Abstract.
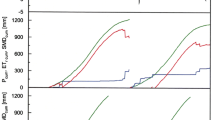
We investigated use of strain gauges for monitoring the water status of trees by measuring changes in the diameter of the largest spreading branch of a 27-year-old Chamaecyparis obtusa tree. The change in xylem diameter in the branch is more closely related than the change in phloem diameter to the change in leaf water potential. Since the diurnal changes in diameter match the diurnal changes in water balance (sap flow velocity – transpiration), measuring the change in xylem diameter using a strain gauge is useful in evaluating the water status of C. obtusa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, M., Shibata, E. Diurnal changes in branch diameter as indicator of water status of Hinoki cypress Chamaecyparis obtusa . Trees 15, 315–318 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004680100113
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004680100113