 93:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-013-0032-0
Volkmann THM, Lyon SW, Gupta HV, Troch PA (2010) Multicriteria design of rain gauge networks for flash flood prediction in semiarid catchments with complex terrain. Water Resour Res 46:W11554. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010WR009145
Wang K, Guan Q, Chen N, Tong D, Hu C, Peng Y, Dong X, Yang C (2017) Optimizing the configuration of precipitation stations in a space-ground integrated sensor network based on spatial-temporal coverage maximization. J Hydrol 548:625–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.03.033
Wang W, Wang D, Singh VP, Wang Y, Wu J, Zhang J, Liu J, Zou Y, He R, Meng D (2019) Evaluation of information transfer and data transfer models of rain-gauge network design based on information entropy. Environ Res 178:108686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2019.108686
Wang K, Gong Y, Peng Y, Hu C, Chen N (2020) An improved fusion crossover genetic algorithm for a time-weighted maximal covering location problem for sensor siting under satellite-borne monitoring. Comput Geosci 136:104406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104406
Xu H, Xu C-Y, Sælthun NR, Xu Y, Zhou B, Chen H (2015) Entropy theory based multi-criteria resampling of rain gauge networks for hydrological modelling—a case study of humid area in southern China. J Hydrol 525:138–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.03.034
Xu P, Wang D, Singh VP, Wang Y, Wu J, Wang L, Zou X, Liu J, Zou Y, He R (2018) A kriging and entropy-based approach to raingauge network design. Environ Res 161:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.10.038
Yeh HC, Chen YC, Chang CH, Ho CH, Wei C (2017) Rainfall network optimization using radar and entropy. Entropy 19:553. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19100553
Yoo C, Jung K, Lee J (2008) Evaluation of rain gauge network using entropy theory: comparison of mixed and continuous distribution function applications. J Hydrol Eng 13:226–235. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2008)13:4(226)
Yu L, Leng G, Python A (2022) A comprehensive validation for GPM IMERG precipitation products to detect extremes and drought over mainland China. Weather Clim Extrem 36:100458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2022.100458
Zandi O, Zahraie B, Nasseri M, Behrangi A (2022) Stacking machine learning models versus a locally weighted linear model to generate high-resolution monthly precipitation over a topographically complex area. Atmos Res 272:106159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106159
Zubieta R, Getirana A, Espinoza JC, Lavado-Casimiro W, Aragon L (2017) Hydrological modeling of the Peruvian-Ecuadorian Amazon basin using GPM-IMERG satellite-based precipitation dataset. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 21:3543–3555. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-21-3543-2017
Funding
The authors did not recieve any funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AG: Conceptualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing-original draft, and visualization. MN: Conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, resources, writing-review and editing, and supervision. BB: Conceptualization, investigation, resources, and writing-review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghomlaghi, A., Nasseri, M. & Bayat, B. Large-scale precipitation monitoring network re-design using ground and satellite datasets: coupled application of geostatistics and meta-heuristic optimization algorithms. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37, 4445–4458 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02517-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-023-02517-x