Abstract
Background
Azithromycin (AZM) is a macrolide antibiotic with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Our aim was to compare the immunomodulatory effects of AZM combined with steroid therapy with that of steroid therapy alone in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS).
Methods
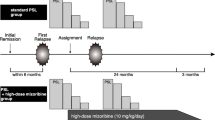
We enrolled 57 patients with SDNS in a multicenter randomized control trial. Patients were classified into two groups: group A (intervention group, N = 29) and group B (control group, N = 28). After achievement of remission with full-dose daily prednisone, patients in group A received AZM in conjunction with steroids which was tapered gradually, while patients in group B received steroids alone. Urine protein creatinine ratio (uPCR) and TNF-α were measured at different points of follow-up throughout the study period (5 months after achieving remission).
Results
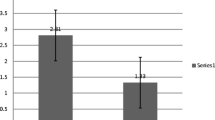
After achievement of remission by full-dose steroids, there were significant differences of TNF-α between the two groups after 1-, 3- and 5-month follow-up (p < 0.001, 0.003, and 0.001, respectively). Also, there was significant difference of TNF-α in both intervention and control groups after exclusion of the relapsed cases at 3- and 5-month follow-up (, p = 0.031 and p = 0.003, respectively). There was significant difference between both groups after 5-month follow-up as regards the number of relapsed patients (group A = 4, group B = 11, p = 0.015).
Conclusion
AZM was capable of reducing serum TNF-α which is one of the inflammatory cytokines implicated in the pathogenesis of NS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarshish P, Tobin JN, Bernstein J, Edelmann CM Jr (1997) Prognostic significance of the early course of minimal change nephrotic syndrome: report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:769–776
Sinha MD, MacLeod R, Rigby E, Clark AG (2006) Treatment of severe steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS) in children with tacrolimus. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1848–1854
Baudouin V, Alberti C, Lapeyraque AL, Bensman A, Andre JL, Broux F, Cailliez M, Decramer S, Niaudet P, Deschenes G, Jacqz-Aigrain E, Loirat C (2012) Mycophenolate mofetil for steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a phase II Bayesian trial. Pediatr Nephrol 27:389–396
Tauber SC, Nau R (2008) Immunomodulatory properties of antibiotics. Curr Mol Pharmacol 1:68–79
Zarogoulidis P, Papanas N, Kioumis I, Chatzaki E, Maltezos E, Zarogoulidis K (2012) Macrolides: from in vitro anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties to clinical practice in respiratory diseases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68:479–503
Raveh D, Shemesh O, Ashkenazi YJ, Winkler R, Barak V (2004) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocking agent as a treatment for nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 19:1281–1284
Weissbach A, Garty BZ, Lagovsky I, Krause I, Davidovits M (2017) Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in children with nephrotic syndrome: a pilot study. Isr Med Assoc J 19:30–33
Bustos C, Gonzalez E, Muley R, Alonso JL, Egido J (1994) Increase of tumour necrosis factor alpha synthesis and gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Eur J Clin Investig 24:799–805
Zhang B, Liu T, Wang W, Zhang X, Fan S, Liu Z, Liu Z, Wu X (2014) A prospective randomly controlled clinical trial on azithromycin therapy for induction treatment of children with nephrotic syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 173:509–515
Eddy AA, Symons JM (2003) Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet 362:629–639
Beck L, Bomback AS, Choi MJ, Holzman LB, Langford C, Mariani LH, Somers MJ, Trachtman H, Waldman M (2013) KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 62:403–441
Hara H, Hirano D (2018) Azithromycin suppressed relapses of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in a child. Clin Kidney J 11:54–55
Asgrimsson V, Gudjonsson T, Gudmundsson GH, Baldursson O (2006) Novel effects of azithromycin on tight junction proteins in human airway epithelia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:1805–1812
Parnham MJ, Erakovic Haber V, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Perletti G, Verleden GM, Vos R (2014) Azithromycin: mechanisms of action and their relevance for clinical applications. Pharmacol Ther 143:225–245
Tamaoki J, Kadota J, Takizawa H (2004) Clinical implications of the immunomodulatory effects of macrolides. Am J Med 117(Suppl 9A):5S–11S
Yamauchi K, Shibata Y, Kimura T, Abe S, Inoue S, Osaka D, Sato M, Igarashi A, Kubota I (2009) Azithromycin suppresses interleukin-12p40 expression in lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma stimulated macrophages. Int J Biol Sci 5:667–678
Cigana C, Assael BM, Melotti P (2007) Azithromycin selectively reduces tumor necrosis factor alpha levels in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:975–981
Khan AA, Slifer TR, Araujo FG, Remington JS (1999) Effect of clarithromycin and azithromycin on production of cytokines by human monocytes. Int J Antimicrob Agents 11:121–132
Ikegaya S, Inai K, Iwasaki H, Naiki H, Ueda T (2009) Azithromycin reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated THP-1 monocytic cells by modification of stress response and p38 MAPK pathway. J Chemother 21:396–402
Suranyi MG, Guasch A, Hall BM, Myers BD (1993) Elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the nephrotic syndrome in humans. Am J Kidney Dis 21:251–259
Laflam PF, Garin EH (2006) Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha and vascular permeability growth factor on albuminuria in rats. Pediatr Nephrol 21:177–181
Pai R, Ha H, Kirschenbaum MA, Kamanna VS (1996) Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on mesangial cell MCP-1 expression and monocyte migration: mechanisms mediated by signal transduction. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:914–923
McCarthy ET, Sharma R, Sharma M, Li JZ, Ge XL, Dileepan KN, Savin VJ (1998) TNF-alpha increases albumin permeability of isolated rat glomeruli through the generation of superoxide. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:433–438
Drewe E, McDermott EM, Powell RJ (2000) Treatment of the nephrotic syndrome with etanercept in patients with the tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome. N Engl J Med 343:1044–1045
Parnham MJ, Culic O, Erakovic V, Munic V, Popovic-Grle S, Barisic K, Bosnar M, Brajsa K, Cepelak I, Cuzic S, Glojnaric I, Manojlovic Z, Novak-Mircetic R, Oreskovic K, Pavicic-Beljak V, Radosevic S, Sucic M (2005) Modulation of neutrophil and inflammation markers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by short-term azithromycin treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 517:132–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
An informed consent was obtained from patients’ caregivers.
Human and animal rights
The research does not include animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawires, H., Abdelaziz, H., Ahmed, H.M. et al. Randomized controlled trial on immunomodulatory effects of azithromycin in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 34, 1591–1597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04251-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-019-04251-5