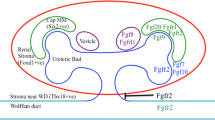
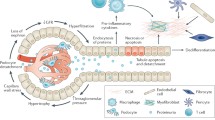
Abstract
Development and homeostasis of the highly specialized cell types and tissues that constitute the organs of the urinary system, the kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra, require the tightly regulated exchange of signals in and between these tissues. Eph/ephrin signaling is a bidirectional signaling pathway that has been functionally implicated in many developmental and homeostatic contexts, most prominently in the vascular and neural system. Expression and knockout analyses have now provided evidence that Eph/ephrin signaling is of crucial relevance for cell and tissue interactions in the urinary system as well. A clear requirement has emerged in the formation of the vesicoureteric junction, in urorectal septation and glomerulogenesis during embryonic development, in maintenance of medullary tubular cells and podocytes in homeostasis, and in podocyte and glomerular injury responses. Deregulation of Eph/ephrin signaling may also contribute to the formation and progression of tumors in the urinary system, most prominently bladder and renal cell carcinoma. While in the embryonic contexts Eph/ephrin signaling regulates adhesion of epithelial cells, in the adult setting, cell-shape changes and cell survival seem to be the primary cellular processes mediated by this signaling module. With progression of the genetic analyses of mice conditionally mutant for compound alleles of Eph receptor and ephrin ligand genes, additional essential functions are likely to arise in the urinary system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saxen L (1987) Organogenesis of the kidney. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mugford JW, Sipila P, McMahon JA, McMahon AP (2008) Osr1 expression demarcates a multi-potent population of intermediate mesoderm that undergoes progressive restriction to an Osr1-dependent nephron progenitor compartment within the mammalian kidney. Dev Biol 324:88–98
Little MH, McMahon AP (2012) Mammalian kidney development: principles, progress, and projections. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4:pii:a008300.
Bohnenpoll T, Kispert A (2014) Ureter growth and differentiation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 36:21–30
Vega QC, Worby CA, Lechner MS, Dixon JE, Dressler GR (1996) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor activates the receptor tyrosine kinase RET and promotes kidney morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:10657–10661
Carroll TJ, Park JS, Hayashi S, Majumdar A, McMahon AP (2005) Wnt9b plays a central role in the regulation of mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions underlying organogenesis of the mammalian urogenital system. Dev Cell 9:283–292
Yu J, Carroll TJ, McMahon AP (2002) Sonic hedgehog regulates proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal cells in the mouse metanephric kidney. Development 129:5301–5312
Shiroyanagi Y, Liu B, Cao M, Agras K, Li J, Hsieh MH, Willingham EJ, Baskin LS (2007) Urothelial sonic hedgehog signaling plays an important role in bladder smooth muscle formation. Differentiation 75:968–977
Gelfand MV, Hong S, Gu C (2009) Guidance from above: common cues direct distinct signaling outcomes in vascular and neural patterning. Trends Cell Biol 19:99–110
Salvucci O, Tosato G (2012) Essential roles of EphB receptors and EphrinB ligands in endothelial cell function and angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res 114:21–57
Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J, Takaku F (1987) A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science 238:1717–1720
Kullander K, Klein R (2002) Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:475–486
Bartley TD, Hunt RW, Welcher AA, Boyle WJ, Parker VP, Lindberg RA, Lu HS, Colombero AM, Elliott RL, Guthrie BA, Holst PL, Skrine JD, Toso RJ, Zhang M, Fernandez E, Trail G, Varnum B, Yarden Y, Hunter T, Fox GM (1994) B61 is a ligand for the ECK receptor protein-tyrosine kinase. Nature 368:558–560
Drescher U (2002) Eph family functions from an evolutionary perspective. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:397–402
Pasquale EB (2010) Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 10:165–180
Klein R (2012) Eph/ephrin signalling during development. Development 139:4105–4109
Himanen JP, Rajashankar KR, Lackmann M, Cowan CA, Henkemeyer M, Nikolov DB (2001) Crystal structure of an Eph receptor-ephrin complex. Nature 414:933–938
Chrencik JE, Brooun A, Kraus ML, Recht MI, Kolatkar AR, Han GW, Seifert JM, Widmer H, Auer M, Kuhn P (2006) Structural and biophysical characterization of the EphB4*ephrinB2 protein–protein interaction and receptor specificity. J Biol Chem 281:28185–28192
Lisabeth EM, Falivelli G, Pasquale EB (2013) Eph receptor signaling and ephrins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5:pii:009159.
Binns KL, Taylor PP, Sicheri F, Pawson T, Holland SJ (2000) Phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the kinase domain and juxtamembrane region regulates the biological and catalytic activities of Eph receptors. Mol Cell Biol 20:4791–4805
Palmer A, Zimmer M, Erdmann KS, Eulenburg V, Porthin A, Heumann R, Deutsch U, Klein R (2002) EphrinB phosphorylation and reverse signaling: regulation by Src kinases and PTP-BL phosphatase. Mol Cell 9:725–737
Cowan CA, Yokoyama N, Saxena A, Chumley MJ, Silvany RE, Baker LA, Srivastava D, Henkemeyer M (2004) Ephrin-B2 reverse signaling is required for axon pathfinding and cardiac valve formation but not early vascular development. Dev Biol 271:263–271
Bong YS, Lee HS, Carim-Todd L, Mood K, Nishanian TG, Tessarollo L, Daar IO (2007) ephrinB1 signals from the cell surface to the nucleus by recruitment of STAT3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:17305–17310
Segura I, Essmann CL, Weinges S, Acker-Palmer A (2007) Grb4 and GIT1 transduce ephrinB reverse signals modulating spine morphogenesis and synapse formation. Nat Neurosci 10:301–310
Redeker C, Schuster-Gossler K, Kremmer E, Gossler A (2013) Normal development in mice over-expressing the intracellular domain of DLL1 argues against reverse signaling by DLL1 in vivo. PLoS One 8, e79050
Egea J, Klein R (2007) Bidirectional Eph-ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol 17:230–238
Depaepe V, Suarez-Gonzalez N, Dufour A, Passante L, Gorski JA, Jones KR, Ledent C, Vanderhaeghen P (2005) Ephrin signalling controls brain size by regulating apoptosis of neural progenitors. Nature 435:1244–1250
Tourneux F (1888) Sur les premiers developpements du cloaques du tubercule genital et de l'anus chez l'embryon de mouton. J Anat 24
Hynes PJ, Fraher JP (2004) The development of the male genitourinary system. I. The origin of the urorectal septum and the formation of the perineum. Br J Plast Surg 57:27–36
Yamada G, Satoh Y, Baskin LS, Cunha GR (2003) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of development of the external genitalia. Differentiation 71:445–460
Larsen WJ (2001) Development of the gastrointestinal tract. Churchill Livingston, Inc., New York
Kluth D (2010) Embryology of anorectal malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg 19:201–208
Warne SA, Hiorns MP, Curry J, Mushtaq I (2011) Understanding cloacal anomalies. Arch Dis Child 96:1072–1076
Shih EM, Graham JM Jr (2014) Review of genetic and environmental factors leading to hypospadias. Eur J Med Genet 57:453–463
Snodgrass W, Bush N (2014) Recent advances in understanding/ management of hypospadias. F1000Prime Rep 6:101.
Pena A, Hong A (2000) Advances in the management of anorectal malformations. Am J Surg 180:370–376
Cho S, Moore SP, Fangman T (2001) One hundred three consecutive patients with anorectal malformations and their associated anomalies. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 155:587–591
Dravis C, Yokoyama N, Chumley MJ, Cowan CA, Silvany RE, Shay J, Baker LA, Henkemeyer M (2004) Bidirectional signaling mediated by ephrin-B2 and EphB2 controls urorectal development. Dev Biol 271:272–290
Price KL, Woolf AS, Long DA (2009) Unraveling the genetic landscape of bladder development in mice. J Urol 181:2366–2374
Stewart K, Bouchard M (2014) Coordinated cell behaviours in early urogenital system morphogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 36:13–20
Chia I, Grote D, Marcotte M, Batourina E, Mendelsohn C, Bouchard M (2011) Nephric duct insertion is a crucial step in urinary tract maturation that is regulated by a Gata3-Raldh2-Ret molecular network in mice. Development 138:2089–2097
Batourina E, Tsai S, Lambert S, Sprenkle P, Viana R, Dutta S, Hensle T, Wang F, Niederreither K, McMahon AP, Carroll TJ, Mendelsohn CL (2005) Apoptosis induced by vitamin A signaling is crucial for connecting the ureters to the bladder. Nat Genet 37:1082–1089
Uetani N, Bertozzi K, Chagnon MJ, Hendriks W, Tremblay ML, Bouchard M (2009) Maturation of ureter-bladder connection in mice is controlled by LAR family receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases. J Clin Invest 119:924–935
Uetani N, Bouchard M (2009) Plumbing in the embryo: developmental defects of the urinary tracts. Clin Genet 75:307–317
Kerecuk L, Schreuder MF, Woolf AS (2008) Renal tract malformations: perspectives for nephrologists. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 4:312–325
NAPRTCS (2007) North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies. Available at https://web.emmes.com/study/ped/annlrept/annlrept2007.pdf
Weiss AC, Airik R, Bohnenpoll T, Greulich F, Foik A, Trowe MO, Rudat C, Costantini F, Adams RH, Kispert A (2014) Nephric duct insertion requires EphA4/EphA7 signaling from the pericloacal mesenchyme. Development 141:3420–3430
Sallstrom J, Peuckert C, Gao X, Larsson E, Nilsson A, Jensen BL, Onozato ML, Persson AE, Kullander K, Carlstrom M (2013) Impaired EphA4 signaling leads to congenital hydronephrosis, renal injury and hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305:F71–F79
Basson MA, Akbulut S, Watson-Johnson J, Simon R, Carroll TJ, Shakya R, Gross I, Martin GR, Lufkin T, McMahon AP, Wilson PD, Costantini FD, Mason IJ, Licht JD (2005) Sprouty1 is a critical regulator of GDNF/RET-mediated kidney induction. Dev Cell 8:229–239
Jenkins D, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Thomasson L, Malcolm S, Warne SA, Feather SA, Flanagan SE, Ellard S, Bingham C, Santos L, Henkemeyer M, Zinn A, Baker LA, Wilcox DT, Woolf AS (2007) Mutational analyses of UPIIIA, SHH, EFNB2 and HNF1beta in persistent cloaca and associated kidney malformations. J Pediatr Urol 3:2–9
Dworschak GC, Draaken M, Marcelis C, de Blaauw I, Pfundt R, van Rooij IA, Bartels E, Hilger A, Jenetzky E, Schmiedeke E, Grasshoff-Derr S, Schmidt D, Marzheuser S, Hosie S, Weih S, Holland-Cunz S, Palta M, Leonhardt J, Schafer M, Kujath C, Rissmann A, Nothen MM, Zwink N, Ludwig M, Reutter H (2013) De novo 13q deletions in two patients with mild anorectal malformations as part of VATER/VACTERL and VATER/VACTERL-like association and analysis of EFNB2 in patients with anorectal malformations. Am J Med Genet A 161A:3035–3041
Hicks PJ, Staten JL, Palmer ND, Langefeld CD, Ziegler JT, Keene KL, Sale MM, Bowden DW, Freedman BI (2008) Association analysis of the ephrin-B2 gene in African-Americans with end-stage renal disease. Am J Nephrol 28:914–920
Abrahamson DR (2009) Development of kidney glomerular endothelial cells and their role in basement membrane assembly. Organogenesis 5:275–287
Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ (1998) Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell 93:741–753
Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C, Diella F, Gale NW, Deutsch U, Risau W, Klein R (1999) Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev 13:295–306
Gerety SS, Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ (1999) Symmetrical mutant phenotypes of the receptor EphB4 and its specific transmembrane ligand ephrin-B2 in cardiovascular development. Mol Cell 4:403–414
Gerety SS, Anderson DJ (2002) Cardiovascular ephrinB2 function is essential for embryonic angiogenesis. Development 129:1397–1410
Sawamiphak S, Ritter M, Acker-Palmer A (2010) Preparation of retinal explant cultures to study ex vivo tip endothelial cell responses. Nat Protoc 5:1659–1665
Sawamiphak S, Seidel S, Essmann CL, Wilkinson GA, Pitulescu ME, Acker T, Acker-Palmer A (2010) Ephrin-B2 regulates VEGFR2 function in developmental and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 465:487–491
Bentley K, Mariggi G, Gerhardt H, Bates PA (2009) Tipping the balance: robustness of tip cell selection, migration and fusion in angiogenesis. PLoS Comput Biol 5, e1000549
Kim I, Ryu YS, Kwak HJ, Ahn SY, Oh JL, Yancopoulos GD, Gale NW, Koh GY (2002) EphB ligand, ephrinB2, suppresses the VEGF- and angiopoietin 1-induced Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in venous endothelial cells. FASEB J 16:1126–1128
Fuller T, Korff T, Kilian A, Dandekar G, Augustin HG (2003) Forward EphB4 signaling in endothelial cells controls cellular repulsion and segregation from ephrinB2-positive cells. J Cell Sci 116:2461–2470
Steinle JJ, Meininger CJ, Forough R, Wu G, Wu MH, Granger HJ (2002) Eph B4 receptor signaling mediates endothelial cell migration and proliferation via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 277:43830–43835
Armulik A, Abramsson A, Betsholtz C (2005) Endothelial/pericyte interactions. Circ Res 97:512–523
Foo SS, Turner CJ, Adams S, Compagni A, Aubyn D, Kogata N, Lindblom P, Shani M, Zicha D, Adams RH (2006) Ephrin-B2 controls cell motility and adhesion during blood-vessel-wall assembly. Cell 124:161–173
Daniel TO, Stein E, Cerretti DP, St John PL, Robert B, Abrahamson DR (1996) ELK and LERK-2 in developing kidney and microvascular endothelial assembly. Kidney Int Suppl 57:S73–81
Takahashi T, Takahashi K, Gerety S, Wang H, Anderson DJ, Daniel TO (2001) Temporally compartmentalized expression of ephrin-B2 during renal glomerular development. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2673–2682
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F, Hau P, Langmann T, Dietmaier W, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2004) Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem 50:490–499
Andres AC, Reid HH, Zurcher G, Blaschke RJ, Albrecht D, Ziemiecki A (1994) Expression of two novel eph-related receptor protein tyrosine kinases in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis. Oncogene 9:1461–1467
Bennett BD, Wang Z, Kuang WJ, Wang A, Groopman JE, Goeddel DV, Scadden DT (1994) Cloning and characterization of HTK, a novel transmembrane tyrosine kinase of the EPH subfamily. J Biol Chem 269:14211–14218
Bohme B, Holtrich U, Wolf G, Luzius H, Grzeschik KH, Strebhardt K, Rubsamen-Waigmann H (1993) PCR-mediated detection of a new human receptor-tyrosine-kinase, HEK 2. Oncogene 8:2857–2862
Ciossek T, Lerch MM, Ullrich A (1995) Cloning, characterization, and differential expression of MDK2 and MDK5, two novel receptor tyrosine kinases of the eck/eph family. Oncogene 11:2085–2095
Gale NW, Baluk P, Pan L, Kwan M, Holash J, DeChiara TM, McDonald DM, Yancopoulos GD (2001) Ephrin-B2 selectively marks arterial vessels and neovascularization sites in the adult, with expression in both endothelial and smooth-muscle cells. Dev Biol 230:151–160
Ikegaki N, Tang XX, Liu XG, Biegel JA, Allen C, Yoshioka A, Sulman EP, Brodeur GM, Pleasure DE (1995) Molecular characterization and chromosomal localization of DRT (EPHT3): a developmentally regulated human protein-tyrosine kinase gene of the EPH family. Hum Mol Genet 4:2033–2045
Kiyokawa E, Takai S, Tanaka M, Iwase T, Suzuki M, Xiang YY, Naito Y, Yamada K, Sugimura H, Kino I (1994) Overexpression of ERK, an EPH family receptor protein tyrosine kinase, in various human tumors. Cancer Res 54:3645–3650
Sajjadi FG, Pasquale EB (1993) Five novel avian Eph-related tyrosine kinases are differentially expressed. Oncogene 8:1807–1813
Baldwin C, Chen ZW, Bedirian A, Yokota N, Nasr SH, Rabb H, Lemay S (2006) Upregulation of EphA2 during in vivo and in vitro renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of Src kinases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F960–971
Xu H, Tian W, Lindsley JN, Oyama TT, Capasso JM, Rivard CJ, Cohen HT, Bagnasco SM, Anderson S, Cohen DM (2005) EphA2: expression in the renal medulla and regulation by hypertonicity and urea stress in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F855–866
Wnuk M, Hlushchuk R, Janot M, Tuffin G, Martiny-Baron G, Holzer P, Imbach-Weese P, Djonov V, Huynh-Do U (2012) Podocyte EphB4 signaling helps recovery from glomerular injury. Kidney Int 81:1212–1225
Hashimoto T, Karasawa T, Saito A, Miyauchi N, Han GD, Hayasaka K, Shimizu F, Kawachi H (2007) Ephrin-B1 localizes at the slit diaphragm of the glomerular podocyte. Kidney Int 72:954–964
Ogawa K, Wada H, Okada N, Harada I, Nakajima T, Pasquale EB, Tsuyama S (2006) EphB2 and ephrin-B1 expressed in the adult kidney regulate the cytoarchitecture of medullary tubule cells through Rho family GTPases. J Cell Sci 119:559–570
Kida Y, Ieronimakis N, Schrimpf C, Reyes M, Duffield JS (2013) EphrinB2 reverse signaling protects against capillary rarefaction and fibrosis after kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:559–572
Grahammer F, Schell C, Huber TB (2013) The podocyte slit diaphragm–from a thin grey line to a complex signalling hub. Nat Rev Nephrol 9:587–598
Wakayama Y, Miura K, Sabe H, Mochizuki N (2011) EphrinA1-EphA2 signal induces compaction and polarization of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells by inactivating Ezrin through negative regulation of RhoA. J Biol Chem 286:44243–44253
Park JE, Son AI, Zhou R (2013) Roles of EphA2 in development and disease. Genes (Basel) 4:334–357
Miao H, Li DQ, Mukherjee A, Guo H, Petty A, Cutter J, Basilion JP, Sedor J, Wu J, Danielpour D, Sloan AE, Cohen ML, Wang B (2009) EphA2 mediates ligand-dependent inhibition and ligand-independent promotion of cell migration and invasion via a reciprocal regulatory loop with Akt. Cancer Cell 16:9–20
Yuan WJ, Ge J, Chen ZK, Wu SB, Shen H, Yang P, Hu B, Zhang GW, Chen ZH (2009) Over-expression of EphA2 and EphrinA-1 in human gastric adenocarcinoma and its prognostic value for postoperative patients. Dig Dis Sci 54:2410–2417
Wang J, Ma J, Dong Y, Shen Z, Ma H, Wang X, Shi S, Wu J, Lu G, Peng L, Zhoud X (2013) High expression of EphA1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with lymph node metastasis and advanced disease. APMIS 121:30–37
Herrem CJ, Tatsumi T, Olson KS, Shirai K, Finke JH, Bukowski RM, Zhou M, Richmond AL, Derweesh I, Kinch MS, Storkus WJ (2005) Expression of EphA2 is prognostic of disease-free interval and overall survival in surgically treated patients with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 11:226–231
Toma MI, Erdmann K, Diezel M, Meinhardt M, Zastrow S, Fuessel S, Wirth MP, Baretton GB (2014) Lack of ephrin receptor A1 is a favorable independent prognostic factor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One 9, e102262
Xu J, Zhang J, Cui L, Zhang H, Zhang S, Bai Y (2014) High EphA2 protein expression in renal cell carcinoma is associated with a poor disease outcome. Oncol Lett 8:687–692
Chen X, Wang X, Ruan A, Han W, Zhao Y, Lu X, Xiao P, Shi H, Wang R, Chen L, Chen S, Du Q, Yang H, Zhang X (2014) miR-141 is a key regulator of renal cell carcinoma proliferation and metastasis by controlling EphA2 expression. Clin Cancer Res 20:2617–2630
Xi HQ, Wu XS, Wei B, Chen L (2012) Eph receptors and ephrins as targets for cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med 16:2894–2909
Abraham S, Knapp DW, Cheng L, Snyder PW, Mittal SK, Bangari DS, Kinch M, Wu L, Dhariwal J, Mohammed SI (2006) Expression of EphA2 and Ephrin A-1 in carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Clin Cancer Res 12:353–360
Li X, Choi WW, Yan R, Yu H, Krasnoperov V, Kumar SR, Schuckman A, Klumpp DJ, Pan CX, Quinn D, Gill IS, Gill PS, Liu R (2014) The differential expression of EphB2 and EphB4 receptor kinases in normal bladder and in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. PLoS One 9, e105326
Ozgur E, Heidenreich A, Dagtekin O, Engelmann U, Bloch W (2011) Distribution of EphB4 and EphrinB2 in normal and malignant urogenital tissue. Urol Oncol 29:78–84
Xia G, Kumar SR, Stein JP, Singh J, Krasnoperov V, Zhu S, Hassanieh L, Smith DL, Buscarini M, Broek D, Quinn DI, Weaver FA, Gill PS (2006) EphB4 receptor tyrosine kinase is expressed in bladder cancer and provides signals for cell survival. Oncogene 25:769–780
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the German Research Council [DFGKI728/7-1; DFGKI728/9-1] to A.K.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiss, AC., Kispert, A. Eph/ephrin signaling in the kidney and lower urinary tract. Pediatr Nephrol 31, 359–371 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3112-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3112-8