Abstract
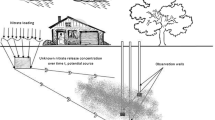
Nitrate represents the most widespread contaminant in shallow aquifers, especially in urban areas, and poses risks to human health, when the contaminated groundwater is ingested. In urban environments, the release of nitrate in groundwater can occur from multiple sources and is frequently associated with sewage leakage and septic tank infiltration. The Rio Claro Aquifer, located on the campus of the São Paulo State University at Rio Claro, offers an attractive example of a shallow aquifer impacted by nitrate contamination. Old sewage spills are considered to be the main sources of contamination; however, their locations remain largely unknown. Because of the scarce data and heterogeneous aquifer geology, the direct backward location approach is unsuitable in this case. Aiming to predict the probable locations of contamination sources, we developed a probabilistic backward location approach to identify the backward location in multiple geological scenarios using stochastic simulations. The numerical flow simulation and backward particle tracking were conducted based on 100 stochastic scenarios generated with Markov chains using lithological data from core descriptions. The multiple backward locations generated by stochastic simulations allowed us to build a density map to identify the region most likely to contain the contamination sources, thus simplifying the investigation and mitigation of the sewage spills.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfaro Soto MA, Kumayama DM, Chang HK (2007) Calibração de um reflectômetro para estudos do fluxo de água em solo não saturado. Geociências 26(4):357–368
Almasri MN, Kaluarachchi JJ (2007) Modeling nitrate contamination of groundwater in agricultural watersheds. J Hydrol 343(3–4):211–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.06.016
Bagtzoglou AC, Dougherty DE, Tompson AF (1992) Application of particle methods to reliable identification of groundwater pollution sources. Water Resour Manage 6(1):15–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00872184
Bourke SA, Iwanyshyn M, Kohn J, Hendry MJ (2019) Sources and fate of nitrate in groundwater at agricultural operations overlying glacial sediments. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 23(3):1355–1373. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-23-1355-2019
Carle SF , Fogg GE (1997) Modeling spatial variability with one and multidimensional continuous-lag Markov chains. Math Geol 29(7):891–918. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022303706942
Cheng WP, Jia Y (2010) Identification of contaminant point source in surface waters based on backward location probability density function method. Adv Water Resour 33(4):397–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2010.01.004
Cinnirella S, Buttafuoco G, Pirrone N (2005) Stochastic analysis to assess the spatial distribution of groundwater nitrate concentrations in the Po catchment (Italy). Environ Pollut 133(3):569–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.06.020
Desbarats AJ (1990) Macrodispersion in sand-shale sequences. Water Resour Res 26(1):153–163. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR026i001p00153
Exner ME, Hirsh AJ, Spalding RF (2014) Nebraska’s groundwater legacy: nitrate contamination beneath irrigated cropland. Water Resour Res 50(5):4474–4489. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013WR015073
Ferreira SR, Caetano-Chang MR (2008) Datação das formações Rio Claro e Piraçununga por termoluminescência. Rem Revista Escola de Minas 61(2):129–134. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0370-44672008000200004
Fetter CW (2004) Applied hydrogeology. Waveland Press
Fleckenstein JH, Fogg GE (2008) Efficient upscaling of hydraulic conductivity in heterogeneous alluvial aquifers. Hydrogeol J 16(7):1239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0312-3
Fogg GE (1986) Groundwater flow and sand body interconnectedness in a thick, multiple-aquifer system. Water Resour Res 22(5):679–694. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR022i005p00679
Gelhar LW (1986) Stochastic subsurface hydrology from theory to applications. Water Resour Res 22(9S):135S–145S. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR022i09Sp0135S
Gómez-Hernández JJ, Butler JJ, Fiori A, Bolster D, Cvetkovic V, Dagan G, Hyndman D (2017) Introduction to special section on Modeling highly heterogeneous aquifers: lessons learned in the last 30 years from the MADE experiments and others. Water Resour Res 53(4):2581–2584. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR020774
Gonçalves RD (2016) Modelagem Numérica e Avaliação Hidrogeológica do Aquífero Rio Claro. Master Thesis in Environment and Geosciences, São Paulo State University (UNESP)
Gonçalves RD, Chang HK (2018) Condutividade hidráulica da Formação Rio Claro a partir de ensaios granulométricos. Holos Environ 18(1):44–58. https://doi.org/10.14295/holos.v18i1.12249
Gonçalves RD, Teramoto EH, Engelbrecht BZ, Alfaro Soto MA, Chang HK, Van Genuchten MT (2019) Quasi-saturated layer: implications for estimating recharge and groundwater modeling. Groundwater 58:235–247. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12916
Grimmeisen F, Lehmann MF, Liesch T, Goeppert N, Klinger J, Zopfi J, Goldscheider N (2017) Isotopic constraints on water source mixing, network leakage and contamination in an urban groundwater system. Sci Total Environ 583:202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.054
Hansen AL, Gunderman D, He X, Refsgaard JC (2014) Uncertainty assessment of spatially distributed nitrate reduction potential in groundwater using multiple geological realizations. J Hydrol 519:225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.07.013
Harbaugh AW (2005) MODFLOW-2005, the US Geological Survey modular ground-water model: the ground-water flow process (6-A16). US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, Reston, VA
Hudon-Gagnon E, Chesnaux R, Cousineau PA, Rouleau A (2015) A hydrostratigraphic simplification approach to build 3D groundwater flow numerical models: example of a quaternary deltaic deposit aquifer. Environ Earth Sci 74(6):4671–4683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4439-y
Jeen SW, Lee H, Kim RH, Jeong HY (2017) A review on nitrate source identification using isotope analysis. J Soil Groundw Environ 22(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.7857/JSGE.2017.22.1.001
Katz BG, Böhlke JK, Hornsby HD (2001) Timescales for nitrate contamination of spring waters, northern Florida, USA. Chem Geol 179(1–4):167–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00321-7
Koltermann CE, Gorelick SM (1996) Heterogeneity in sedimentary deposits: a review of structure-imitating, process-imitating, and descriptive approaches. Water Resour Res 32(9):2617–2658. https://doi.org/10.1029/96WR00025
Krumbein WC, Dacey MF (1969) Markov chains and embedded Markov chains in geology. J Int Assoc Math Geol 1(1):79–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02047072
Lee SM, Min KD, Woo NC, Kim YJ, Ahn CH (2003) Statistical models for the assessment of nitrate contamination in urban groundwater using GIS. Environ Geol 44(2):210–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-002-0747-0
Lockhart KM, King AM, Harter T (2013) Identifying sources of groundwater nitrate contamination in a large alluvial groundwater basin with highly diversified intensive agricultural production. J Contam Hydrol 151:140–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2013.05.008
Maxwell RM, Carle SF, Tompson AF (2008) Contamination, risk, and heterogeneity: on the effectiveness of aquifer remediation. Environ Geol 54(8):1771–1786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0955-8
Melo MS, Coimbra AM, Cuchierato G (1997) Fácies sedimentares da Formação Rio Claro, neocenozóico da depressão periférica paulista. Rev Inst Geol 18(1/2):49–63. https://doi.org/10.5935/0100-929X.19970004
Moeck C, Molson J, Schirmer M (2020) Pathline density distributions in a Null-Space Monte Carlo approach to assess groundwater pathways. Groundwater 58(2):189–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12900
Moreno L, Tsang CF (1994) Flow channeling in strongly heterogeneous porous media: a numerical study. Water Resour Res 30(5):1421–1430. https://doi.org/10.1029/93WR02978
Neto DC, Chang HK, van Genuchten MT (2016) A mathematical view of water table fluctuations in a shallow aquifer in Brazil. Groundwater 54(1):82–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12329
Neupauer RM, Lin R (2006) Identifying sources of a conservative groundwater contaminant using backward probabilities conditioned on measured concentrations. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005WR004115
Neupauer RM, Wilson JL (1999) Adjoint method for obtaining backward-in-time location and travel time probabilities of a conservative groundwater contaminant. Water Resour Res 35(11):3389–3398. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999WR900190
Neupauer RM, Wilson JL (2002) Backward probabilistic model of groundwater contamination in non-uniform and transient flow. Adv Water Resour 25(7):733–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0309-1708(02)00073-8
Oliva A, Chang HK, Caetano-Chang MR (2005) Determinação da condutividade hidráulica da Formação Rio Claro: análise comparativa através de análise granulométrica e ensaios com permeâmetro guelph e testes de slug. Águas Subterr. https://doi.org/10.14295/ras.v19i2.8223
Oliva A (2006) Estudo hidrofaciológico do aqüífero Rio Claro no município de Rio Claro-SP. Dissertation Thesis at Geosciências e Meio Ambiente, São Paulo State University
Peña-Haro S, Pulido-Velazquez M, Llopis-Albert C (2011) Stochastic hydro-economic modeling for optimal management of agricultural groundwater nitrate pollution under hydraulic conductivity uncertainty. Environ Model Softw 26(8):999–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2011.02.010
Perinotto JADJ, Etchebehere MLDC, Zaine JE, Saad AR (2006) Nova contribuiçao ao conhecimento da formação Rio Claro (T) na Folha Rio Claro (SP). Geociências 297–306
Pollock DW (1988) Semianalytical computation of path lines for finite-difference models. Ground Water 26(6):743–750
Pollock DW (2012) User guide for MODPATH version 6: a particle tracking model for MODFLOW. US Geological Survey, Reston. https://doi.org/10.3133/tm6A41
Rubin Y, Gómez-Hernández JJ (1990) A stochastic approach to the problem of upscaling of conductivity in disordered media: theory and unconditional numerical simulations. Water Resour Res 26(4):691–701. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR026i004p00691
Silverman BW (1986) Density estimation for statistics and data analysis. Chapman and Hall, New York
Stradioto MR, Teramoto EH, Chang HK (2019) Nitrato em águas subterrâneas do estado de São Paulo. Rev Inst Geol 40(3):1–12. https://doi.org/10.33958/revig.v40i3.672
Teramoto EH, da Costa PPB, Gonçalves RD, Engelbrecht BZ, Chang HK (2019) Monitoring of nitrate contamination in groundwater: case study of the campus of UNESP, Rio Claro/SP. Ciência e Natura 41:54. https://doi.org/10.5902/2179460X33188
Vystavna Y, Diadin D, Rossi PM, Gusyev M, Hejzlar J, Mehdizadeh R, Huneau F (2018) Quantification of water and sewage leakages from urban infrastructure into a shallow aquifer in East Ukraine. Environ Earth Sci 77(22):748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7936-y
Wang L, Stuart ME, Lewis MA, Ward RS, Skirvin D, Naden PS, Collins AL, Ascott MJ (2016) The changing trend in nitrate concentrations in major aquifers due to historical nitrate loading from agricultural land across England and Wales from 1925 to 2150. Sci Total Environ 542:694–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.127
Weissmann GS, Fogg GE (1999) Multi-scale alluvial fan heterogeneity modeled with transition probability geostatistics in a sequence stratigraphic framework. J Hydrol 226(1–2):48–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(99)00160-2
Wilson JL, Liu J (1995) Backward tracking to find the source of the pollution in waste management. In: Bahda R (ed) Waste management: from risk to reduction. ECM Press, Albuquerque, New Mexico, pp 181–199
World Health Organization (2000) The world health report 2000: health systems: improving performance. World Health Organization
Xian C, Ouyang Z, Li Y, Xiao Y, Ren Y (2016) Variation in nitrate isotopic signatures in sewage for source apportionment with urbanization: a case study in Beijing, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(22):22871–22881. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7498-z
Xu T, Gómez-Hernández JJ (2018) Simultaneous identification of a contaminant source and hydraulic conductivity via the restart normal-score ensemble Kalman filter. Adv Water Resour 112:106–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.12.011
Zhang WL, Tian ZX, Zhang N, Li XQ (1996) Nitrate pollution of groundwater in northern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 59(3):223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-8809(96)01052-3
Zhang Y, Gable CW, Sheets B (2010) Equivalent hydraulic conductivity of three-dimensional heterogeneous porous media: an upscaling study based on an experimental stratigraphy. J Hydrol 388(3–4):304–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.05.009
Zhang Y, Green CT, Fogg GE (2013) The impact of medium architecture of alluvial settings on non-Fickian transport. Adv Water Resour 54:78–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.01.004
Zhang Q, Sun J, Liu J, Huang G, Lu C, Zhang Y (2015) Driving mechanism and sources of groundwater nitrate contamination in the rapidly urbanized region of south China. J Contam Hydrol 182:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2015.09.009
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the FUNDUNESP/UNESP and the National Council for Technological and Scientific Development. We would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their beneficial comments and criticisms that significantly improved this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EHT and HKC developed the project concept. BZE and RDG carried out most of the data organization with some help by the other co-authors. EHT, BZE and RDG performed the simulations. EHT, BZE, RDG and HKC did the manuscript preparation. BZE and RDG did the preparation of figures and tables, and the calculations, guided and verified by EHT and HKC. All authors discussed the results, and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teramoto, E.H., Engelbrecht, B.Z., Gonçalves, R.D. et al. Probabilistic backward location for the identification of multi-source nitrate contamination. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 35, 941–954 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01966-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01966-y