Abstract
Background
We report the case of a patient with Shiga toxin (Stx)-associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) (STEC-HUS) with a concomitant heterozygous mutation of the gene coding for complement Factor H (CFH).
Case diagnosis/treatment
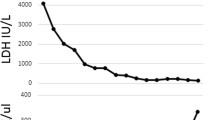
An 18-month-old patient presented with hemolytic anemia and thrombotic microangiopathy in the context of acute gastroenteritis. While the patient did not show kidney or other organ failure, he had persistent hemolysis and complement 3 activation (low C3), leading to the decision to commence immunotherapy with eculizumab (Soliris®) together with transient antibiotic coverage and meningococcal vaccination. Patient outcome was favorable. Diagnostic work-up identified Escherichia coli-associated Type 2 Shiga toxin. Complement analysis showed a heterozygous mutation of the CFH gene (c.2103 G>A, p. Trp701X) resulting in a quantitative CFH defect.
Conclusions
We report a case of STEC-HUS with a quantitative CFH defect caused by a mutation of the CFH gene. To the best of our knowledge, very few cases of STEC-HUS with complement gene mutation have been reported, but none to date with a CFH mutation. We therefore suggest that complement analyses be performed in patients diagnosed with STEC-HUS in association with low C3 levels, especially in patients presenting with severe or unexpected clinical symptoms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noris M, Remuzzi G (2005) Hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1035–1050
Noris M, Remuzzi G (2009) Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med 361:1676–1687
Waters AM, Licht C (2011) aHUS caused by complement dysregulation: new therapies on the horizon. Pediatr Nephrol 26:41–57
Loirat C, Noris M, Fremeaux-Bacchi V (2008) Complement and the atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1957–1972
Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Fakhouri F, Garnier A, Bienaime F, Dragon-Durey MA, Ngo S, Moulin B, Servais A, Provot F, Rostaing L, Burtey S, Niaudet P, Deschênes G, Lebranchu Y, Zuber J, Loirat C (2013) Genetics and outcome of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome: a nationwide French series comparing children and adults. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:554–562
Thurman JM, Marians R, Emlen W, Wood S, Smith C, Akana H, Holers VM, Lesser M, Lesser M, Kline M, Hoffman C, Christen E, Trachtman H (2009) Alternative pathway of complement in children with diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1920–1924
Ferraris JR, Ferraris V, Acquier AB, Sorroche PB, Saez MS, Ginaca A, Mendez CF (2015) Activation of the alternative pathway of complement during the acute phase of typical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 181:118–125
Orth D, Wurzner R (2010) Complement in typical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:620–624
Orth D, Khan AB, Naim A, Grif K, Brockmeyer J, Karch H, Joannidis M, Clark SJ, Day AJ, Fidanzi S, Stoiber H, Dierich MP, Zimmerhackl LB, Würzner R (2009) Shiga toxin activates complement and binds factor H: evidence for an active role of complement in hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Immunol 182:6394–6400
National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents (2004) The fourth report on the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 114[2 Suppl 4th Report]:555–576
Trachtman H (2013) HUS and TTP in children. Pediatr Clin N Am 60:1513–1526
Borgatta B, Kmet-Lunacek N, Rello J (2012) E. coli O104:H4 outbreak and haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. Med Intensiva 36:576–583
Venables JP, Strain L, Routledge D, Bourn D, Powell HM, Warwicker P, Diaz-Torres ML, Sampson A, Mead P, Webb M, Pirson Y, Jackson MS, Huguess A, Woods KM, Goodship JA, Goodship THJ (2006) Atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome associated with a hybrid complement gene. PLoS Med 3:e431
Malina M, Roumenina LT, Seeman T, Le Quintrec M, Dragon-Durey MA, Schaefer F, Fremeaux-Bacchi V (2012) Genetics of hemolytic uremic syndromes. Presse Med 41:e105–114
Roumenina LT, Loirat C, Dragon-Durey MA, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L, Sautes-Fridman C, Fremeaux-Bacchi V (2011) Alternative complement pathway assessment in patients with atypical HUS. J Immunol Methods 365:8–26
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Dragon-Durey MA, Macher MA, Niaudet P, Guest G, Boudailliez B, Bouissou F, Deschênes G, Gie S, Tsimaratos M, Fischbach M, Morin D, Nivet H, Alberti C, Loirat C (2007) Differential impact of complement mutations on clinical characteristics in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2392–2400
Dragon-Durey MA, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Loirat C, Blouin J, Niaudet P, Deschênes G, Coppo P, Herman Fridman W, Weiss L (2004) Heterozygous and homozygous Factor H deficiencies associated with hemolytic uremic syndrome or membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis : report and genetic analysis of 16 cases. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:787–795
Noris M, Caprioli J, Bresin E, Mossali C, Pianetti G, Gamba S, Daina E, Fenili C, Castelletti F, Sorosina A, Piras R, Donadelli R, Maranta R, Van der Meer I, Conway EM, Zipfel PF, Goodship TH, Remuzzi G (2010) Relative role of genetic complement abnormalities in sporadic and familial aHUS and their impact on clinical phenotype. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1844–1859
Legendre CM, Licht C, Muus P, Greenbaum LA, Babu S, Bedrosian C, Bingham CC, Cohen DJ, Delmas Y, Douglas K, Eitner F, Feldkamp T, Fougue D, Furman RR, Gaber O, Herthelius M, Houmant M, Karpman D, Lebranchu Y, Mariat C, Menne J, Moulin B, Nürnberger J, Ogawa M, Remuzzi G, Richard T, Sberro-Soussan R, Severino B, Sheerin NS, Trivelli A, Zimmerhackl LB, Goodship T, Loirat C (2013) Terminal complement inhibitor eculizumab in atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med 368:2169–2181
Lapeyraque AL, Malina M, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Boppel T, Kirschfink M, Oualha M, Proulx MJ, Le Deist F, Niaudet P, Schaefer F (2011) Eculizumab in severe Shiga-toxin-associated HUS. N Engl J Med 364:2561–2563
Braune SA, Wichmann D, von Heinz MC, Nierhaus A, Becker H, Meyer TN, Meyer GP, Müller-Schulz M, Fricke J, De Weerth A, Hoepker WW, Fiehler J, Magnus T, Gerloff C, Panzer U, Stahl RAK, Wegsheider K, Kluge S (2013) Clinical features of critically ill patients with Shiga toxin-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Crit Care Med 41:1702–1710
Morigi M, Galbusera M, Gastoldi S, Locatelli M, Buelli S, Pezzotta A, Pagani C, Noris M, Gobbi M, Stravalaci M, Rottoli D, Tedesco F, Remuzzi G, Zoja C (2011) Alternative pathway activation of complement by Shiga toxin promotes exuberant C3a formation that triggers microvascular thrombosis. J Immunol 187:172–180
Locatelli M, Buelli S, Pezzotta A, Corna D, Perico L, Tomasoni S, Rottoli D, Rizzo P, Conti D, Thurman JM, Remuzzi G, Zoja C, Morigi M (2014) Shiga toxin promotes podocyte injury in experimental hemolytic uremic syndrome via activation of the alternative pathway of complement. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:1786–1798
Ehrlenbach S, Rosales A, Posch W, Wilflingseder D, Hermann M, Brockmeyer J, Karch H, Satchell SC, Würzner R, Orth-Höller D (2013) Shiga toxin 2 reduces complement inhibitor CD59 expression on human renal tubular epithelial and glomerular endothelial cells. Infect Immun 81:2678–2685
Orth D, Ehrlenbach S, Brockmeyer J, Khan AB, Huber G, Karch H, Sarg B, Lindner H, Würzner R (2010) EspP, a serine protease of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli, impairs complement activation by cleaving complement factors C3/C3b and C5. Infect Immun 78:4294–4301
Arvidsson I, Stahl AL, Hedstrom MM, Kristoffersson AC, Rylander C, Westman JS, Storry JR, Olsson ML, Karpman D (2015) Shiga toxin-induced complement-mediated hemolysis and release of complement-coated red blood cell-derived microvesicles in hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Immunol 194:2309–2318
Stahl AL, Sartz L, Karpman D (2011) Complement activation on platelet-leukocyte complexes and microparticles in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 117:5503–5513
Poolpol K, Orth-Holler D, Speth C, Zipfel PF, Skerka C, de Cordoba SR, Brockmeyer J, Bielaszewska M, Würzner R (2014) Interaction of Shiga toxin 2 with complement regulators of the factor H protein family. Mol Immunol 58:77–84
Paixao-Cavalcante DBM, Cook HT, Pickering MC (2008) Shiga toxin-2 results in renal tubular injury but not thrombotic microangiopathy in heterozygous factor H-deficient mice. Clin Exp Immunol 155:339–347
Noris M, Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Orisio S, Caprioli J, Skerka C, Vasile B, Zipfel PF, Remuzzi G (1999) Hypocomplementemia discloses genetic predisposition to hemolytic uremic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: role of factor H abnormalities. Italian Registry of Familial and Recurrent Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome/Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:281–293
Alberti M, Valoti E, Piras R, Bresin E, Galbusera M, Tripodo C, Thaiss F, Remuzzi G, Noris M (2013) Two patients with history of STEC-HUS, posttransplant recurrence and complement gene mutations. Am J Transplant 13:2201–2206
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caillaud, C., Zaloszyc, A., Licht, C. et al. CFH gene mutation in a case of Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome (STEC-HUS). Pediatr Nephrol 31, 157–161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3207-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3207-2