Abstract
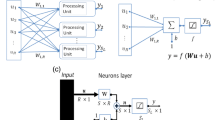
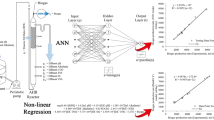
A three-layer Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model (9:12:1) for the prediction of Chemical Oxygen Demand Removal Efficiency (CODRE) of Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) reactors treating real cotton textile wastewater diluted with domestic wastewater was presented. To validate the proposed method, an experimental study was carried out in three lab-scale UASB reactors to investigate the treatment efficiency on total COD reduction. The reactors were operated for 80 days at mesophilic conditions (36–37.5°C) in a temperature-controlled water bath with two hydraulic retention times (HRT) of 4.5 and 9.0 days and with organic loading rates (OLR) between 0.072 and 0.602 kg COD/m3/day. Five different dilution ratios of 15, 30, 40, 45 and 60% with domestic wastewater were employed to represent seasonal fluctuations, respectively. The study was undertaken in a pH range of 6.20–8.06 and an alkalinity range of 1,350–1,855 mg/l CaCO3. The concentrations of volatile fatty acids (VFA) and total suspended solids (TSS) were observed between 420 and 720 mg/l CH3COOH and 68–338 mg/l, respectively. In the study, a wide range of influent COD concentrations (CODi) between 651 and 4,044 mg/l in feeding was carried out. CODRE of UASB reactors being output parameter of the conducted anaerobic treatment was estimated by nine input parameters such as HRT, pH, CODi concentration, operating temperature, alkalinity, VFA concentration, dilution ratio (DR), OLR, and TSS concentration. After backpropagation (BP) training combined with principal component analysis (PCA), the ANN model predicted CODRE values based on experimental data and all the predictions were proven to be satisfactory with a correlation coefficient of about 0.8245. In the ANN study, the Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm (LMA) was found as the best of 11 BP algorithms. In addition to determination of the optimal ANN structure, a linear-nonlinear study was also employed to investigate the effects of input variables on CODRE values in this study. Both ANN outputs and linear-nonlinear study results were compared and advantages and further developments were evaluated.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluumasri MN, Kaluarachchi JJ (2005) Modular neural networks to predict the nitrate distribution in groundwater using the onground nitrogen loading and recharge data. Env Modell Soft 20(7):851–871
Alp M, Cigizoglu HK (2007) Suspended sediment estimation by feed forward back propagation method using hydro meteorological data. Env Modell Soft 22(1):2–13
Amatya PL (1996) Anaerobic treatment of tapioca starch industry wastewater by bench scale upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor. MSc Thesis, Asian Institute of Technology School of Environment, Resources and Development Bangkok, Thailand
APHA-AWWA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. Washington
ASCE Task Committee (2000a) Artificial neural networks in Hydrology I. J Hydrol Eng 5(2):115–123
ASCE Task Committee (2000b) Artificial neural networks in Hydrology II. J Hydrol Eng 5(2):124–132
Cigizoglu HK (2003a) Estimation, forecasting and extrapolation of flow data by artificial neural networks. Hydrol Sci J 48(3):349–361
Cigizoglu HK (2003b) Incorporation of ARMA models into flow forecasting by artificial neural networks. Environmetrics 14(4):417–427
Cigizoglu HK (2004) Estimation and forecasting of daily suspended sediment data by multi layer perceptrons. Adv Water Res 27(2):185–195
Cigizoglu HK (2005a) Application of the generalized regression neural networks to intermittent flow forecasting and estimation. J Hydrol Eng 10(4):336–341
Cigizoglu HK (2005b) Generalized regression neural network in monthly flow forecasting. Civ Eng Env Syst 22(2):71–84
Cigizoglu HK, Kisi O (2006) Methods to improve the neural network performance in suspended sediment estimation. J Hydrol 317(3–4):221–238
Cigizoglu HK, Askin P, Ozturk A et al (2007) Artificial neural network models in rainfall-runoff modelling of Turkish rivers. International Congress on River Basin Management, chapter 4, 118
Crujeiras RM, Fernández-Casal R (2006) On the spectral simulation of spatial dependence structure. Departmento De Estatistica E Investigacion Operative, Universidade De Santiago De Compostela, Reports in Statistics and Operation Research, Report 06–05
Daneshvar N, Khataee AR, Djafarzadeh N (2006) The use of artificial neural networks (ANN) for modeling of decolorization of textile dye solution containing C. I. Basic Yellow 28 by electrocoagulation process. J Haz Mat 137(3):1788–1795
Garcelon J, Clark J (2000) Waste Digester design, instructor’s materials. University of Florida Civil Engineering. http://www.ce.ufl.edu/activities/waste/wddins.html
Grieu S, Thiery F, Traore A et al (2006) KSOM and MLP neural networks for on-line estimating the efficiency of an activated sludge process. Chem Eng J 116(1):1–11
Huang X (2005) Diagnostics of air gap eccentricity in closedloop drive-connected induction motors. PhD Thesis, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Georgia
Isik M, Sponza DT (2004) Anaerobic/aerobic sequential treatment of a cotton textile mill wastewater. J Chem Tech Biotech 79(11):1268–1274
Kinson T, Greer T, Mohamad, S (2001) Water effluent from pig farms in Sabah-a preliminary investigation of key environmental issues. ECD-CAB Background paper, No12, Pig Tuaran Survey 130301, State of Environmental Conservation Department, (ECD), Sabah Malaysia
Lahav O, Loewenthal RE (2000) Measurement of VFA in anaerobic digestion: the five-point titration method revisited. Water SA 26(3):389–392
López OAM, Lagunas ÁAM, Espinoza IL, Contreras JVH (2007) Best linear unbiased predictor for general combining ability and combined analysis of Griffing’s designs one and three. Téc Pecu Méx 45(2):131–146
Maier HR, Dandy GC (2000) Neural network for the prediction and forecasting of water resources variables: a review of modeling issues and applications. Env Modell Soft 15(1):101–124
McCann DW (2005) NNICE—a neural network aircraft icing algorithm. Env Modell Soft 20(10):1335–1342
Mohanty S, Scholz M, Slater MJ (2002) Neural network simulation of the chemical oxygen demand reduction in a biological activated-carbon filter. Wat Env J 16 (1):58–64
Molga E, Cherbanski R, Szpyrkowicz L (2006) Modeling of an industrial full-scale plant for biological treatment of textile wastewaters: application of neural networks. Ind Eng Chem Res 45(3):1039–1046
Oliveira-Esquerre KP, Mori M, Bruns RE (2002) Simulation of an industrial wastewater treatment plant using artificial neural networks and principal components analysis. Braz J Chem Eng 19(4):365–370
Onkal-Engin G, Demir I, Engin SN (2005) Determination of the relationship between sewage odour and BOD by neural networks. Env Modell Soft 20(7):843–850
Ozturk I (1999) Anaerobic biotechnology and its applications in waste treatment. Turkish Water Foundation Publishing Corp., Istanbul, pp 11–46
Perendeci A, Arslan S, Tanyolac A et al (2007) Evaluation of input variables in adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system modeling for an anaerobic wastewater treatment plant under unsteady state. J Environ Eng 133(7):765–771
Raduly B, Gernaey KV, Capodaglio AG et al (2007) Artificial neural networks for rapid WWTP performance evaluation: methodology and case study. Env Modell Soft 22(8):1208–1216
Roth MW (1988) Neural network technology and its applications. John Hopkins Appl Tech Dig 242–253
Sapci Z (2002) Investigation of anaerobic treatability of textile wastewaters. MSc Thesis, Institute of Science, Yildiz Technical University, Istanbul
Sapci Z, Ustun B (2003) The removal of color and COD from textile wastewater by using waste pumice. Electron J Environ Agric Food Chem 2(2):286–290
Stanley J (1988) Introduction of Neural Networks. California Scientific Software, p 255
Stevenson WJ (1991) The use of artificial neural nets in mechanical engineering. Council for Scientific and Industrial Research Tech Rep AERO 91/198
Talarposhti AM, Donnelly T, Andersonm GK (2001) Colour Removal from a simulated dye wastewater using a two-phase anaerobic packed bed reactor. Water Res 35(2):425–432
Torkian A, Eqbali A, Hashemian SJ (2003) The effect of organic loading rate on the performance of UASB reactor treating slaughterhouse effluent. Resour Conserv Recyc 40(1):1–11
Yetilmezsoy K, Saral A (2007) Stochastic modeling approaches based on neural network and linear–nonlinear regression techniques for the determination of single droplet collection efficiency of countercurrent spray towers. Env Model Assess 12(1):13–26
Zhang TC (2004) Development of sulfur-limestone autotrophic denitrification processes for treatment of nitrate-contaminated groundwater in small communities, midwest technology assistance center (MTAC). Final Report, 46 p
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank to Assist. Prof. Dr. F. Ilter Aydinol for her experience in this study. The authors would also like to thank to Tekel Brewery Inc., Istanbul, Turkey for supply of granular biomass used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yetilmezsoy, K., Sapci-Zengin, Z. Stochastic modeling applications for the prediction of COD removal efficiency of UASB reactors treating diluted real cotton textile wastewater. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23, 13–26 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-007-0191-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-007-0191-5