Abstract
Background
Acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) is associated with poor short-term and long-term outcomes. Greater awareness of long-term AKI-associated outcomes is needed to optimally plan follow-up and management after ICU discharge. We used propensity score methods to study associations between pediatric AKI and major adverse kidney outcomes, including mortality.
Methods
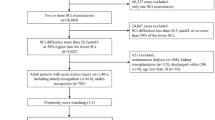
We included all children 6 months–18 years admitted to PICU at Seattle Children’s Hospital from 7/1/2009 to 12/31/2018. Our primary outcome measure was Major Adverse Kidney Events at 30 days (MAKE30): creatinine > 200% of baseline, eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, dialysis dependence, or mortality. Propensity scores for AKI development in PICU were generated using demographic, medical history, admission, and PICU hospitalization variables. Patients with AKI were matched to control patients without AKI. Logistic regression was used to test association between AKI status and MAKE30.
Results
In the unmatched cohort (n = 878), patients with AKI had lower platelet count (160 vs. 222) and higher PRISM III score (11 vs. 3.5). After propensity score matching, those with AKI vs. no AKI had similar PRISM III scores (9 vs. 10) and platelet count (163 vs. 159). AKI was significantly associated with MAKE30 after propensity score matching (OR: 2.97; 95% CI 1.82–4.84).
Conclusions
Propensity score matching significantly reduced imbalance in baseline characteristics between those with and without AKI. After matching, AKI remained significantly associated with MAKE30. Patients who developed AKI were more likely to have abnormal kidney function at 30 and 90 days after ICU admission and may be at high risk for developing CKD in the future.
Graphical abstract
A higher resolution version of the Graphical abstract is available as Supplementary information




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Upon request, may be subject to IRB approval by the Seattle Children’s Research Institute.
Code availability
Upon request.
References
Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R (2017) Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in children worldwide, including developing countries. Pediatr Nephrol 32:1301–1314
Sutherland SM, Byrnes JJ, Kothari M, Longhurst CA, Dutta S, Garcia P, Goldstein SL (2015) AKI in hospitalized children: comparing the pRIFLE, AKIN, and KDIGO definitions. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:554–561
Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, Goldstein SL (2017) Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N Engl J Med 376:11–20
Sanchez-Pinto LN, Goldstein SL, Schneider JB, Khemani RG (2015) Association between progression and improvement of acute kidney injury and mortality in critically ill children*. Pediatr Crit Care Med 16:703–710
Palevsky PM, Molitoris BA, Okusa MD, Levin A, Waikar SS, Wald R, Chertow GM, Murray PT, Parikh CR, Shaw AD, Go AS, Faubel SG, Kellum JA, Chinchilli VM, Liu KD, Cheung AK, Weisbord SD, Chawla LS, Kaufman JS, Devarajan P, Toto RM, Hsu CY, Greene T, Mehta RL, Stokes JB, Thompson AM, Thompson BT, Westenfelder CS, Tumlin JA, Warnock DG, Shah SV, Xie Y, Duggan EG, Kimmel PL, Star RA (2012) Design of clinical trials in acute kidney injury: report from an NIDDK workshop on trial methodology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:844–850
Billings FT 4th, Shaw AD (2014) Clinical trial endpoints in acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract 127:89–93
Weiss SL, Balamuth F, Thurm CW, Downes KJ, Fitzgerald JC, Laskin BL (2019) Major adverse kidney events in pediatric sepsis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 14:664–672
McCoy IE, Chertow GM (2020) AKI—a relevant safety end point? Am J Kidney Dis 75:508–512
McMurry TL, Hu Y, Blackstone EH, Kozower BD (2015) Propensity scores: methods, considerations, and applications in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 150:14–19
Menon S, Goldstein SL, Mottes T, Fei L, Kaddourah A, Terrell T, Arnold P, Bennett MR, Basu RK (2016) Urinary biomarker incorporation into the renal angina index early in intensive care unit admission optimizes acute kidney injury prediction in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 31:586–594
Khwaja A (2012) KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clinical Pract 120:c179–c184
Austin PC, Laupacis A (2011) A tutorial on methods to estimating clinically and policy-meaningful measures of treatment effects in prospective observational studies: a review. Int J Biostat 7:0000102202155746791285
Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG, Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ, Kent AL (2015) Neonatal acute kidney injury. Pediatrics 136:e463-473
Sutherland SM, Kwiatkowski DM (2017) Acute kidney injury in children. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 24:380–387
Austin PC (2009) Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations. Biom J 51:171–184
Austin PC (2011) Optimal caliper widths for propensity-score matching when estimating differences in means and differences in proportions in observational studies. Pharm Stat 10:150–161
Hsu C-y, Chinchilli VM, Coca S, Devarajan P, Ghahramani N, Go AS, Hsu RK, Ikizler TA, Kaufman J, Liu KD, Parikh CR, Reeves WB, Wurfel M, Zappitelli M, Kimmel PL, Siew ED, ASSESS-AKI Investigators (2020) Post-Acute kidney injury proteinuria and subsequent kidney disease progression: the Assessment, Serial Evaluation, and Subsequent Sequelae in Acute Kidney Injury (ASSESS-AKI) Study. JAMA Intern Med 180:402–410
Selewski DT, Hyatt DM, Bennett KM, Charlton JR (2018) Is acute kidney injury a harbinger for chronic kidney disease? Curr Opin Pediatr 30:236–240
Goldstein SL, Devarajan P (2008) Progression from acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease: a pediatric perspective. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 15:278–283
Jetton JG, Boohaker LJ, Sethi SK, Wazir S, Rohatgi S, Soranno DE, Chishti AS, Woroniecki R, Mammen C, Swanson JR, Sridhar S, Wong CS, Kupferman JC, Griffin RL, Askenazi DJ, Selewski DT, Sarkar S, Kent A, Fletcher J, Abitbol CL, DeFreitas M, Duara S, Charlton JR, Guillet R, D’Angio C, Mian A, Rademacher E, Mhanna MJ, Raina R, Kumar D, Ambalavanan N, Arikan AA, Rhee CJ, Goldstein SL, Nathan AT, Bhutada A, Rastogi S, Bonachea E, Ingraham S, Mahan J, Nada A, Brophy PD, Colaizy TT, Klein JM, Cole FS, Davis TK, Dower J, Milner L, Smith A, Fuloria M, Reidy K, Kaskel FJ, Gien J, Gist KM, Hanna MH, Hingorani S, Starr M, Joseph C, DuPont T, Ohls R, Staples A, Khokhar S, Perazzo S, Ray PE, Revenis M, Synnes A, Wintermark P (2017) Incidence and outcomes of neonatal acute kidney injury (AWAKEN): a multicentre, multinational, observational cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health 1:184–194
Austin PC (2007) The performance of different propensity score methods for estimating marginal odds ratios. Stat Med 26:3078–3094
Greenland S (1987) Interpretation and choice of effect measures in epidemiologic analyses. Am J Epidemiol 125:761–768
Sandokji I, Yamamoto Y, Biswas A, Arora T, Ugwuowo U, Simonov M, Saran I, Martin M, Testani JM, Mansour S, Moledina DG, Greenberg JH, Wilson FP (2020) A time-updated, parsimonious model to predict AKI in hospitalized children. J Am Soc Nephrol 31:1348
Ugwuowo U, Yamamoto Y, Arora T, Saran I, Partridge C, Biswas A, Martin M, Moledina DG, Greenberg JH, Simonov M, Mansour SG, Vela R, Testani JM, Rao V, Rentfro K, Obeid W, Parikh CR, Wilson FP (2020) Real-time prediction of acute kidney injury in hospitalized adults: implementation and proof of concept. Am J Kidney Dis 76:806-814.e1
Funding
This work was funded by an internal grant through the Center for Clinical and Translational Research at the Seattle Children’s Research Institute. Additionally, this work was supported by Seattle Children’s Hospital/University of Washington NIH T32DK997662.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AJK and SM developed concept, with additional guidance from JMS. BS procured and managed study data. PQ, AJK, and SM participated in statistical analysis. AJK, PQ, BS, JMS, and SM were involved in constructing, drafting, and editing of manuscript. All authors approved submission of final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kula, A.J., Qu, P., Strub, B. et al. Major adverse kidney events after acute kidney injury in the pediatric intensive care unit: a propensity score–matched cohort study. Pediatr Nephrol 37, 2099–2107 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-05348-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-021-05348-6