Abstract
Background
Continuous kidney replacement therapy (CKRT) is a common modality for treatment of severe acute kidney injury (AKI) in children. Adult technologies routinely utilized to provide this therapy have a large extracorporeal volume. The Prismaflex™ HF20 filter set has a relatively low extracorporeal blood volume of 60 mL, which provides technological benefit for smaller children compared with current filter sets available in the USA.
Methods
We conducted a multicenter, open-label single group study to evaluate whether the Prismaflex™ HF20 filter set delivers efficacious and safe CKRT to support patients with AKI, fluid overload, or both in pediatric patients weighing ≥ 8 to 20 kg.
Results
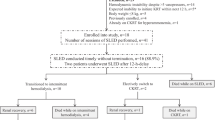
Twenty-three patients were enrolled between April 24, 2016 and April 8, 2018. The mean reduction in blood urea nitrogen from baseline to 24 h was 58.12 ± 20.08% (95% CI, − 68.45 and − 47.79 (p = 0.0008)). Median cumulative normalized effluent rate at 24 h was 60.8 mL/kg/h (25.9, 83.7). None of the patients participating in the study suffered a serious adverse event; thus, no obvious safety concerns were noted.
Conclusions
We suggest that the Prismaflex HF20™ filter set used in conjunction with the Prismaflex™ System Software Version 7.10 or 7.20 is a suitable alternative to larger filter sets for use in pediatric patients weighing less than 20 kg.

Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warady BA, Bunchman T (2000) Dialysis therapy for children with acute renal failure: survey results. Pediatr Nephrol 15:11–13
Sethi SK, Chakraborty R, Joshi H, Raina R (2020) Renal replacement therapy in pediatric acute kidney injury. Indian J Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-019-03150-9
Available from: www.baxter.com
Symons JM, Brophy PD, Gregory MJ, McAfee N, Somers MJG, Bunchman TE, Goldstein SL (2003) Continuous renal replacement therapy in children up to 10 kg. Am J Kidney Dis 41:984–989
Symons JM, Chua AN, Somers MJ, Baum MA, Bunchman TE, Benfield MR, Brophy PD, Blowey D, Fortenberry JD, Chand D, Flores FX, Hackbarth R, Alexander SR, Mahan J, McBryde KD, Goldstein SL (2007) Demographic characteristics of pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy: a report of the prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy registry. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:732–738
Brophy PD, Mottes TA, Kudelka TL, McBryde KD, Gardner JJ, Maxvold NJ, Bunchman TE (2001) AN-69 membrane reactions are pH-dependent and preventable. Am J Kidney Dis 38:173–178
Howie SR (2011) Blood sample volumes in child health research: review of safe limits. Bull World Health Organ 89:46–53
Basu RK, Kaddourah A, Terrell T, Mottes T, Arnold P, Jacobs J, Andringa J, Goldstein SL, Prospective Pediatric AKI Research Group (ppAKI) (2015) Assessment of worldwide acute kidney injury, renal angina and epidemiology in critically ill children (AWARE): study protocol for a prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol 16:24
Flores FX, Brophy PD, Symons JM, Fortenberry JD, Chua AN, Alexander SR, Mahan JD, Bunchman TE, Blowey D, Somers MJG, Baum M, Hackbarth R, Chand D, McBryde K, Benfield M, Goldstein SL (2008) Continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) after stem cell transplantation. A report from the prospective pediatric CRRT registry group. Pediatr Nephrol 23:625–630
Askenazi DJ, Goldstein SL, Koralkar R, Fortenberry J, Baum M, Hackbarth R, Blowey D, Bunchman TE, Brophy PD, Symons J, Chua A, Flores F, Somers MJ (2013) Continuous renal replacement therapy for children ≤10 kg: a report from the prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy registry. J Pediatr 162:587–92.e3
Sutherland SM, Goldstein SL, Alexander SR (2014) The prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy (ppCRRT) registry: a critical appraisal. Pediatr Nephrol 29:2069–2076
Goldstein SL, Somers MJ, Brophy PD, Bunchman TE, Baum M, Blowey D, Mahan JD, Flores FX, Fortenberry JD, Chua A, Alexander SR, Hackbarth R, Symons JM (2004) The prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy (ppCRRT) registry: design, development and data assessed. Int J Artif Organs 27:9–14
Sutherland SM, Byrnes JJ, Kothari M, Longhurst CA, Dutta S, Garcia P, Goldstein SL (2015) AKI in hospitalized children: comparing the pRIFLE, AKIN, and KDIGO definitions. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:554–561
Sutherland SM, Zappitelli M, Alexander SR, Chua AN, Brophy PD, Bunchman TE, Hackbarth R, Somers MJ, Baum M, Symons JM, Flores FX, Benfield M, Askenazi D, Chand D, Fortenberry JD, Mahan JD, McBryde K, Blowey D, Goldstein SL (2010) Fluid overload and mortality in children receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: the prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy registry. Am J Kidney Dis 55:316–325
Brown EG, Wood L, Wood S (1999) The medical dictionary for regulatory activities (MedDRA). Drug Saf 20:109–117
Rödl S, Marschitz I, Mache CJ, Koestenberger M, Madler G, Zobel G (2011) Continuous renal replacement therapy with Prismaflex HF20 disposable set in children from 4 to 15 kg. ASAIO J 57:451–455
Cavagnaro Santa María F, Roque Espinosa J, Guerra Hernández P (2018) Continuous venovenous hemofiltration in neonates with hyperammonemia. A case series. Rev Chil Pediatr 89:74–78
Liu ID, Ng KH, Lau PY, Yeo WS, Koh PL, Yap HK (2013) Use of HF20 membrane in critically ill unstable low-body-weight infants on inotropic support. Pediatr Nephrol 28:819–822
Santiago MJ, López-Herce J (2011) Prismaflex HF20 for continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill children. Artif Organs 35:1194
Liu KD, Himmelfarb J, Paganini E, Ikizler TA, Soroko SH, Mehta RL, Chertow GM (2006) Timing of initiation of dialysis in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:915–919
VA/NIH Acute Renal Failure Trial Network, Palevsky PM, Zhang JH, O'Connor TZ, Chertow GM, Crowley ST, Choudhury D, Finkel K, Kellum JA, Paganini E, Schein RM, Smith MW, Swanson KM, Thompson BT, Vijayan A, Watnick S, Star RA, Peduzzi P (2008) Intensity of renal support in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med 359:7–20
Miklaszewska M, Korohoda P, Zachwieja K, Kobylarz K, Stefanidis CJ, Sobczak A, Drożdż D (2017) Filter size not the anticoagulation method is the decisive factor in continuous renal replacement therapy circuit survival. Kidney Blood Press Res 42:327–337
de Galasso L, Picca S, Guzzo I (2020) Dialysis modalities for the management of pediatric acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol 35:753–765
Acknowledgments
Patrick D. Brophy, University of Iowa Stead Family Children’s Hospital, Iowa City, IA; Dawn Eding, Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital, Grand Rapids, MI; Jennifer Ehrlich, University of Iowa Stead Family Children’s Hospital, Iowa City, IA; Emily Gleason, Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital, Grand Rapids, MI; Diane Gollhofer, Children’s Medical Center, Dallas, TX; Megan Kelton, Seattle Children’s, Seattle, WA; Elisabeth Merkel, Stanford University Medical Center, Stanford, CA; Theresa Mottes, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital, Cincinnati, OH; Mary Lee Neuberger, University of Iowa Stead Family Children’s Hospital, Iowa City, IA; Jules Rathbun, Helen DeVos Children’s Hospital, Grand Rapids, MI; Jordan M. Symons, Seattle Children’s, Seattle, WA; Brynna Van Wyk, University of Iowa Stead Family Children’s Hospital, Iowa City, IA
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Stuart L. Goldstein: Baxter Healthcare provided funding for the current study. Dr. Goldstein receives other grant funding, consultancy fees and is on the Expert Speaker panel for Baxter Healthcare. None of these activities were related to the current study. Scott M. Sutherland: Expert Speaker panel for Baxter Healthcare. None of these activities were related to the current study. Jorge Echeverri: Global Medical Director, Acute Therapies for Baxter Healthcare Corporation.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PPTX 77 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munshi, R., Lee-Son, K., Hackbarth, R.M. et al. Clinical evaluation of the Prismaflex™ HF 20 set and Prismaflex™ system 7.10 for acute continuous kidney replacement therapy (CKRT) in children. Pediatr Nephrol 35, 2345–2352 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04664-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04664-7