Abstract
Key message
Nonlinear error-in-variable models can advance the development of the systems of additive biomass equations and lead to much higher prediction accuracy of tree biomass than nonlinear seemingly unrelated regression.
Abstract
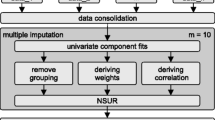
In this study, the approach of nonlinear error-in-variable models (NEIVM) was compared with nonlinear seemingly unrelated regressions (NSUR) for developing a system of nonlinear additive biomass equations using the data collected in Southern China for Pinus massoniana Lamb. Various tree variables were assessed to explore their contributions to improvement of biomass prediction using the systems of equations. It was found that diameter at breast height (D), total tree height (H) and crown width (CW) significantly contributed to the increase of prediction accuracy. The combinations of D, H, and CW led to three sets of independent variables: (1) D alone; (2) both D and H; and (3) D, H and CW together, which were used for the development of one-predictor, two-predictor and three-predictor systems of biomass equations, respectively. The results showed that both NEIVM and NSUR had high prediction accuracy of biomass for all the systems of biomass equations. For the one-predictor systems of biomass equations, both NEIVM and NSUR led to very similar predictions. However, for the two-predictor and three-predictor systems of biomass equations, the prediction accuracy of NEIVM was much higher than that of NSUR. When the two-predictor system of equations was used, in particular, NEIVM with one-step procedure, that is, by directly partitioning total tree biomass into four basic components, showed a higher accuracy of biomass prediction than NSUR for all the one-predictor, two-predictor and three-predictor systems of equations. This study implies that the NEIVM approach could provide a greater potential to develop a system of biomass equations that are dependent on the predictors with significant measurement errors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adame P, Río MD, Cañellas I (2008) A mixed nonlinear height-diameter model for Pyrenean oak (Quercus pyrenaica Willd.). For Ecol Manag 256:88–98
Arabatzis AA, Burkhart HE (1992) An evaluation of sampling methods and model forms for estimating height-diameter relationships in loblolly pine plantations. For Sci 38:192–198
Arlot S, Celisse A (2010) A survey of cross-validation procedures for model selection. Stat Surv 4:40–79
Bi H, Birk E, Turner J, Lambert M, Jurskis V (2001) Converting stem volume to biomass with additivity, bias corrections and confidence bands for two Australian tree species. N Z J For Sci 31:298–319
Bi H, Turner J, Lambert MJ (2004) Additive biomass equations for native eucalypt forest trees of temperate Australia. Trees 18:467–479
Bi H, Long Y, Turner J, Lei Y, Snowdon P, Li Y, Harper R, Zerihun A, Ximenes F (2010) Additive prediction of aboveground biomass for Pinus radiata (D. Don) plantations. For Ecol Manag 259:2301–2314
Calama R, Montero G (2005) Multilevel linear mixed model for tree diameter increment in stone pine (pinus pinea): a calibrating approach. Silva Fenn 39(1):37–54
Carroll RJ, Ruppert D, Stefanski LA, Crainiceanu CM (2006) Measurement error in nonlinear models: a modern perspective, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton
Fang Z, Bailey RL (2001) Nonlinear mixed effects modeling for slash pine dominant height growth following intensive silvicultural treatments. For Sci 47:287–300
Fu L, Sun H, Sharma RP, Lei Y, Zhang H, Tang S (2013) Nonlinear mixed-effects crown width models for individual trees of Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) in south-central China. For Ecol Manag 302:210–220
Fu L, Lei Y, Sun W, Tang S, Zeng W (2014) Development of compatible biomass models for trees from different stand origin. Acta Ecol Sin 34(6):1–10 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Fuller WA (1987) Measurement error models. Wiley, New York
Greene WH (1999) Econometric analysis, 4th edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Huuskonen S, Miina J (2007) Stand-level growth models for young scots pine stands in Finland. For Ecol Manag 241:49–61
Judge GG, Hill RC, Griffiths WE, Lutkepohl H, Lee TC (1988) Introduction to the theory and practice of econometrics, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Kangas AS (1998) Effect of errors-in-variables on coefficients of a growth model and on prediction of growth. For Ecol Manag 102:203–212
Kiernan DH, Bevilacqua E, Nyland RD (2008) Individual-tree diameter growth model for sugar maple trees in uneven-aged northern hardwood stands under selection system. For Ecol Manag 256:1579–1586
Kincaid C (2007) Guidelines for selecting the covariance structure in mixed model analysis. Paper 198–30. http://www2.sas.com/proceedings/sugi30/toc.html. Accessed April 2007
Kittredge J (1944) Estimation of the amount of foliage of trees and stand. J For 42:905–912
Kozak A (1970) Methods of ensuring additivity of biomass components by regression analysis. For Chron 46:402–404
Lei X, Zhang H, Bi H (2012) Additive aboveground biomass equations for major species in over-logged forest region in northeast China. In: IEEE proceedings of IEEE 4th international symposium on plant growth modelling, simulation, visualization and applications
Li Y, Tang S (2006) Study on impact of measurement error on model and compare of parameter estimate methods. J Biomath 21:285–290
Littell RC, Milliken GA, Stroup WW, Wolfinger RD, Schabenberber O (2006) SAS for mixed models, 2nd edn. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Marshall HD, Murphy GE, Boston K (2006) Evaluation of the economic impacts of length and diameter measurement error on mechanical harvesters and processors operating in pine stands. Can J For Res 36:1661–1673
Návar J (2009) Biomass component equations for Latin American species and groups of species. Ann For Sci 66(2):208
Parresol BR (1999) Assessing tree and stand biomass: a review with examples and critical comparisons. For Sci 45(4):573–593
Parresol BR (2001) Additivity of nonlinear biomass equations. Can J For Res 31:865–878
Pinheiro JC, Bates DM (2000) Mixed-effects models in S and S-PLUS. Springer, New York
Rencher AC, Schaalje GB (2008) Linear models in statistics, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Ruark GA, Martin GL, Bockheim JG (1987) Comparison of constant and variable allometric ratios for estimating populus tremuloides biomass. For Sci 33:294–300
Tang S (1991) Develop stand dominant height and average height model using dual regression and structure relationship. For Res 4(suppl):57–62 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tang S, Li Y (2002) Statistical foundation for biomathematical models. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Tang S, Wang Y (2002) A parameter estimation program for the errors-in-variable model. Ecol Model 156(2–3):225–236
Tang S, Zhang S (1998) Measurement error models and their applications. J Biomath 13:161–166
Tang S, Li Y, Wang Y (2001) Simultaneous equations, errors-in-variable models, and model integration in systems ecology. Ecol Model 142(3):285–294
Tang SZ, Lang KJ, Li HK (2008) Statistics and computation of biomathematical models (ForStat Course). Science Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
The MathWorks Inc (2001) MATLAB: the language of technical computing. The Math Works Inc, Natick
Vanclay JK (1994) Modelling forest growth and yield, application to mixed tropical forests. CAB International, Wallingford
Yang Y, Huang S (2011) Comparison of different methods for fitting nonlinear mixed forest models and for making predictions. Can J For Res 41(8):1671–1686
Zellner A (1962) An efficient method of estimating seemingly unrelated regressions and tests for aggregation bias. J Am Stat Assoc 57:348–368
Zeng WS, Tang SZ (2010) Using measurement error modeling method to establish compatible single-tree biomass equations system. For Res 23(6):797–802 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zeng WS, Zhang HR, Tang SZ (2011) Using the dummy variable model approach to construct compatible single-tree biomass equations at different scales—a case study for Masson Pine (Pinus massoniana) in southern China. Can J For Res 41:1547–1554
Zhang W, Ke Y, Quackenbush LJ, Zhang L (2010) Using errors-in-variable regression to predict tree diameter and crown width from remotely sensed imagery. Can J For Res 40:1095–1108
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National High-tech R&D Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2012AA102002), the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Nos. 31170588, 31300534, 31570628), the Lecture and Study Program for Outstanding Scholars from Home and Abroad (CAFYBB2011007), Chinese Academy of Forestry, and the Central South University of Forestry and Technology (No. 112-0990) for the financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by R. Grote.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Lei, Y., Wang, G. et al. Comparison of seemingly unrelated regressions with error-in-variable models for developing a system of nonlinear additive biomass equations. Trees 30, 839–857 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-015-1325-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-015-1325-x