Abstract
Background
To evaluate whether there are differences in the phenotype of primary distal renal tubular acidosis (dRTA) patients according to the causal defective gene.
Methods
Twenty-seven non-oriental patients with genetically confirmed dRTA were grouped according to the identified underlying mutations in either ATP6V1B1 (n = 10), ATP6V0A4 (n = 12), or SLC4A1 (n = 5) gene. Demographic features, growth impairment, biochemical variables and presence of deafness, nephrocalcinosis, and urolithiasis at diagnosis were compared among the three groups.
Results
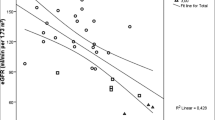
Patients with SLC4A1 mutations presented later than those with ATP6V1B1 or ATP6V0A4 defects (120 vs. 7 and 3 months, respectively). Hearing loss at diagnosis was present in the majority of patients with ATP6V1B1 mutations, in two patients with ATP6V0A4 mutations, and in none of cases harboring SLC4A1 mutations. Serum potassium concentration (X ± SD) was higher in SLC4A1 group (3.66 ± 0.44 mEq/L) than in ATP6V0A4 group (2.96 ± 0.63 mEq/L) (p = 0.046). There were no differences in the other clinical or biochemical variables analyzed in the three groups.
Conclusions
This study indicates that non-oriental patients with dRTA caused by mutations in the SLC4A1 gene present later and have normokalemia or milder hypokalemia. Hypoacusia at diagnosis is characteristically associated with ATP6V1B1 gene mutations although it may also be present in infants with ATP6V0A4 defects. Other phenotypical manifestations do not allow predicting the involved gene.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- dRTA:
-
distal renal tubular acidosis
- ATP6V0A4:
-
ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit A4
- ATP6V1B1:
-
ATPase H+ transporting V1 dubunit B1
- SLC4A1:
-
Solute carrier family 4 member 1
References
Rodríguez Soriano J (2002) Renal tubular acidosis: the clinical entity. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2160–2170
Gil-Peña H, Mejía N, Santos F (2014) Renal tubular acidosis. J Pediatr 164:691–698
Bockenhauer D, Bichet DG (2013) Inherited secondary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: concentrating on humans. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 304:F1037–F1042
Escobar L, Mejia N, Gil H, Santos F (2013) Distal renal tubular acidosis: a hereditary disease with an inadequate urinary H+ excretion. Nefrología 33:289–296
Nijenhuis T, Renkema KY, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ (2006) Acid-base status determines the renal expression of Ca2+ and Mg2+ transport proteins. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:617–626
Smith AN, Jouret F, Bord S, Borthwick KJ, Al-Lamki RS, Wagner CA, Ireland DC, Cormier-Daire V, Frattini A, Villa A, Kornak U, Devuyst O, Karet FE (2005) Vacuolar H+-ATPase d2 subunit: molecular characterization, developmental regulation, and localization to specialized proton pumps in kidney and bone. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1245–1256
Karet FE, Finberg KE, Nelson RD, Nayir A, Mocan H, Sanjad SA, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Santos F, Cremers CW, Di Pietro A, Hoffbrand BI, Winiarski J, Bakkaloglu A, Ozen S, Dusunsel R, Goodyer P, Hulton SA, Wu DK, Skvorak AB, Morton CC, Cunningham MJ, Jha V, Lifton RP (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding B1 subunit of H+-ATPase cause renal tubular acidosis with sensorineural deafness. Nat Genet 21:84–90
Gil H, Santos F, García E, Alvarez MV, Ordoñez FA, Málaga S, Coto E (2007) Distal RTA with nerve deafness: clinical spectrum and mutational analysis in five children. Pediatr Nephrol 22:825–828
Bruce LJ, Cope DL, Jones GK, Schofield AE, Burley M, Povey S, Unwin RJ, Wrong O, Tanner MJ (1997) Familial distal renal tubular acidosis is associated with mutations in the red cell anion exchanger (band 3, AE1) gene. J Clin Invest 100:1693–1707
Jarolim P, Shayakul C, Prabakaran D, Jiang L, Stuart-Tilley A, Rubin HL, Simova S, Zavadil J, Herrin JT, Brouillette J, Somers MJ, Seemanova E, Brugnara C, Guay-Woodford LM, Alper SL (1998) Autosomal dominant distal renal tubular acidosis is associated in three families with heterozygosity for the R589H mutation in the AE1 (band 3) Cl-/HCO3 exchanger. J Biol Chem 273:6380–6388
Karet FE, Gainza FJ, Györy AZ, Unwin RJ, Wrong O, Tanner MJ, Nayir A, Alpay H, Santos F, Hulton SA, Bakkaloglu A, Ozen S, Cunningham MJ, di Pietro A, Walker WG, Lifton RP (1998) Mutations in the chloride-bicarbonate exchanger gene AE1 cause autosomal dominant but not autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:6337–6342
Tanphaichitr VS, Sumboonnanonda A, Ideguchi H, Shayakul C, Brugnara C, Takao M, Veerakul G, Alper SL (1998) Novel AE1 mutations in recessive distal renal tubular acidosis. Loss-of-function is rescued by glycophorin A. J Clin Invest 102:2173–2179
Vasuvattakul S, Yenchitsomanus PT, Vachuanichsanong P, Thuwajit P, Kaitwatcharachai C, Laosombat V, Malasit P, Wilairat P, Nimmannit S (1999) Autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis associated with Southeast Asian ovalocytosis. Kidney Int 56:1674–1682
Bruce LJ, Wrong O, Toye AM, Young MT, Ogle G, Ismail Z, Sinha AK, McMaster P, Hwaihwanje I, Nash GB, Hart S, Lavu E, Palmer R, Othman A, Unwin RJ, Tanner MJ (2000) Band 3 mutations, renal tubular acidosis and South-East Asian ovalocytosis in Malaysia and Papua New Guinea: loss of up to 95% band 3 transport in red cells. Biochem J 350:41–51
Enerbäck S, Nilsson D, Edwards N, Heglind M, Alkanderi S, Ashton E, Deeb A, Kokash FEB, Bakhsh ARA, Van't Hoff W, Walsh SB, D'Arco F, Daryadel A, Bourgeois S, Wagner CA, Kleta R, Bockenhauer D, Sayer JA (2018) Acidosis and deafness in patients with recessive mutations in FOXI1. J Am SocNephrol 29:1041–1048
Mejía N, Santos F, Claverie-Martín F, Garcia-Nieto V, Ariceta G, Castaño L, Renal Tube Group (2013) RenalTube: a network tool for clinical and genetic diagnosis of primary tubulopathies. Eur J Pediatr 172:775–780
Garcia-Nieto V, Santos F (2006) Función renal basal. In: Garcia-Nieto V, Rodríguez-Iturbe B, Santos F (ed) Nefrologia Pediátrica, 2nd ed. Aula Médica, Madrid
Gomez J, Gil-Peña H, Santos F, Coto E, Arango A, Hernández O, Rodríguez J, Nadal I, Cantos V, Chocrón S, Vergara I, Madrid Á, Vazquez C, González LE, Blanco F (2016) Primary renal distal tubular acidosis: novel findings in patients studied by next-generation sequencing. Pediatr Res 79:496–501
Batlle D, Haque SK (2012) Genetic causes and mechanisms of distal renal tubular acidosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:3691–3704
Palazzo V, Provenzano A, Becherucci F, Sansavini G, Mazzinghi B, Orlandini V, Giunti L, Roperto RM, Pantaleo M, Artuso R, Andreucci E, Bargiacchi S, Traficante G, Stagi S, Murer L, Benetti E, Emma F, Giordano M, Rivieri F, Colussi G, Penco S, Manfredini E, Caruso MR, Garavelli L, Andrulli S, Vergine G, Miglietti N, Mancini E, Malaventura C, Percesepe A, Grosso E, Materassi M, Romagnani P, Giglio S (2017) The genetic and clinical spectrum of a large cohort of patients with distal renal tubular acidosis. Kidney Int 91:1243–1255
Besouw MT, Bienias M, Walsh P, Kleta R, Van't Hoff WG, Ashton E, Jenkins L, Bockenhauer D (2017) Clinical and molecular aspects of distal renal tubular acidosis in children. Pediatr Nephrol 32:987–996
Nagara M, Voskarides K, Nouira S, Ben Halim N, Kefi R, Aloulou H, Romdhane L, Ben Abdallah R, Ben Rhouma F, Aissa K, Boughamoura L, Kammoun T, Azzouz H, Abroug S, Ben Turkia H, Ayadi A, Mrad R, Chabchoub I, Hachicha M, Chemli J, Deltas C, Abdelhak S (2014) Molecular investigation of distal renal tubular acidosis in Tunisia, evidence for founder mutations. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 18:741–748
Sritippayawan S, Kirdpon S, Vasuvattakul S, Wasanawatana S, Susaengrat W, Waiyawuth W, Nimmannit S, Malasit P, Yenchitsomanus PT (2003) A de novo R589C mutation of anion exchanger 1 causing distal renal tubular acidosis. Pediatr Nephrol 18:644–648
Yenchitsomanus PT (2003) Human anion exchanger1 mutations and distal renal tubular acidosis. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 34:651–658
Rungroj N, Devonald MA, Cuthbert AW, Reimann F, Akkarapatumwong V, Yenchitsomanus PT, Bennett WM, Karet FE (2004) A novel missense mutation in AE1 causing autosomal dominant distal renal tubular acidosis retains normal transport function but is mistargeted in polarized epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 279:13833–13838
Shao L, Xu Y, Dong Q, Lang Y, Yue S, Miao Z (2010) A novel SLC4A1 variant in an autosomal dominant distal renal tubular acidosis family with a severe phenotype. Endocrine 37:473–478
Fry AC, Su Y, Yiu V, Cuthbert AW, Trachtman H, Karet Frankl FE (2012) Mutation conferring apical-targeting motif on AE1 exchanger causes autosomal dominant distal RTA. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1238–1249
Smith AN, Skaug J, Choate KA, Nayir A, Bakkaloglu A, Ozen S, Hulton SA, Sanjad SA, Al-Sabban EA, Lifton RP, Scherer SW, Karet FE (2000) Mutations in ATP6N1B, encoding a new kidney vacuolar proton pump 116-kD subunit, cause recessive distal renal tubular acidosis with preserved hearing. Nat Genet 26:71–75
Batlle D, Ghanekar H, Jain S, Mitra A (2001) Hereditary distal renal tubular acidosis: new understandings. Annu Rev Med 52:471–484
Batlle D, Moorthi KM, Schlueter W, Kurtzman N (2006) Distal renal tubular acidosis and the potassiumenigma. Semin Nephrol 26:471–478
Feldman M, Prikis M, Athanasiou Y, Elia A, Pierides A, Deltas CC (2006) Molecular investigation and long-term clinical progress in Greek Cypriot families with recessive distal renal tubular acidosis and sensorineural deafness due to mutations in the ATP6V1B1 gene. Clin Genet 69:135–144
Mohebbi N, Vargas-Poussou R, Hegemann SC, Schuknetch B, Kistler AD, Wüthrich RP, Wagner CA (2013) Homozygous and compound heterozygous mutations in the ATP6V1B1 gene in patients with renal tubular acidosis and sensorineural hearing loss. Clin Genet 83:274–278
Subasioglu Uzak A, Cakar N, Comak E, Yalcinkaya F, Tekin M (2013) ATP6V1B1 mutations in distal renal tubular acidosis and sensorineural hearing loss: clinical and genetic spectrum of five families. Ren Fail 35:1281–1284
Stover EH, Borthwick KJ, Bavalia C, Eady N, Fritz DM, Rungroj N, Giersch AB, Morton CC, Axon PR, Akil I, Al-Sabban EA, Baguley DM, Bianca S, Bakkaloglu A, Bircan Z, Chauveau D, Clermont MJ, Guala A, Hulton SA, Kroes H, Li Volti G, Mir S, Mocan H, Nayir A, Ozen S, Rodriguez Soriano J, Sanjad SA, Tasic V, Taylor CM, Topaloglu R, Smith AN, Karet FE (2002) Novel ATP6V1B1 and ATP6V0A4 mutations in autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis with new evidence for hearing loss. J Med Genet 39:796–803
Elhayek D, Perez de Nanclares G, Chouchane S, Hamami S, Mlika A, Troudi M, Leban N, Ben Romdane W, Gueddiche MN, El Amri F, Mrabet S, Ben Chibani J, Castaño L, Haj Khelil A, Ariceta G (2013) Molecular diagnosis of distal renal tubular acidosis in Tunisian patients: proposed algorithm for northern Africa populations for the ATP6V1B1, ATP6V0A4 and SCL4A1 genes. BMC Med Genet 14:119
Miura K, Sekine T, Takahashi K, Takita J, Harita Y, Ohki K, Park MJ, Hayashi Y, Tajima A, Ishihara M, Hisano M, Murai M, Igarashi T (2013) Mutational analyses of the ATP6V1B1 and ATP6V0A4 genes in patients with primary distal renal tubular acidosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:2123–2130
Boualla L, Jdioui W, Soulami K, Ratbi I, Sefiani A (2016) Clinical and molecular findings in three Moroccan families with distal renal tubular acidosis and deafness: Report of a novel mutation of ATP6V1B1 gene. Curr Res Transl Med 64:5–8
Escobar LI, Simian C, Treard C, Hayek D, Salvador C, Guerra N, Matos M, Medeiros M, Enciso S, Camargo MD, Vargas-Poussou R (2016) Mutations in ATP6V1B1 and ATP6V0A4 genes cause recessive distal renal tubular acidosis in Mexican families. Mol Genet Genomic Med 4:303–311
Zeinali F, Mohseni M, Fadaee M, Fattahi Z, Najmabadi H, Otukesh H, Kahrizi K (2014) Investigation of ATP6V1B1 and ATP6V0A4 genes causing hereditary hearing loss associated with distal renal tubular acidosis in Iranian families. J Laryngol Otol 128:1056–1059
Gao Y, Xu Y, Li Q, Lang Y, Dong Q, Shao L (2014) Mutation analysis and audiologic assessment in six Chinese children with primary distal renal tubular acidosis. Ren Fail 36:1226–1232
Vargas-Poussou R, Houillier P, Le Pottier N, Strompf L, Loirat C, Baudouin V, Macher MA, Déchaux M, Ulinski T, Nobili F, Eckart P, Novo R, Cailliez M, Salomon R, Nivet H, Cochat P, Tack I, Fargeot A, Bouissou F, Kesler GR, Lorotte S, Godefroid N, Layet V, Morin G, Jeunemaître X (2006) Genetic investigation of autosomal recessive distal renal tubular acidosis: evidence for early sensorineural hearing loss associated with mutations in the ATP6V0A4 gene. J Am SocNephrol 17:1437–1443
Lorente-Cánovas B, Ingham N, Norgett EE, Golder ZJ, Karet Frankl FE, Steel KP (2013) Mice deficient in H+-ATPase a4 subunit have severe hearing impairment associated with enlarged endolymphatic compartments within the inner ear. Dis Model Mech 6:434–442
Andreucci E, Bianchi B, Carboni I, Lavoratti G, Mortilla M, Fonda C, Bigozzi M, Genuardi M, Giglio S, Pela I (2009) Inner ear abnormalities in four patients with dRTA and SNHL: clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Pediatr Nephrol 24:2147–2153
Funding
This work was supported partially by GRUPIN 14-020 grant from “Principado de Asturias” Funds, ISCIII FIS PI14/00702, Plan Estatal I+D+I 2013-2016, FEDER Funds, and FundaciónNutrición y Crecimiento.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
There are no prior publications or submissions with any overlapping information.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alonso-Varela, M., Gil-Peña, H., Coto, E. et al. Distal renal tubular acidosis. Clinical manifestations in patients with different underlying gene mutations. Pediatr Nephrol 33, 1523–1529 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3965-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-3965-8