Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the association between the occurrence of acute kidney injury (AKI) according to pediatric RIFLE (pRIFLE) criteria and adverse outcomes in children after heart surgery.
Methods
Children undergoing heart surgery in a tertiary hospital in Southern Brazil were followed during their stay in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) or until death. The exposure variable was occurrence of AKI according to pRIFLE criteria which place AKI in three categories: R (risk), I (injury), and F (failure). The outcomes studied were death, length of mechanical ventilation (MV), and length of PICU stay.
Results
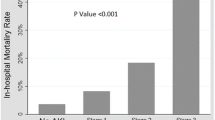
Eighty-five children were enrolled in the study. Of these, 47 (55.3 %) did not have AKI, while 22 (25.9 %), seven (8.2 %), and nine (10.6 %) were classified into pRIFLE categories R, I, and F, respectively. The incidence of death was 18.4 and 4.2 % in patients with and without AKI, respectively. Compared to children who did not develop AKI, the adjusted odds ratio for death was 1.05 [95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.09–11.11], 8.36 (95 % CI 1.32–52.63), and 7.85 (95 % CI 1.53–40.29) in the R, I, and F groups, respectively (p = 0.022). Duration of MV and of PICU stay were significantly higher in those children with AKI.
Conclusions
The occurrence of AKI according to pRIFLE criteria is associated to adverse outcomes in children after heart surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P (2004) Acute renal failure—definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the second international consensus conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) group. Crit Care 8:R204–R212
Hoste EA, Clermont G, Kersten A, Venkataraman R, Angus DC, De Bacquer D, Kellum JA (2006) RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury are associated with hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a cohort analysis. Crit Care 10:R73
Kuitunen A, Vento A, Suojaranta-Ylinen R, Pettila V (2006) Acute renal failure after cardiac surgery: evaluation of the RIFLE classification. Ann Thorac Surg 81:542–546
Uchino S, Bellomo R, Goldsmith D, Bates S, Ronco C (2006) An assessment of the RIFLE criteria for acute renal failure in hospitalized patients. Crit Care Med 34:1913–1917
Bagshaw SM, George C, Dinu I, Bellomo R (2008) A multi-centre evaluation of the RIFLE criteria for early acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1203–1210
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C (2007) Defining and classifying acute renal failure: from advocacy to consensus and validation of the RIFLE criteria. Intensive Care Med 33:409–413
Ostermann M, Chang RW (2007) Acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit according to RIFLE. Critical Care Med 35:1837–1843, quiz 1852
Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, Washburn KK, Jefferson LS, Goldstein SL (2007) Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 71:1028–1035
Chesney RW, Kaplan BS, Freedom RM, Haller JA, Drummond KN (1975) Acute renal failure: an important complication of cardiac surgery in infants. J Pediatr 87:381–388
Rigden SP, Barratt TM, Dillon MJ, De Leval M, Stark J (1982) Acute renal failure complicating cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Arch Dis Child 57:425–430
Baxter P, Rigby ML, Jones OD, Lincoln C, Shinebourne EA (1985) Acute renal failure following cardiopulmonary bypass in children: results of treatment. Int J Cardiol 7:235–243
tot Echten JE K-v H, Goedvolk CA, Doornaar MB, van der Vorst MM, Bosman-Vermeeren JM, Brand R, van der Heijden AJ, Schoof PH, Hazekamp MG (2001) Acute renal insufficiency and renal replacement therapy after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Pediatr Cardiol 22:321–326
Pedersen KR, Povlsen JV, Christensen S, Pedersen J, Hjortholm K, Larsen SH, Hjortdal VE (2007) Risk factors for acute renal failure requiring dialysis after surgery for congenital heart disease in children. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 51:1344–1349
Chien JC, Hwang BT, Weng ZC, Meng LC, Lee PC (2009) Peritoneal dialysis in infants and children after open heart surgery. Pediatr Neonatol 50:275–279
Li S, Krawczeski CD, Zappitelli M, Devarajan P, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Coca SG, Kim RW, Parikh CR (2011) Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med 39:1493–1499
Pedersen KR, Hjortdal VE, Christensen S, Pedersen J, Hjortholm K, Larsen SH, Povlsen JV (2008) Clinical outcome in children with acute renal failure treated with peritoneal dialysis after surgery for congenital heart disease. Kidney Int Suppl 108:S81–S86
Krawczeski CD, Vandevoorde RG, Kathman T, Bennett MR, Woo JG, Wang Y, Griffiths RE, Devarajan P (2010) Serum cystatin C is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1552–1557
Hassinger AB, Backer CL, Lane JC, Haymond S, Wang D, Wald EL (2012) Predictive power of serum cystatin C to detect acute kidney injury and pediatric-modified RIFLE class in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Pediatr Crit Care Med 13:435–440
Blinder JJ, Goldstein SL, Lee VV, Baycroft A, Fraser CD, Nelson D, Jefferies JL (2012) Congenital heart surgery in infants: effects of acute kidney injury on outcomes. J Thorac Carediovasc Surg 143:368–374
Zappitelli M, Bernier PL, Saczkowski RS, Tchervenkov CI, Gottesman R, Dancea A, Hyder A, Alkandari O (2009) A small post-operative rise in serum creatinine predicts acute kidney injury in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Kidney Int 76:885–892
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A (1976) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58:259–263
Boer DP, de Rijke YB, Hop WC, Cransberg K, Dorresteijn EM (2010) Reference values for serum creatinine in children younger than 1 year of age. Pediatr Nephrol 25:2107–2113
Jenkins KJ, Gauvreau K, Newburger JW, Spray TL, Moller JH, Iezzoni LI (2002) Consensus-based method for risk adjustment for surgery for congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 123:110–118
Slater A, Shann F, Pearson G (2003) PIM2: a revised version of the paediatric index of mortality. Intensive Care Med 29:278–285
Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A (2005) International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med 6:2–8
Proulx F, Fayon M, Farrell CA, Lacroix J, Gauthier M (1996) Epidemiology of sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in children. Chest 109:1033–1037
Morgan CJ, Zappitelli M, Robertson CM, Alton GY, Sauve RS, Joffe AR, Ross DB, Rebeyka IM (2013) Risk factors for and outcomes of acute kidney injury in neonates undergoing complex cardiac surgery. J Pediatr 162(120–127):e121
Freire KMS, Bresolin NL, Farah ACF, Carvalho FLC, Góes JEC (2010) Lesão renal aguda em crianças: incidência e fatores prognósticos em pacientes gravemente enfermos. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 22:166–174
Schneider J, Khemani R, Grushkin C, Bart R (2010) Serum creatinine as stratified in the RIFLE score for acute kidney injury is associated with mortality and length of stay for children in the pediatric intensive care unit. Critical Care Med 38:933–939
Ricci Z, Ronco C (2010) Pulmonary/renal interaction. Curr Opin Crit Care 16:13–18
Joao PR, Faria Junior F (2003) Immediate post-operative care following cardiac surgery. J Pediatr (Rio J) 79[Suppl 2]:S213–S222
Moura HV, Pomerantzeff PMA, Gomes WJ (2001) Síndrome da resposta inflamatória sistêmica na circulação extracorpórea: papel das interleucinas. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc 16:376–387
Picca S, Ricci Z, Picardo S (2008) Acute kidney injury in an infant after cardiopulmonary bypass. Semin Nephrol 28:470–476
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was performed at Hospital da Criança Santo Antônio, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos El Halal, M.G., Carvalho, P.R.A. Acute kidney injury according to pediatric RIFLE criteria is associated with negative outcomes after heart surgery in children. Pediatr Nephrol 28, 1307–1314 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2495-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-013-2495-7