Abstract
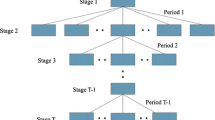
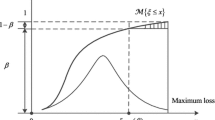
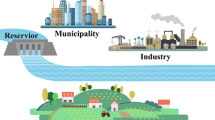
In this paper, a conditional value-at-risk based factorial stochastic programming approach is proposed to address random uncertainties and their interactions in a systematic manner. Random variables can be addressed through a risk-averse method within the two-stage stochastic programming framework. Interactions between random variables are examined through conducting a multi-level factorial analysis. The proposed approach is applied to a case study of water resources management to demonstrate its validity and applicability. A number of decision alternatives are obtained under different risk coefficients, which are useful for decision-makers to make sound water management plan and to perform an in-depth analysis of trade-offs between economic objectives and associated risks. Results obtained from the factorial experiment uncover the multi-level interactions between uncertain parameters and their contributions to the variability of net benefits. The performance of the proposed approach is compared with a factorial two-stage stochastic programming method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S (2006) Convexity and decomposition of mean-risk stochastic programs. Math Program 106(3):433–446
Birge JR, Louveaux FV (1988) A multicut algorithm for two-stage stochastic linear programs. Eur J Oper Res 34(3):384–392
Carneiro MC, Ribas GP, Hamacher S (2010) Risk management in the oil supply chain: a CVaR approach. Ind Eng Chem Res 49(7):3286–3294
Chan TC, Mahmoudzadeh H, Purdie TG (2014) A robust-CVaR optimization approach with application to breast cancer therapy. Eur J Oper Res 238(3):876–885
Claessens S, Kreuser J (2004) A framework for strategic foreign reserves risk management. European Central Bank, Germany
Ezenwaji EE, Anyadike RN, Igu NI (2014) Optimal allocation of public water supply to the urban sectors of Enugu, Nigeria: a linear programming approach. Appl Water Sci 4(1):73–78
Fan YR, Huang GH, Guo P, Yang AL (2012) Inexact two-stage stochastic partial programming: application to water resources management under uncertainty. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 26(2):281–293
Ganji A, Khalili D, Karamouz M, Ponnambalam K, Javan M (2008) A fuzzy stochastic dynamic Nash game analysis of policies for managing water allocation in a reservoir system. Water Resour Manag 22(1):51–66
Han Y, Huang Y, Wang G (2011) Interval-parameter linear optimization model with stochastic vertices for land and water resources allocation under dual uncertainty. Environ Eng Sci 28(3):197–205
Haro D, Paredes J, Solera A, Andreu J (2012) A model for solving the optimal water allocation problem in river basins with network flow programming when introducing non-linearities. Water Resour Manag 26(14):4059–4071
Huang GH (1996) IPWM: an interval parameter water quality management model. Eng Optim + A35 26(2):79–103
Huang GH, Chang NB (2003) The perspectives of environmental informatics and systems analysis. J Environ Inf 1(1):1–7
Huang GH, Loucks DP (2000) An inexact two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Civ Eng Syst 17(2):95–118
Karamouz M, Houck MH (1987) Comparision of stochastic and deterministic dynamic programming for reservoir operating rule generation. J Am Water Resour Assoc 23:1–9
Lewis SM, Dean AM (2001) Detection of interactions in experiments on large numbers of factors. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 63(4):633–672
Li CY, Zhang L (2015) An inexact two-stage allocation model for water resources management under uncertainty. Water Resour Manag 29(6):1823–1841
Li YP, Huang GH, Huang YF, Zhou HD (2009) A multistage fuzzy-stochastic programming model for supporting sustainable water-resources allocation and management. Environ Model Softw 24(7):786–797
Li W, Li YP, Li CH, Huang GH (2010) An inexact two-stage water management model for planning agricultural irrigation under uncertainty. Agric Water Manag 97(11):1905–1914
Li W, Wang B, Xie YL, Huang GH, Liu L (2015) An inexact mixed risk-aversion two-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(4):2964–2975
Luo B, Maqsood I, Yin YY, Huang GH, Cohen SJ (2003) Adaption to climate change through water trading under uncertainty: an inexact two-stage nonlinear programming approach. J Environ Inf 2(2):58–68
Maqsood I, Huang GH (2003) A two-stage interval-stochastic programming model for waste management under uncertainty. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 53(5):540–552
Maqsood I, Huang G, Huang Y, Chen B (2005) ITOM: an interval-parameter two-stage optimization model for stochastic planning of water resources systems. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19(2):125–133
Montgomery DC (2000) Design and analysis of experiments, 5th edn. Wiley, New York
Montgomery DC, Runger GC (2003) Applied statistics and probability for engineers, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Qin XS, Huang GH, Chakma A (2008) Modeling groundwater contamination under uncertainty: a factorial-design-based stochastic approach. J Environ Inf 11(1):11–20
Quaranta AG, Zaffaroni A (2008) Robust optimization of conditional value at risk and portfolio selection. J Bank Finance 32(10):2046–2056
Reca J, Roldán J, Alcaide M, López R, Camacho E (2001) Optimisation model for water allocation in deficit irrigation systems: I. Description of the model. Agric Water Manag 48(2):103–116
Rockafellar RT, Uryasev S (2000) Optimization of conditional value-at-risk. J Risk 2:21–42
Rockafellar RT, Uryasev S (2002) Conditional value-at-risk for general loss distributions. J Bank Finance 26(7):1443–1471
Wang S, Huang GH (2013a) Interactive fuzzy boundary interval programming for air quality management under uncertainty. Water Air Soil Pollut 224(5):1–16
Wang S, Huang GH (2013b) An interval-parameter two-stage stochastic fuzzy program with type-2 membership functions: an application to water resources management. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27(6):1493–1506
Wang S, Huang GH (2013c) A coupled factorial-analysis-based interval programming approach and its application to air quality management. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 63(2):179–189
Wang S, Huang GH (2015) A multi-level Taguchi-factorial two-stage stochastic programming approach for characterization of parameter uncertainties and their interactions: an application to water resources management. Eur J Oper Res 240(2):572–581
Wang S, Huang GH (2016) Risk-based factorial probabilistic inference for optimization of flood control systems with correlated uncertainties. Eur J Oper Res. 249(1): 258–269 doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2015.08.023
Wang S, Huang GH, Baetz BW, Huang W (2015) A polynomial chaos ensemble hydrologic prediction system for efficient parameter inference and robust uncertainty assessment. J Hydrol 530:716–733
Wang LZ, Fang L, Hipel KW (2003) Water resources allocation: a cooperative game theoretic approach. J Environ Inf 2(2):11–22
Wang JF, Cheng GD, Gao YG, Long AH, Xu ZM, Li X et al (2008) Optimal water resource allocation in arid and semi-arid areas. Water Resour Manag 22(2):239–258
Wang X, Cui Q, Li S (2012) An optimal water allocation model based on water resources security assessment and its application in Zhangjiakou region, northern china. Resour Conserv Recycl 69(12):57–65
Wang YY, Huang GH, Wang S, Li W (2015) A stochastic programming with imprecise probabilities model for planning water resources systems under multiple uncertainties. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 1–10
Wang YY, Huang GH, Wang S, Li W, Guan PB (2016) A risk-based interactive multi-stage stochastic programming approach for water resources planning under dual uncertainties. Adv Water Resour 94:217–230
Webby RB, Adamson PT, Boland J, Howlett PG, Metcalfe AV, Piantadosi J (2007) The Mekong—applications of value at risk (VaR) and conditional value at risk (CVaR) simulation to the benefits, costs and consequences of water resources development in a large river basin. Ecol Model 201(1):89–96
Xevi E, Khan S (2005) A multi-objective optimization approach to water management. J Environ Manag 77(4):269–277
Zhou Y, Huang GH (2011) Factorial two-stage stochastic programming for water resources management. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25(1):67–78
Zhou Y, Huang GH, Yang B (2013) Water resources management under multi-parameter interactions: a factorial multi-stage stochastic programming approach. Omega 41(3):559–573
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51225904, 51190095 and 51109077), the 111 Project (B14008), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2014XS69). The authors would like to express thanks to the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y.Y., Huang, G.H. & Wang, S. CVaR-based factorial stochastic optimization of water resources systems with correlated uncertainties. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 31, 1543–1553 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1276-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1276-9