Abstract
Key message
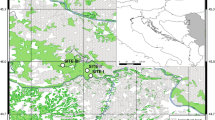
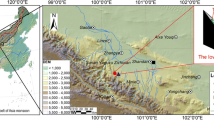
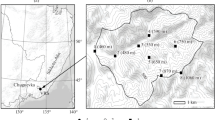
The heterogeneous stem radial growth of Populus euphratica and its correlation with hydrology and climate factors were investigated by a tree-ring study in Ejina Oasis in Northwest China.
Abstract
Over the last several decades, riparian forests in Northwest China have been extremely vulnerable to the increasing pressures from human activity and climate change. However, it is unclear how forests correlate with these influences over time and on a wide scale. In the present study, we developed 28 tree-ring chronologies of Populus euphratica in the Ejina Oasis, in the lower reaches of Northwestern China’s Heihe River, to evaluate the oasis-scale riparian forest growth variation and its correlation with the runoff regulation. We identified three hydrologic periods using regime-shift analysis: a natural runoff period from 1954 to 1989, when the oasis was sustained by natural river flows; a degradation period from 1990 to 2002, when excessive upstream withdrawals of runoff decreased flows to the oasis; and a recovery period, from 2003 to 2010, when water allocation projects restored flows. In general, stem radial growth of poplar trees in the oasis showed decreasing and increasing trends in the degradation period and recovery period, respectively, with high spatial heterogeneity in each period. Our analysis of the relationship between the chronologies and corresponding hydrologic and climatic data revealed that the runoff-recharged hyporheic groundwater depth was the major factor that limited tree stem radial growth. Thus, it is important to allocate water between the middle and lower reaches, and inside the lower reaches, to mitigate or prevent the adverse effects of low runoff. Our study also demonstrates that researchers must carefully consider the high spatial heterogeneity during dendrochronological research in an arid riparian forest.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan JD, Erickson DL, Fay J (1997) The influence of catchment land use on stream integrity across multiple spatial scales. Freshw Biol 37:149–161
Bai SF, Wang JX, Zhou XZ (1990) Research on environment geology of the desert plain area in the lower reaches of Heihe River Basin. The Second Hydro-Geological and Engineering Geology Team, Zhangye
Biondi F (1999) Comparing tree-ring chronologies and repeated timber inventories as forest monitoring tools. Ecol Appl 9:216–227
Briffa KR (1995) Interpreting high-resolution proxy climate data—the example of dendroclimatology. In: Von Storch H, Navarra A (eds) Analysis of climate variability: applications of statistical techniques. Springer, Berlin, pp 77–94
Briffa KR, Jones PD (1990) Basic chronology statistics and assessment. In: Cook ER, Kairiukstis LA (eds) Methods of dendrochronology: applications in the environmental sciences. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 137–152
Chang YS, Bao DWL, Bao YH (2011) Satellite monitoring of the ecological environment recovery effect in the Heihe River downstream region for the last 11 years. Procedia Environ Sci 10:2385–2392
Chen YN, Chen YP, Li WH, Zhang HF (2003) Response of the accumulation of proline in the bodies of Populus euphratica to the change of groundwater level at the lower reaches of Tarim River. Chin Sci Bull 48:1995–1999
Chen YN, Zilliacus H, Li WH, Zhang HF, Chen YP (2006) Ground-water level affects plant species diversity along the lower reaches of the Tarim river, Western China. J Arid Environ 66:231–246
Cheng GD, Xiao HL, Zhao WZ, Feng Q, Xu ZM, Li X (2009a) Preface. In: Cheng GD, Xiao HL, Zhao WZ, Feng Q, Xu ZM, Li X (eds) Study on the integrated management of the water-ecology-economy system of Heihe River basin. Science press, Beijing, pp 1–3
Cheng GD, Xiao HL, Zhao WZ, Feng Q, Xu ZM, Li X (2009b) Study on the integrated management of the water-ecology-economy system of Heihe River basin. Science Press, Beijing
Cheng GD, Xiao HL, Chen YN (2010) Study on the water-ecology of typical inland basins in West China. China Meteorological Press, Beijing
Cook ER (1985) A time series analysis approach to tree-ring standardization. Vol Ph. D. University of Arizona, Tuscon, Arizona, USA
Cook ER, Krusic PJ (2007) ARSTAN Version 41d: a tree-ring standardization program based on detrending and autoregressive time series modeling, with interactive graphics. Tree-Ring Laboratory, Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University. Palisades, NY. http://www.ldeo.columbia.edu/tree-ring-laboratory. Accessed 17 Sept 2015
Cook ER, Johnson AH, Blasing TJ (1987) Forest decline: modeling the effect of climate in tree rings. Tree Physiol 3:27–40
Cook ER, Anchukaitis KJ, Buckley BM, D’Arrigo RD, Jacoby GC, Wright WE (2010) Asian monsoon failure and megadrought during the last millennium. Science 328:486–489
Cook ER, Palmer JG, Ahmed M, Woodhouse CA, Fenwick P, Zafar MU, Wahab M, Khan N (2013) Five centuries of Upper Indus River flow from tree rings. J Hydrol 486:365–375
Edmondson J, Friedman J, Meko D, Touchan R, Scott J, Edmondson A (2014) Dendroclimatic potential of plains cottonwood (Populus deltoides subsp. monilifera) from the Northern Great Plains, USA. Tree-Ring Res 70:21–30
González E, Sher AA, Tabacchi E, Masip A, Poulin M (2015) Restoration of riparian vegetation: a global review of implementation and evaluation approaches in the international, peer-reviewed literature. J Environ Manage 158:85–94
Gregory SV, Swanson FJ, McKee WA, Cummins KW (1991) An ecosystem perspective of riparian zones. Bioscience 41:540–551
Grissino-Mayer HD (2001) Evaluating crossdating accuracy: a manual and tutorial for the computer program COFECHA. Tree Ring Bull 57:205–221
Guo QL, Feng Q, Li JL (2009) Environmental changes after ecological water conveyance in the lower reaches of Heihe River, northwest China. Environ Geol 58:1387–1396
Guo QL, Yang YS, Chen ZH (2010) Remote sensing monitoring vegetation cover change in Ejina oasis after Heihe River water was distributed. J Water Resour Water Eng 21:65–71 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Jacoby GC, Lovelius NV, Shumilov OI, Raspopov OM, Karbainov JM, Frank DC (2000) Long-term temperature trends and tree growth in the Taymir region of northern Siberia. Quat Res 53:312–318
Jin XM, Hu GC, Li WM (2008) Hysteresis effect of runoff of the Heihe River on vegetation cover in the Ejina Oasis in Northwestern China. Earth Sci Front 15:198–203
Leonel DSLS (2001) Savanna–forest hysteresis in the tropics. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 10:369–378
Li HX (2013) A study on the temporal-spatial process of oasis change and driving mechanism in the lower reaches of Heihe River Basin. vol Master. Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, p 72
Liang E, Ren P, Zhang S, Shao X, Eckstein D (2013) How can Populus euphratica cope with extremely dry growth conditions at 2,800 m asl on the northern Tibetan Plateau? Trees 27:447–453
Liao J, Wang T, Xue X, Guo J, Wen X (2011) Evolution of the Heihe River Basin oasis in the last 35 years. Remote sensing, environment and transportation engineering (RSETE). In: 2011 International conference on remote sensing. IEEE, Nanjing, pp 4027–4030
Lite SJ, Stromberg JC (2005) Surface water and ground-water thresholds for maintaining Populus-Salix forests, San Pedro River, Arizona. Biol Conserv 125:153–167
Liu PX, Chen FH, Jin LY, Gou XH, Zhang YX, Peng JF (2007a) About 100-year reconstruction of spring stream flow based on tree ring in the lower reaches of Heihe River. Arid Land Geogr 30:696–700 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Liu PX, Peng JF, Chen FH (2007b) Hydrological response of populus euphratica Olve. [sic] radial growth in Ejinaa [sic] Banner, Inner Mongolia. J Integr Plant Biol 49:150–156
Liu W, Wang ZJ, Xi HY (2008) Variations of physical and chemical properties of water and soil and their significance to ecosystem in the lower reaches of Heihe River. J Glaciol Geocryol 30:88–95 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Liu Xh, Wang Wz Xu, Gb Zeng Xm, Gj Wu, Xw Zhang, Qin Dh (2014) Tree growth and intrinsic water-use efficiency of inland riparian forests in northwestern China: evaluation via δ13C and δ18O analysis of tree rings. Tree Physiol 34:966–980
Lu ZY, Tan DS, Zheng B, Zhu CQ (2011) Post-evaluation of the ecological impact of water diversion and recent management in the downstream Heihe River. Acta Sci Circumst 31:1556–1561 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Mahoney JM, Rood SB (1992) Response of a hybrid poplar to water table decline in different substrates. For Ecol Manage 54:141–156
Mann ME, Bradley RS, Hughes MK (1998) Global-scale temperature patterns and climate forcing over the past six centuries. Nature 392:779–787
Meko DM, Friedman JM, Touchan R, Edmondson JR, Griffin ER, Scott JA (2015) Alternative standardization approaches to improving streamflow reconstructions with ring-width indices of riparian trees. Holocene 25(7):1093–1101
Naiman RJ, Décamps H (1997) The ecology of interfaces: riparian zones. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 28:621–658
Naiman RJ, Decamps H, McClain ME (2010) Riparia: ecology, conservation, and management of streamside communities. Academic Press, Elsevier, Amsterdam
Nilsson C, Berggren K (2000) Alterations of riparian ecosystems caused by river regulation. Bioscience 50:783–792
Peng JZ, Si JH, Feng Q, Chang ZQ (2011) The spatial heterogeneity of groundwater level depth in Ejina oasis based on geostatistics. J Arid Land Resour Environ 25:94–99 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Peng XM, Xiao SC, Xiao HL (2013) Preliminary dendrochronological studies on Populus euphratica in the lower reaches of the Heihe River basin in northwest China. Dendrochronologia 31:242–249
Potts DL, Huxman TE, Enquist BJ, Weltzin JF, Williams DG (2006) Resilience and resistance of ecosystem functional response to a precipitation pulse in a semi-arid grassland. J Ecol 94:23–30
Qin C, Yang B, Burchardt I, Hu X, Kang X (2010) Intensified pluvial conditions during the twentieth century in the inland Heihe River Basin in arid northwestern China over the past millennium. Global Planet Change 72:192–200
Rodionov SN (2004) A sequential algorithm for testing climate regime shifts. Geophys Res Lett 31:L09204
Rodionov SN, Overland JE (2005) Application of a sequential regime shift detection method to the Bering Sea ecosystem. ICES J Mar Sci J du Conseil 62:328–332
Sarris D, Christodoulakis D, Körner C (2011) Impact of recent climatic change on growth of low elevation eastern Mediterranean forest trees. Clim Change 106:203–223
Scott St G (2014) An overview of tree-ring width records across the Northern Hemisphere. Quat Sci Rev 95:132–150
Scott ML, Shafroth PB, Auble GT (1999) Responses of riparian cottonwoods to alluvial water table declines. Environ Manage 23:347–358
Scott RL, Shuttleworth WJ, Goodrich DC, Maddock Iii T (2000) The water use of two dominant vegetation communities in a semiarid riparian ecosystem. Agric For Meteorol 105:241–256
Shao XM, Xu Y, Yin ZY, Liang EY, Zhu HF, Wang S (2010) Climatic implications of a 3585-year tree-ring width chronology from the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Quat Sci Rev 29:2111–2122
Si JH, Feng Q, Zhang XY, Chang ZQ, Su YH, Xi HY (2007) Sap flow of Populus euphratica in a desert riparian forest in an extreme arid region during the growing season. J Integr Plant Biol 49:425–436
Si J, Feng Q, Cao S, Yu T, Zhao C (2014) Water use sources of desert riparian Populus euphratica forests. Environ Monit Assess 186:5469–5477
Singer MB, Stella JC, Dufour S, Piégay H, Wilson RJS, Johnstone L (2013) Contrasting water-uptake and growth responses to drought in co-occurring riparian tree species. Ecohydrology 6:402–412
Singer MB, Sargeant CI, Piegay H, Riquier J, Wilson RJ, Evans CM (2014) Floodplain ecohydrology: climatic, anthropogenic, and local physical controls on partitioning of water sources to riparian trees. Water Resour Res 50:4490–4513
Smith SD, Devitt DA, Sala A, Cleverly JR, Busch DE (1998) Water relations of riparian plants from warm desert regions. Wetlands 18:687–696
Speer JH (2010) Fundamentals of tree-ring research. The University of Arizona Press, Tucson, pp 18–20
Stella JC, Riddle J, Piégay H, Gagnage M, Trémélo M-L (2013a) Climate and local geomorphic interactions drive patterns of riparian forest decline along a Mediterranean Basin river. Geomorphology 202:101–114
Stella JC, Rodríguez-González PM, Dufour S, Bendix J (2013b) Riparian vegetation research in Mediterranean-climate regions: common patterns, ecological processes, and considerations for management. Hydrobiologia 719:291–315
Stoffel M, Wilford DJ (2012) Hydrogeomorphic processes and vegetation: disturbance, process histories, dependencies and interactions. Earth Surf Proc Land 37:9–22
Stokes MA, Smiley TL (1996) An introduction to tree-ring dating. University of Arizona Press, Tucson
Stromberg JC (2001) Influence of stream flow regime and temperature on growth rate of the riparian tree, Platanus wrightii, in Arizona. Freshw Biol 46:227–239
Stromberg J, Patten D (1996) Instream flow and cottonwood growth in the eastern Sierra Nevada of California, USA. Regulat Rivers Res Manag 12:1–12
Su YH, Feng Q, Zhu GF, Si JH, Zhang YW (2007) Identification and evolution of groundwater chemistry in the Ejin Sub-Basin of the Heihe River, Northwest China. Pedosphere 17:331–342
Su YH, Zhu G, Feng Q, Li Z, Zhang F (2009) Environmental isotopic and hydrochemical study of groundwater in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. Environ Geol 58:601–614
Sun JY, Liu Y, Cai QF, Park WK, Li BS, Shi JF, Yi L, Song HM, Li Q (2006) Climatic and hydrological changes of Ejin, Inner Mongolia, China, during the past 233 years record in tree-rings of Populus euphratica. Quat Sci 26:799–809 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Thoms MC, Beyer PJ, Rogers KH (2006) Variability, complexity and diversity; the geomorphology of river ecosystems in dryland regions. In: Kingsford R (ed) Ecology of desert rivers. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 47–75
Wang P, Zhang YC, Yu JJ, Fu GB, Ao F (2011a) Vegetation dynamics induced by groundwater fluctuations in the lower Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. J Plant Ecol 4:77–90
Wang YB, Feng Q, Si JH, Su YH, Chang ZQ, Xi HY (2011b) The changes of vegetation cover in Ejina Oasis based on water resources redistribution in Heihe River. Environ Earth Sci 64:1965–1973
Wang P, Yu JJ, Zhang YC, Liu CM (2013) Groundwater recharge and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. J Hydrol 476:72–86
Ward J, Tockner K, Arscott D, Claret C (2002) Riverine landscape diversity. Freshw Biol 47:517–539
Wigley TML, Briffa KR, Jones PD (1984) On the average value of correlated time series, with applications in dendroclimatology and hydrometeorology. J Clim Appl Meteorol 23:201–213
Woodhouse CA (2001) A tree-ring reconstruction of streamflow for the Colorado Front Range. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37:561–569
Xi HY (2009) Study on the groundwater dynamics variation and numerical simulation in Ejina Basin. vol Ph. D. University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, pp 37–71
Xi HY, Feng Q, Si JH, Chang ZQ, Cao SK (2010) Impacts of river recharge on groundwater level and hydrochemistry in the lower reaches of Heihe River Watershed, northwestern China. Hydrogeol J 18:791–801
Xi HY, Feng Q, Si JH, Chang ZQ, Su YH (2013) Response of NDVI to groundwater level change in the lower reaches of the Heihe River, China. J Desert Res 33:574–582 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Xiao SC, Xiao HL, Lan YC, Yang YG (2011) Water issues and the integrated water resources management in Heihe River Basin in recent 50 years. J Glaciol Geocryol 31:529–535 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Xiao SC, Xiao HL, Peng XM, Tian QY (2014) Daily and seasonal stem radial activity of Populus euphratica and its association with hydroclimatic factors in the lower reaches of China’s Heihe River Basin. Environ Earth Sci 72:609–621
Yang B, Qin C, Wang J, He M, Melvin TM, Osborn TJ, Briffa KR (2014) A 3,500-year tree-ring record of annual precipitation on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:2903–2908
Yin L, Zhao LJ, Ruan YF, Xiao HL, Cheng GD, Zhou MX, Wang F, Li CZ (2012) Study of the replenishment sources of typical ecosystems water and dominant plant water in the lower reaches of the Heihe, China. J Glaciol Geocryol 34:1478–1486 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Zhang QB, Cheng GD, Yao TD, Kang XC, Huang JG (2003) A 2,326-year tree-ring record of climate variability on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geophys Res Lett 30:1739–1742
Zhang QB, Li ZS, Liu PX, Xiao SC (2012) On the vulnerability of oasis forest to changing environmental conditions: perspectives from tree rings. Landsc Ecol 27:343–353
Zhao WZ, Chang XL, He ZB (2004) Responses of distribution pattern of desert riparian forests to hydrologic process in Ejina oasis. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 47:21–31
Zhao LJ, Xiao HL, Cheng GD, Song YX, Zhao L, Li CZ, Yang Q (2008) A preliminary study of water sources of riparian plants in the lower reaches of the Heihe Basin. Acta Geoscientica Sinica 29:709–718 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Zhong HP, Liu H, Wang Y, Tuo Y, Geng LH, Yan ZJ (2002) Relationship between Ejina oasis and water resources in the lower Heihe River basin. Adv Water Sci 13:223–228 (in Chinese, with English abstract)
Zhou HH, Chen YN, Li WH, Chen YP (2010) Photosynthesis of Populus euphratica in relation to groundwater depths and high temperature in arid environment, northwest China. Photosynthetica 48:257–268
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91125026, No. 41471082) and the STS Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KFJ-EW-STS-00502). We thank Haoxu Li, Junjun Yang, Jun Du, and Heng Wei for their help during the field work and data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by E. Liang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, X., Xiao, S., Cheng, G. et al. Human activity impacts on the stem radial growth of Populus euphratica riparian forests in China’s Ejina Oasis, using tree-ring analysis. Trees 31, 379–392 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-015-1287-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-015-1287-z