Abstract
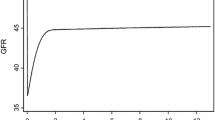
Following treatment, survivors of unilateral Wilms tumor (WT) develop structural and functional changes in the remnant kidney. A disproportional increase in functional over structural changes results in hyperfiltration, a condition that may lead to renal damage. We studied adaptation of renal function after uninephrectomy in ten WT patients and a child with renal cell carcinoma. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (measured by inulin and creatinine clearances), renal plasma flow (RPF) by para-aminohippurate (PAH) clearances and segmental tubular Na+ transport were studied before and following a protein load (renal functional reserve). Nine patients showed a well-adapted kidney function with a GFR of 82.27 (±5.6), an RPF of 429.71 (±65.6) ml/min/1.73 m2 and a filtration fracton (FF) of 20%. Absolute proximal Na+ reabsorption was 65.2 (±9.6) ml/min/1.73 m2, distal tubular delivery was 18.2 (±3.9) ml/min/1.73 m2 and absolute distal Na+ reabsorption was 2146 (±435) µM/min. A peculiar finding was the high baseline creatinine clearances (176.17 ml/min/1.73 m2) related to increased baseline tubular creatinine secretion. Over 120 min following the protein load, GFR increased by 20%, RPF by 6% and FF remained unchanged. Absolute proximal reabsorption increased by 20% and distal reabsorption by 22%. While most changes in renal function induced by a protein load are similar in healthy individuals and uninephrectomized patients, a more predominant contribution to Na+ reabsorption by the proximal tubule was noted. Postload fractional proximal reabsorption remained at 77% while in healthy persons a decrease from 77% to 62% was reported. Two patients showed dysfunctional changes following nephrectomy characterized by an increased GFR (130 ml/min/1.73 m2), increased filtration fraction (29%) and inability to increase glomerular and tubular functions following a protein load (loss of functional reserve). The significance of these abnormalities is not known and requires long-term follow-up to evaluate whether hyperfiltration will lead to renal damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 August 2000 / Revised: 21 February 2001 / Accepted: 22 February 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donckerwolcke, R., Coppes, M. Adaptation of renal function after unilateral nephrectomy in children with renal tumors. Pediatr Nephrol 16, 568–574 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670100615
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670100615