Abstract
Background
Non-calcium-containing phosphate binders, such as sevelamer preparations, are being increasingly used in patients on dialysis due to their lower association with hypercalcemia and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. While minor gastrointestinal side effects are quite common with the use of sevelamer, more serious gastrointestinal toxicities have only rarely been reported.
Case—diagnosis/treatment
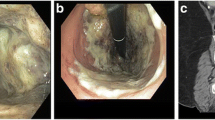
We report a pediatric patient on maintenance dialysis receiving sevelamer hydrochloride who developed severe abdominal pain and a high-grade stricture of the sigmoid colon. The patient underwent exploratory laparotomy, resulting in a partial colectomy and colostomy. Histopathologic examination showed colonic mucosal injury and characteristic “fish-scale”-like sevelamer hydrochloride crystals within the mucosa.
Conclusions
Whether the sevelamer crystals were causal, contributory or purely incidental remains to be clearly elucidated. However, our case raises sufficient concern to warrant additional investigation into whether there is a causal relationship between sevelamer use and intestinal mucosal injury.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Navaneethan SD, Sakhuja A, Arrigain S, Sharp J, Schold JD, Nally JV Jr (2014) Practice patterns of phosphate binder use and their associations with mortality in chronic kidney disease. Clin Nephrol 82:16–25
Chen N, Wu X, Ding X, Mei C, Fu P, Jiang G, Li X, Chen J, Liu B, La Y, Hou F, Ni Z, Fu J, Xing C, Yu X, Huang C, Zuo L, Wang L, Hunter J, Dillon M, Plone M, Neylan J (2014) Sevelamer carbonate lowers serum phosphorus effectively in haemodialysis patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-titration study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:152–160
Wang C, Liu X, Zhou Y, Li S, Chen Y, Wang Y, Lou T (2015) New conclusions regarding comparison of sevelamer and calcium-based phosphate binders in coronary-artery calcification for dialysis patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One 10:e0133938
Madan P, Bhayana S, Chandra P, Hughes JI (2008) Lower gastrointestinal bleeding: association with sevelamer use. World J Gastroenterol 14:2615–2616
Swanson BJ, Limketkai BN, Liu TC, Montgomery E, Nazari K, Park JY, Santangelo WC, Torbenson MS, Voltaggio L, Yearsley MM, Arnold CA (2013) Sevelamer crystals in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT): a new entity associated with mucosal injury. Am J Surg Pathol 37:1686–1693
Chang JF, Feng YF, Peng YS, Hsu SP, Pai MF, Chen HY, Wu HY, Yang JY (2014) Combined alkaline phosphatase and phosphorus levels as a predictor of mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 93:e106
Rastogi A (2013) Sevelamer revisited: pleiotropic effects on endothelial and cardiovascular risk factors in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 7:322–342
Perry CM, Plosker GL (2014) Sevelamer carbonate: a review in hyperphosphataemia in adults with chronic kidney disease. Drugs 74:771–792
Iwasaki Y, Takami H, Tani M, Yamaguchi Y, Goto H, Goto Y, Goto Y, Shigematsu T (2005) Efficacy of combined sevelamer and calcium carbonate therapy for hyperphosphatemia in Japanese hemodialysis patients. Ther Apher Dial 9:347–351
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Olson, K. & Butani, L. Sevelamer crystals in the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract in a teenager with end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 31, 339–341 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3269-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3269-1