Abstract.
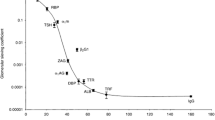
Renal lesions have repeatedly been described in Wilson’s disease (WD). We investigated the excretion of total protein, albumin, low (LMW) and high molecular weight (HMW) proteins, N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG), and calcium, as well as creatinine clearance, in 24-h urine samples of 41 patients with WD aged 6 – 37 (mean 17) years who had been treated for a period of 0 – 15 (mean 4.5) years with D-penicillamine (900 mg/day). The amount of all protein excreted was significantly increased compared with controls, 39% of patients presenting with total proteinuria more than two standard deviations from the mean of controls. The changes in protein excretion depended on the duration of treatment. LMW proteinuria was elevated almost exclusively in the first 2 years after the start of treatment, indicating early tubular damage. This is supported by an initially high excretion of β2-microglobulin, NAG, and calcium. Increased excretion of HMW proteins, including albumin, persisted over longer periods, which suggests glomerular injury in some patients, possibly related to the use of D-penicillamine. Creatinine clearance remained roughly within normal limits. We propose that renal function should regularly be checked in patients with WD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received October 26, 1995; received in revised form August 27, 1996; accepted September 20, 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sözeri, E., Feist, D., Ruder, H. et al. Proteinuria and other renal functions in Wilson’s disease. Pediatr Nephrol 11, 307–311 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050282
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050282