Abstract
Background
The national average for achieving the KDOQI-recommended hemoglobin (Hgb) target level of 11–12 g/dL is low with the current anemia management protocol of measuring Hgb levels every 2–4 weeks to guide intervention. The objective of this study was to correlate initial Hgb readings from the CRIT-LINE monitor with actual serum Hgb levels in pediatric patients on hemodialysis (HD).
Methods
Data were collected from pediatric HD patients who had Hgb tests ordered for routine and/or clinical reasons. Hgb concentrations were read with the CRIT–LINE after 0.5 or 1 L of blood had been processed by HD in patients with a body weight of ≤20 or >20 kg, respectively. Ultrafiltration was kept at a minimum until the CRIT-LINE Hgb was read.
Results
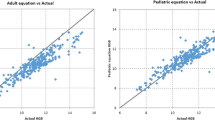
In total, 217 Hgb readings from 23 HD patients were analyzed. Results showed a statistically significant correlation between CRIT-LINE readings and laboratory Hgb measurements (r = 0.94, p < 0.0001) using Pearson correlation coefficients for well-distributed data. The mean Hgb levels measured by CRIT-LINE and the laboratory were 11.12 ± 1.63 and 11.31 ± 1.69 g/dL, respectively.
Conclusions
The CRIT-LINE monitor is an accurate instrument for monitoring Hgb levels in HD patients. Further studies will be needed to evaluate whether using CRIT-LINE Hgb levels to guide anemia management will improve the percentage of children with Hgb levels within target.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eschbach JW, Adamson JW (1985) Anemia of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Kidney Int 28:1–5
Kazmi WH, Kausz AT, Khan S, Abichandani R, Ruthazer R, Obrador GT, Pereira BJ (2001) Anemia: an early complication of chronic renal insufficiency. Am J Kidney Dis 38:803–812
Obrador GT, Arora P, Kausz AT, Pereira BJ (1998) Pre-end-stage renal disease care in the United States: a state of disrepair. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:S44–S54
Collins AJ, Ma JZ, Ebben J (2000) Impact of hematocrit on morbidity and mortality. Semin Nephrol 20:345–349
Collins AJ (2002) Influence of target hemoglobin in dialysis patients on morbidity and mortality. Kidney Int Suppl:44–48
Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Harnett JD, Kent GM, Murray DC, Barre PE (1996) The impact of anemia on cardiomyopathy, morbidity, and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 28:53–61
Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Kent GM, Harnett JD, Murray DC, Barre PE (1998) Long-term evolution of cardiomyopathy in dialysis patients. Kidney Int 54:1720–1725
Chavers BM, Li S, Collins AJ, Herzog CA (2002) Cardiovascular disease in pediatric chronic dialysis patients. Kidney Int 62:648–653
Groothoff JW, Gruppen MP, Offringa M, Hutten J, Lilien MR, Van De Kar NJ, Wolff ED, Davin JC, Heymans HS (2002) Mortality and causes of death of end-stage renal disease in children: a Dutch cohort study. Kidney Int 61:621–629
Parekh RS, Carroll CE, Wolfe RA, Port FK (2002) Cardiovascular mortality in children and young adults with end-stage kidney disease. J Pediatr 141:191–197
Warady BA, Ho M (2003) Morbidity and mortality in children with anemia at initiation of dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 18:1055–1062
Beusterien KM, Nissenson AR, Port FK, Kelly M, Steinwald B, Ware JE Jr (1996) The effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on functional health and well-being in chronic dialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:763–773
Evans RW, Rader B, Manninen DL (1990) The quality of life of hemodialysis recipients treated with recombinant human erythropoietin. Coop Multicenter EPO Clin Trial Group. JAMA 263:825–830
Marsh JT, Brown WS, Wolcott D, Carr CR, Harper R, Schweitzer SV, Nissenson AR (1991) rHuEPO treatment improves brain and cognitive function of anemic dialysis patients. Kidney Int 39:155–163
Moreno F, Aracil FJ, Perez R, Valderrabano F (1996) Controlled study on the improvement of quality of life in elderly hemodialysis patients after correcting end-stage renal disease-related anemia with erythropoietin. Am J Kidney Dis 27:548–556
Painter P, Moore G, Carlson L, Paul S, Myll J, Phillips W, Haskell W (2002) Effects of exercise training plus normalization of hematocrit on exercise capacity and health-related quality of life. Am J Kidney Dis 39:257–265
Pattaragarn A, Warady BA, Sabath RJ (2004) Exercise capacity in pediatric patients with end-stage renal disease. Perit Dial Int 24:274–280
Eschbach JW, Abdulhadi MH, Browne JK, Delano BG, Downing MR, Egrie JC, Evans RW, Friedman EA, Graber SE, Haley NR, Korbet S, Krantz SB, Lundin AP, Nissenson AR, Ogden DA, Paganini EP, Rader B, Rutsky EA, Stivelman J, Stone WJ, Teschan P, Van Stone JC, Van Wyck DB, Zuckerman K, Adamson JW (1989) Recombinant human erythropoietin in anemic patients with end-stage renal disease. Results of a phase III multicenter clinical trial. Ann Intern Med 111:992–1000
Eschbach JW, Egrie JC, Downing MR, Browne JK, Adamson JW (1987) Correction of the anemia of end-stage renal disease with recombinant human erythropoietin. Results of a combined phase I and II clinical trial. N Engl J Med 316:73–78
McGonigle RJ, Boineau FG, Beckman B, Ohene-Frempong K, Lewy JE, Shadduck RK, Fisher JW (1985) Erythropoietin and inhibitors of in vitro erythropoiesis in the development of anemia in children with renal disease. J Lab Clin Med 105:449–458
Singh AK, Szczech L, Tang KL, Barnhart H, Sapp S, Wolfson M, Reddan D (2006) Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 355:2085–2098
KDOQI; National Kidney Foundation (2006) KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis 47 [Suppl 3]:S11-145
Neu AM, Ho PL, McDonald RA, Warady BA (2002) Chronic dialysis in children and adolescents. The 2001 NAPRTCS annual report. Pediatr Nephrol 17:656–663
Chavers BM, Herzog CA (2004) The spectrum of cardiovascular disease in children with predialysis chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 11:319–327
Ebben JP, Gilbertson DT, Foley RN, Collins AJ (2006) Hemoglobin level variability: associations with comorbidity, intercurrent events, and hospitalizations. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1205–1210
Fishbane S, Berns JS (2005) Hemoglobin cycling in hemodialysis patients treated with recombinant human erythropoietin. Kidney Int 68:1337–1343
Ho WR, Germain MJ, Garb J, Picard S, Mackie MK, Bartlett C, Will EJ (2010) Use of 12×/month haemoglobin monitoring with a computer algorithm reduces haemoglobin variability. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:2710–2714
Gaweda AE, Nathanson BH, Jacobs AA, Aronoff GR, Germain MJ, Brier ME (2010) Determining optimum hemoglobin sampling for anemia management from every-treatment data. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1939–1945
Leypoldt JK, Cheung AK, Steuer RR, Harris DH, Conis JM (1995) Determination of circulating blood volume by continuously monitoring hematocrit during hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 6:214–219
Rodriguez HJ, Domenici R, Diroll A, Goykhman I (2005) Assessment of dry weight by monitoring changes in blood volume during hemodialysis using Crit-Line. Kidney Int 68:854–861
Stavinoha A, Modem V, Quigley R (2013) Using noninvasive hemoglobin measurements to estimate measured hemoglobin in a pediatric hemodialysis unit. Hemodial Int 17[Suppl 1]:S7–S10
Groothoff JW, Lilien MR, van de Kar NC, Wolff ED, Davin JC (2005) Cardiovascular disease as a late complication of end-stage renal disease in children. Pediatr Nephrol 20:374–379
Atkinson MA, Furth SL (2011) Anemia in children with chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 7:635–641
Jabs K, Harmon WE (1996) Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in children on dialysis. Adv Ren Replace Ther 3:24–36
Morris KP, Sharp J, Watson S, Coulthard MG (1993) Non-cardiac benefits of human recombinant erythropoietin in end stage renal failure and anaemia. Arch Dis Child 69:580–586
Silberberg J, Racine N, Barre P, Sniderman AD (1990) Regression of left ventricular hypertrophy in dialysis patients following correction of anemia with recombinant human erythropoietin. Can J Cardiol 6:1–4
Benz RL, Pressman MR, Hovick ET, Peterson DD (1999) A preliminary study of the effects of correction of anemia with recombinant human erythropoietin therapy on sleep, sleep disorders, and daytime sleepiness in hemodialysis patients (The SLEEPO study). Am J Kidney Dis 34:1089–1095
Chavers BM, Roberts TL, Herzog CA, Collins AJ, St Peter WL (2004) Prevalence of anemia in erythropoietin-treated pediatric as compared to adult chronic dialysis patients. Kidney Int 65:266–273
Acknowledgments
We thank all dialysis nurses, staff and patients in the participating hemodialysis unit for their support and assistance in conducting this study, especially Kathleen Cagan, RN, Vivien Paquia, RN, Dennis Zorills, RN, Germaine Wilkom, RN, Jeanne Shaffer, RN and Paul Bayona, RN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garro, R., Sutherland, S., Bayes, L. et al. CRIT-LINE: a noninvasive tool to monitor hemoglobin levels in pediatric hemodialysis patients. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 991–998 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2986-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2986-1