Abstract
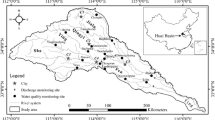
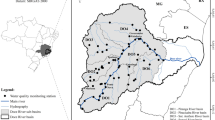
The surface water quality monitoring is an important concern of public organizations due to its relevance to the public health. Statistical methods are taken as consistent and essential tools in the monitoring procedures in order to prevent and identify environmental problems. This work presents the study case of the hydrological basin of the river Vouga, in Portugal. The main goal is discriminate the water monitoring sites using the monthly dissolved oxygen concentration dataset between January 2002 and May 2013. This is achieved through the extraction of trend and seasonal components in a linear mixed-effect state space model. The parameters estimation is performed with both maximum likelihood method and distribution-free estimators in a two-step procedure. The application of the Kalman smoother algorithm allows to obtain predictions of the structural components as trend and seasonality. The water monitoring sites are discriminated through the structural components by a hierarchical agglomerative clustering procedure. This procedure identified different homogenous groups relatively to the trend and seasonality components and some characteristics of the hydrological basin are presented in order to support the results.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Mohmood I, Coelho JP, Pacheco M, Santos MA, Duarte AC, Pereira E (2012) Role of non-enzymatic antioxidants on the bivalves’ adaptation to environmental mercury: organ-specificities and age effect in Scrobicularia plana inhabiting a contaminated lagoon. Environ Pollut 163:218–225
Amisigo BA, Van De Giesen NC (2005) Using a spatio-temporal dynamic state-space model with the EM algorithm to patch gaps in daily riverflow series. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 9:209–224
Arya FK, Zhang L (2015) Time series analysis of water quality parameters at Stillaguamish River using order series method. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29(1):227–239
Ato AF, Samuel O, Oscar YD, Moi PA (2010) Mining and heavy metal pollution: assessment of aquatic environments in Tarkwa (Ghana) using multivariate statistical analysis. J Environ Stat 1:1–13
Brockwell PJ, Davis RA (2002) Introduction to times series and forecasting, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York
Cerqueira MA, Silva JF, Magalhães FP, Soares FM, Pato JJ (2008) Assessment of water pollution in the Antuã River basin (Northwestern Portugal). Env Monit Assess 142:325–335
Costa M, Alpuim T (2010) Parameter estimation of state space models for univariate observations. J Stat Plan Inference 140:1889–1902
Costa M, Gonçalves AM (2011) Clustering and forecasting of dissolved oxygen concentration on a river basin. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25:151–163
Costa M, Gonçalves AM (2012) Combining statistical methodologies in water quality monitoring in a hydrological basin—space and time approaches. In: Voudouris K, Voutsa D (eds) Water quality monitoring and assessment. Intech, Croatia, pp 121–142
Costa M, Monteiro M (2015a) Statistical modeling of water quality time series - the River Vouga basin case study. In: Lee TS (ed) Research and practices in water quality. Intech, Croatia (in press)
Costa M, Monteiro M (2015b) A mixed-effect state space model to environmental data. In: Proceedings of the international conference on numerical analysis and applied mathematics 2014 (ICNAAM-2014), vol 1648. AIP Publishing, p 110002
Duan K, Xiao W, Mei Y, Liu D (2014) Multi-scale analysis of meteorological drought risks based on a Bayesian interpolation approach in Huai River basin, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28(8):1985–1998
Everitt BS, Landau S, Leese M (2011) Cluster analysis, 5th edn. Wiley, Chichester
Finazzi F, Haggarty R, Miller C, Scott M, Fassò A (2014) A comparison of clustering approaches for the study of the temporal coherence of multiple time series. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. doi:10.1007/s00477-014-0931-2
Gonçalves AM, Alpuim T (2011) Water quality monitoring using cluster analysis and linear models. Environmetrics 22:933–945
Gonçalves AM, Costa M (2013) Predicting seasonal and hydro-meteorological impact in environmental variables modelling via Kalman filtering. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 27(5):1021–1038
Helena B, Pardo R, Vega M, Barrado E, Fernandez JM, Fernandez L (2000) Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga river, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res 34:807–816
Irincheeva I, Cantoni E, Genton MG (2012) A non-Gaussian spatial generalized linear latent variable model. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 17:332–353
Khoshnevisan B, Bolandnazar E, Barak S, Shamshirband S, Maghsoudlou H, Altameem TA, Gani A (2014) A clustering model based on an evolutionary algorithm for better energy use in crop production. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. doi:10.1007/s00477-014-0972-6
Kokic P, Crimp S, Howden M (2011) Forecasting climate variables using a mixed-effect state-space model. Environmetrics 22:409–419
Lopes JF, Silva CI (2006) Temporal and spatial distribution of dissolved oxygen in the Ria de Aveiro lagoon. Ecol Model 197:67–88
Lopes JF, Silva CI, Cardoso AC (2008) Validation of a water quality model for the Ria de Aveiro lagoon, Portugal. Environ Modell Softw 23(4):479–494
MARETEC (2014). http://maretec.mohid.com. Accessed 12 Aug 2014
Rudolf A, Ahumada R, Pérez C (2002) Dissolved oxygen content as an index of water quality in San Vicente Bay, Chile (36 degrees, 450S). Env Monit Assess 78:89–100
Sánchez E, Colmenarejo MF, Vicente J, Rubio A, García MG, Travieso L, Borja R (2007) Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution. Ecol Ind 7:315–328
Shumway RH, Stoffer D (2006) Time series analysis and its applications: with R examples. Springer, New York
Tsai JP, Chen YW, Chang LC, Chen WF, Chiang CJ, Chen YC (2015) The assessment of high recharge areas using DO indicators and recharge potential analysis: a case study of Taiwan’s Pingtung plain. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29(3):815–832
Varol M, Sen B (2009) Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of Behrimaz Stream, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 159:543–553
Zhang Y, Guo F, Meng W, Wang X-Q (2009) Water quality assessment and source identification of Daliao river basin using multivariate statistical methods. Environ Monit Assess 152:105–121
Zhang Y, Zhu C (2013) Water quality analysis in Jining City using clustering methods. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 12(4):685–690
Zhou J, Han L, Liu S (2013) Nonlinear mixed-effects state space models with applications to HIV dynamics. Stat Probab Lett 83(5):1448–1456
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Associated Editor and the anonymous reviewers for their helpful and constructive comments that greatly contributed to improving the final version of the paper. Authors were partially supported by Portuguese funds through the CIDMA - Center for Research and Development in Mathematics and Applications, and the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (“FCT– Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia”), within Project UID/MAT/04106/2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, M., Monteiro, M. Discrimination of water quality monitoring sites in River Vouga using a mixed-effect state space model. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30, 607–619 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1137-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1137-y