Abstract
Background
The clinical efficacy and safety of low-dose levothyroxine in the treatment of idiopathic nephritic syndrome accompanied by thyroid dysfunction have not been established.
Methods
One hundred and sixty-four patients were divided into three groups according to the levels of thyroid hormone and treatment. The thyroid status, efficacy and adverse reactions of thyroid treatment were observed in each group.
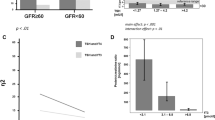
Results
Thyroid dysfunction was found in 73 patients. 40 cases were treated with steroids combined with levothyroxine. Proteinuria, cholesterol and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels were significantly higher in patients with thyroid dysfunction, whereas serum albumin and free and total T3 and T4 levels were lower than those of euthyroid patients. The time for proteinuria remission in patients receiving levothyroxine therapy was shorter and their serum albumin higher than for patients without levothyroxine treatment.
Conclusions
Thyroid hormonal changes are related to the degree of both proteinuria and serum albumin in patients with INS. Combined treatment with low-dose levothyroxine supplementation and steroids in children with INS and thyroid dysfunction is associated with reduced proteinuria and increased plasma albumin compared with patients treated with steroids only.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaptein EM, Feinstein EI, Massry SG (1982) Thyroid hormone metabolism in renal diseases. Contrib Nephrol 33:122–135
Feinstein EI, Kaptein EM, Nicoloff JT, Massry SG (1982) Thyroid function in patients with nephrotic syndrome and normal renal function. Am J Nephrol 2:70–76
Junglee NA, Scanlon MF, Rees DA (2006) Increasing thyroxine requirements in primary hypothyroidism: don’t forget the urinalysis! J Postgrad Med 52:201–203
Kaptein EM, Hoopes MT, Parise M, Massry SG (1991) rT3 metabolism in patients with nephrotic syndrome and normal GFR compared with normal subjects. Am J Physiol 260:E641–E650
Dagan A, Cleper R, Krause I, Blumenthal D, Davidovits M (2012) Hypothyroidism in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:2171–2175
Holmberg C, Antikainen M, Ronnholm K, Ala HM, Jalanko H (1995) Management of congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type. Pediatr Nephrol 9:87–93
Ito S, Kano K, Ando T, Ichimura T (1994) Thyroid function in children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 8:412–415
Ikeda K, Maruyama Y, Yokoyama M, Kato N, Yamanoto H, Kaguchi Y, Nakayama M, Shimada T, Tojo K, Kawamura T, Hosoya T (2001) Association of Graves’ disease with Evans’ syndrome in a patient with IgA nephropathy. Intern Med 40:1004–1010
Dizdar O, Kahraman S, Genctoy G, Ertoy D, Arici M, Altun B, Yasavul U, Turgan C (2004) Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:988–989
Nishimoto A, Tomiyoshi Y, Sakemi T, Kanegae F, Nakamura M, Ikeda Y, Shimazu K, Yonemitsu N (2000) Simultaneous occurrence of minimal change glomerular disease, sarcoidosis and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Am J Nephrol 20:425–428
Kagiyama S, Tsuruta H, Tominaga M, Morishita K, Doi Y, Onoyama K (1999) Minimal-change nephrotic syndrome and acute renal failure in a patient with aged onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and autoimmune thyroiditis. Am J Nephrol 19:369–372
Iglesias P, Diez JJ (2009) Thyroid dysfunction and kidney disease. Eur J Endocrinol 160:503–515
Katz AI, Emmanouel DS, Lindheimer MD (1975) Thyroid hormone and the kidney. Nephron 15:223–249
Mariani LH, Berns JS (2012) The renal manifestations of thyroid disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:22–26
Capasso G, De Tommaso G, Pica A, Anastasio P, Capasso J, Kinne R, De Santo NG (1999) Effects of thyroid hormones on heart and kidney functions. Miner Electrolyte Metab 25:56–64
Gumieniak O, Perlstein TS, Hopkins PN, Brown NJ, Murphey LJ, Jeunemaitre X, Hollenberg NK, Williams GH (2004) Thyroid function and blood pressure homeostasis in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3455–3461
Chadha V, Alon US (1999) Bilateral nephrectomy reverses hypothyroidism in congenital nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 13:209–211
Mattoo TK (1994) Hypothyroidism in infants with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 8:657–659
Gattineni J, Sas D, Dagan A, Dwarakanath V, Baum M (2008) Effect of thyroid hormone on the postnatal renal expression of NHE8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294:F198–F204
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Qy., Zhu, Qj., Liu, Yf. et al. Steroids combined with levothyroxine to treat children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a retrospective single-center study. Pediatr Nephrol 29, 1033–1038 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2727-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2727-x