Abstract
Background
Urine proteins may help in understanding physiology and diagnosing disease in premature infants. Determining how urine proteins vary by degree of prematurity, sex, and postnatal day is warranted.
Methods
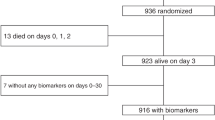
We performed a prospective cohort study to assess the independent correlation of 14 urine biomarkers (measured on postnatal days 1–4) with gestational age (GA), sex, and postnatal age in 81 premature infants (mean, 1017 g) without acute kidney injury using a random-effects mixed model.
Results
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) showed significant associations for sex, GA, and postnatal age. Cystatin C, osteopontin (OPN), and trefoil factor 3 (TFF3) were associated with postnatal age and GA, but not sex. Epithelial growth factor (EGF) and uromodulin were associated with GA only. Clusterin was associated with postnatal age and sex. Albumin was associated with sex only. Beta-2-microglbulin (B2M), osteoactivin, kidney injury molecule −1 (KIM-1), and alpha glutathione S-transferase (αGST) were associated with postnatal age only.
Conclusions
Postnatal age affects B2M, cystatin C, NGAL, OPN, clusterin, Kim-1, osteoactivin, TFF3, VEGF, αGST. GA affects cystatin C, EGF, NGAL, OPN, UMOD, TFF3, and VEGF. Sex affects albumin, NGAL, and clusterin. Interpretation of urine biomarkers will need to account for these associations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Hundley HE, Montesanti A, Parwar P, Sonjara S, Ambalavanan N (2012) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury in newborns. J Pediatr 161:270–275
Askenazi DJ, Montesanti A, Hunley H, Koralkar R, Pawar P, Shuaib F, Liwo A, Devarajan P, Ambalavanan N (2011) Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and mortality in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr 159:907–912
Shemin D, Dworkin LDZ (2011) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for early acute kidney injury. Crit Care Clin 27:379–389
Parikh CR, Garg AX (2009) Testing new biomarkers for acute kidney injury: association, prediction, and intervention. Am J Kidney Dis 54:987–989
Li Y, Fu C, Zhou X, Xiao Z, Zhu X, Jin M, Li X, Feng X (2012) Urine interleukin-18 and cystatin-C as biomarkers of acute kidney injury in critically ill neonates. Pediatr Nephrol 27:851–860
Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, Thadhani R, Bonventre JV (2002) Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int 62:237–244
Chuasuwan A, Kellum JA (2011) Acute kidney injury and its management. Contrib Nephrol 171:218–225
Goldstein SL (2011) Acute kidney injury in children: prevention, treatment and rehabilitation. Contrib Nephrol 174:163–172
Himmelfarb J, Joannidis M, Molitoris B, Schietz M, Okusa MD, Warnock D, Laghi F, Goldstein SL, Prielipp R, Parikh CR, Pannu N, Lobo SM, Shah S, D’Intini V, Kellum JA (2008) Evaluation and initial management of acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:962–967
Soni SS, Ronco C, Katz N, Cruz DN (2009) Early diagnosis of acute kidney injury: the promise of novel biomarkers. Blood Purif 28:165–174
Ostermann M, Philips BJ, Forni LG (2012) Clinical review: biomarkers of acute kidney injury: where are we now? Crit Care 16:233
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Levitan EB, Goldstein SL, Devarajan P, Khandrika S, Mehta RL, Ambalavanan N (2011) Baseline values of candidate urine Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) biomarkers vary by gestational age in premature infants. Pediatr Res 70:302–306
Huynh TK, Bateman DA, Parravicini E, Lorenz JM, Nemerofsky SL, Sise ME, Bowman TM, Polesana E, Barasch JM (2009) Reference values of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res 66:528–532
Bennett MR, Nehus E, Haffner C, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2015) Pediatric reference ranges for acute kidney injury biomarkers. Pediatr Nephrol 30:677–685
Coca SG, Yalavarthy R, Concato J, Parikh CR (2008) Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int 73:1008–1016
Dent CL, Ma Q, Dastrala S, Bennett M, Mitsnefes MM, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2007) Plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts acute kidney injury, morbidity and mortality after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective uncontrolled cohort study. Crit Care 11:R127
Devarajan P (2011) Biomarkers for the early detection of acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Pediatr 23:194–200
Sarafidis K, Tsepkentzi E, Diamanti E, Agakidou E, Taparkou A, Soubasi V, Papachristou F, Drossou V (2014) Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin to predict acute kidney injury in preterm neonates. A pilot study. Pediatr Nephrol 29:305–310
Genc G, Ozkaya O, Avci B, Aygun C, Kucukoduk S (2013) Kidney injury molecule-1 as a promising biomarker for acute kidney injury in premature babies. Am J Perinatol 30:245–252
Soto K, Coelho S, Rodrigues B, Martins H, Frade F, Lopes S, Cunha L, Papoila AL, Devarajan P (2010) Cystatin C as a marker of acute kidney injury in the emergency department. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1745–1754
Lavery AP, Meinzen-Derr JK, Anderson E, Ma Q, Bennett MR, Devarajan P, Schibler KR (2008) Urinary NGAL in premature infants. Pediatr Res 64:423–428
Statement of financial support
Research reported in this publication was supported by the Norman Siegel Career Development Award from the American Society of Nephrology and the UAB-UCSD O'Brien Center and Grant NIH P30-DK079337. Dr. Askenazi receives funding from the NIH (R01 DK13608-01) and the Pediatric and Infant Center for Acute Nephrology (PICAN) which is sponsored by Children’s of Alabama and the University of Alabama at Birmingham’s School of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics and Center for Clinical and Translational Science (CCTS) under award number UL1TR00165. Dr. Ambalavanan receives funding from NIH (grant # U01 HL122626; R01 HD067126; R01 HD066982; U10 HD34216). Dr. Griffin receives funding from UAB CCTS, and PICAN.
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Askenazi is speaker for The AKI Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saeidi, B., Koralkar, R., Griffin, R.L. et al. Impact of gestational age, sex, and postnatal age on urine biomarkers in premature neonates. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 2037–2044 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3129-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3129-z