Abstract
Background
Children and adolescents with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are chronically exposed to high levels of inflammation, placing them at an increased risk of secondary health complications. Regular exercise may represent an effective therapy to reduce inflammation. The aims of this pilot study were to determine the effects of acute exercise on inflammation and immune cell counts in CKD.
Methods
Nine children and adolescents (4 males) with CKD stages III–V performed a graded exercise test to determine peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak). Following a 10-min break, participants cycled for 20 min at 50 % of VO2peak. Blood samples were collected before and after the exercise period for the determination of complete blood counts, natural killer cells (NKbright, NKdim) and circulating progenitor cell (CPC) counts, as well as interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) concentrations.
Results
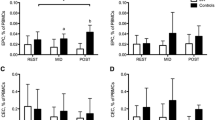
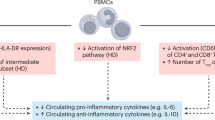
Complete blood counts and NKdim cell and CPC counts were unchanged with exercise. Following exercise, NKbright cell counts increased (7.4 ± 4.3 vs. 12.2 ± 8.3 × 106 cells/L; p = 0.02), while trends were observed for an increase in IL-6 (2.1 ± 2.2 vs. 2.7 ± 2.6 pg/mL; p = 0.08), decrease in TNF-α (4.5 ± 1.2 vs. 4.2 ± 1.0 pg/mL; p = 0.08) and an increase in the IL-6:TNF-α ratio (0.6 ± 0.7 vs. 0.8 ± 0.8; p = 0.07).
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that acute exercise may create an anti-inflammatory environment in children and adolescents with CKD stages III–V.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beddhu S, Baird BC, Zitterkoph J, Neilson J, Greene T (2009) Physical activity and mortality in chronic kidney disease (NHANES III). Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1901–1906
Heiwe S, Jacobson SH (2011) Exercise training for adults with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 5: CD003236
Ploeger HE, Takken T, de Greef MH, Timmons BW (2009) The effects of acute and chronic exercise on inflammatory markers in children and adults with a chronic inflammatory disease: a systematic review. Exerc Immunol Rev 15:6–41
Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Ng AV, Mulligan K, Carey S, Schoenfeld PY, Kent-Braun JA (2000) Physical activity levels in patients on hemodialysis and healthy sedentary controls. Kidney Int 57:2564–2570
O’Hare AM, Tawney K, Bacchetti P, Johansen KL (2003) Decreased survival among sedentary patients undergoing dialysis: results from the dialysis morbidity and mortality study wave 2. Am J Kidney Dis 41:447–454
Bohm CJ, Ho J, Duhamel TA (2010) Regular physical activity and exercise therapy in end-stage renal disease: how should we move forward? J Nephrol 23:235–243
Goldberg AP, Hagberg JM, Delmez JA, Haynes ME, Harter HR (1980) Metabolic effects of exercise training in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 18:754–761
Moore GE, Brinker KR, Stray-Gundersen J, Mitchell JH (1993) Determinants of VO2peak in patients with end-stage renal disease: on and off dialysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:18–23
Sietsema KE, Amato A, Adler SG, Brass EP (2004) Exercise capacity as a predictor of survival among ambulatory patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 65:719–724
Akber A, Portale AA, Johansen KL (2012) Pedometer-assessed physical activity in children and young adults with CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:720–726
Clapp EL, Bevington A, Smith AC (2012) Exercise for children with chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease. Pediatr Nephrol 27:165–172
Kuizon BD, Salusky IB (1999) Growth retardation in children with chronic renal failure. J Bone Miner Res 14:1680–1690
Gleeson M, Bishop NC, Stensel DJ, Lindley MR, Mastana SS, Nimmo MA (2011) The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:607–615
Timmons BW (2006) Exercise and the cytokine balance: a paediatric perspective. J Sports Sci 24:1–2
Timmons BW, Tarnopolsky MA, Snider DP, Bar-Or O (2006) Puberty effects on NK cell responses to exercise and carbohydrate intake in boys. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:864–874
Park JH, Miyashita M, Kwon YC, Park HT, Kim EH, Park JK, Park KB, Yoon SR, Chung JW, Nakamura Y, Park SK (2012) A 12-week after-school physical activity programme improves endothelial cell function in overweight and obese children: a randomised controlled study. BMC Pediatr 12:111
Duda DG, Cohen KS, Scadden DT, Jain RK (2007) A protocol for phenotypic detection and enumeration of circulating endothelial cells and circulating progenitor cells in human blood. Nat Protoc 2:805–810
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Girndt M, Sester U, Sester M, Kaul H, Kohler H (1999) Impaired cellular immune function in patients with end-stage renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:2807–2810
Pereira BJ, Shapiro L, King AJ, Falagas ME, Strom JA, Dinarello CA (1994) Plasma levels of IL-1 beta, TNF alpha and their specific inhibitors in undialyzed chronic renal failure, CAPD and hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 45:890–896
Nairn J, Hodge G, Henning P (2005) Changes in leukocyte subsets: clinical implications for children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 20:190–196
Silverstein DM (2009) Inflammation in chronic kidney disease: role in the progression of renal and cardiovascular disease. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1445–1452
Cirillo P, Sautin YY, Kanellis J, Kang DH, Gesualdo L, Nakagawa T, Johnson RJ (2009) Systemic inflammation, metabolic syndrome and progressive renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:1384–1387
Viana JL, Kosmadakis GC, Watson EL, Bevington A, Feehally J, Bishop NC, Smith AC (2014) Evidence for anti-inflammatory effects of exercise in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:2121–2130
Scheller J, Chalaris A, Schmidt-Arras D, Rose-John S (2011) The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:878–888
Cohen T, Nahari D, Cerem LW, Neufeld G, Levi BZ (1996) Interleukin 6 induces the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem 271:736–741
Baumann H, Gauldie J (1994) The acute phase response. Immunol Today 15:74–80
Greiwe JS, Cheng B, Rubin DC, Yarasheski KE, Semenkovich CF (2001) Resistance exercise decreases skeletal muscle tumor necrosis factor alpha in frail elderly humans. FASEB J 15:475–482
Lang CH, Frost RA, Nairn AC, MacLean DA, Vary TC (2002) TNF-a impairs heart and skeletal muscle protein synthesis by altering translation initiation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282:E336–E347
Starkie R, Ostrowski SR, Jauffred S, Febbraio M, Pedersen BK (2003) Exercise and IL-6 infusion inhibit endotoxin-induced TNF-alpha production in humans. FASEB J 17:884–886
Timmons BW, Raha S (2008) A pediatric perspective on inflammation and oxidative stress in response to exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33:411–419
Timmons BW (2005) Immune responses to exercise in children: a brief review. Pediatr Exerc Sci 18:290–299
Biron CA, Nguyen KB, Pien GC, Cousens LP, Salazar-Mather TP (1999) Natural killer cells in antiviral defense: function and regulation by innate cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 17:189–220
Brittenden J, Heys SD, Ross J, Eremin O (1996) Natural killer cells and cancer. Cancer 77:1226–1243
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA (2001) The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol 22:633–640
Timmons BW, Cieslak T (2008) Human natural killer cell subsets and acute exercise: a brief review. Exerc Immunol Rev 14:8–23
Timmons BW, Bar-Or O (2007) Evidence of sex-based differences in natural killer cell responses to exercise and carbohydrate intake in children. Eur J Appl Physiol 101:233–240
Lash GE, Schiessl B, Kirkley M, Innes BA, Cooper A, Searle RF, Robson SC, Bulmer JN (2006) Expression of angiogenic growth factors by uterine natural killer cells during early pregnancy. J Leukoc Biol 80:572–580
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Turner SC, Chen KS, Ghaheri BA, Ghayur T, Carson WE, Caligiuri MA (2001) Human natural killer cells: a unique innate immunoregulatory role for the CD56(bright) subset. Blood 97:3146–3151
Ojo AO (2006) Cardiovascular complications after renal transplantation and their prevention. Transplantation 82:603–611
Civin CI, Strauss LC, Brovall C, Fackler MJ, Schwartz JF, Shaper JH (1984) Antigenic analysis of hematopoiesis. III. A hematopoietic progenitor cell surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody raised against KG-1a cells. J Immunol 133:157–165
Mackie AR, Losordo DW (2011) CD34-positive stem cells: in the treatment of heart and vascular disease in human beings. Tex Heart Inst J 38:474–485
Brenner W, Aicher A, Eckey T, Massoudi S, Zuhayra M, Koehl U, Heeschen C, Kampen WU, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S, Henze E (2004) 111In-labeled CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells in a rat myocardial infarction model. J Nucl Med 45:512–518
Jakob P, Landmesser U (2013) Current status of cell-based therapy for heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep 10:165–176
Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ, Takuma S, Burkhoff D, Wang J, Homma S, Edwards NM, Itescu S (2001) Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human bone-marrow-derived angioblasts prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis, reduces remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med 7:430–436
Lenk K, Uhlemann M, Schuler G, Adams V (2011) Role of endothelial progenitor cells in the beneficial effects of physical exercise on atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. J Appl Physiol 111:321–328
Jie KE, Zaikova MA, Bergevoet MW, Westerweel PE, Rastmanesh M, Blankestijn PJ, Boer WH, Braam B, Verhaar MC (2010) Progenitor cells and vascular function are impaired in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:1875–1882
Jie KE, Lilien MR, Goossens MH, Westerweel PE, Klein MK, Verhaar MC (2010) Reduced endothelial progenitor cells in children with hemodialysis but not predialysis chronic kidney disease. Pediatrics 126:e990–e993
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the participants and their families for their time and effort, as well as Andrew Kuo for his technical assistance. BW Timmons is supported by a CIHR New Investigator Award. This research was made possible with funding from the Department of Pediatrics, McMaster University and Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lau, K.K., Obeid, J., Breithaupt, P. et al. Effects of acute exercise on markers of inflammation in pediatric chronic kidney disease: a pilot study. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 615–621 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2971-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2971-8