Abstract
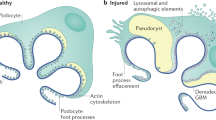
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is an important cause of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome in adults and children. It is responsible for 5–20% of all cases of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in the United States. The pathogenesis of FSGS has not been fully elucidated; however, data from molecular studies of familial cases in the last two decades suggest that FSGS is a defect of the podocyte. The therapeutic agents available for treatment of FSGS are not very effective and only a small percentage of affected individuals will achieve complete remission. Recent data from molecular biology and molecular genetics has provided insight into the mechanisms of action of old agents and also identification of other novel therapeutic targets. This review focuses on recent advances in the molecular pathogenesis of FSGS and currently available therapeutic agents as well as potential novel therapies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cameron JS (2003) Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in adults. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18 [Suppl 6]:vi45-vi51
Rich AR (1957) A hitherto undescribed vulnerability of the juxtamedullary glomeruli in lipoid nephrosis. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 100:173–186
Churg J, Habib R, White RH (1970) Pathology of the nephrotic syndrome in children: a report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet 760:1299–1302
Kitiyakara C, Kopp JB, Eggers P (2003) Trends in the epidemiology of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Semin Nephrol 23:172–182
U.S. Renal Data System (2007) USRDS 2007 Annual Data Report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD
Kitiyakara C, Eggers P, Kopp JB (2004) Twenty-one-year trend in ESRD due to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 44:815–825
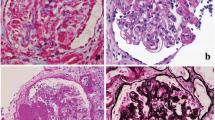
D’Agati VD, Fogo AB, Bruijn JA, Jennette JC (2004) Pathologic classification of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a working proposal. Am J Kidney Dis 43:368–382
Stokes MB, Valeri AM, Markowitz GS, D’Agati VD (2006) Cellular focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: clinical and pathologic features. Kidney Int 70:1783–1792
Deegens JK, Steenbergen EJ, Borm GF, Wetzels JF (2008) Pathological variants of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in an adult Dutch population—epidemiology and outcome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:186–192
Silverstein DM, Craver R (2007) Presenting features and short-term outcome according to pathologic variant in childhood primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2:700–707
Canaud G, Dion D, Zuber J, Gubler MC, Sberro R, Thervet E, Snanoudj R, Charbit M, Salomon R, Martinez F, Legendre C, Noel LH, Niaudet P (2010) Recurrence of nephrotic syndrome after transplantation in a mixed population of children and adults: course of glomerular lesions and value of the Columbia classification of histological variants of focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Nephrol Dial Transplant 55:558–565
Johnstone DB, Holzman LB (2006) Clinical impact of research on the podocyte slit diaphragm. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 2:271–282
Smoyer WE, Mundel P (1998) Regulation of podocyte structure during the development of nephrotic syndrome. J Mol Med 76:172–183
White RH, Glasgow EF, Mills RJ (1970) Clinicopathological study of nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet 1:1353–1359
Haraldsson B, Nyström J, Deen WM (2008) Properties of the glomerular barrier and mechanisms of proteinuria. Physiol Rev 88:451–487
Partanen TA, Arola J, Saaristo A, Jussila L, Ora A, Miettinen M, Stacker SA, Achen MG, Alitalo K (2000) VEGF-C and VEGF-D expression in neuroendocrine cells and their receptor, VEGFR-3, in fenestrated blood vessels in human tissues. FASEB J 14:2087–2096
Rostgaard J, Qvortrup K (2002) Sieve plugs in fenestrae of glomerular capillaries—site of the filtration barrier? Cells Tissues Organs 170:132–138
Weinbaum S, Tarbell JM, Damiano ER (2007) The structure and function of the endothelial glycocalyx layer. Annu Rev Biomed 9:121–167
Ballermann BJ, Stan RV (2007) Resolved: capillary endothelium is a major contributor to the glomerular filtration barrier. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2432–2438
Vaughan MR, Quaggin SE (2008) How do mesangial and endothelial cells form the glomerular tuft? J Am Soc Nephrol 19:24–33
Shalhoub RJ (1974) Pathogenesis of lipoid nephrosis: a disorder of T-cell function. Lancet 2:556–560
Savin VJ, Sharma R, Sharma M, McCarthy ET, Swan SK, Ellis E, Lovell H, Warady B, Gunwar S, Chonko AM, Artero M, Vincenti F (1996) Circulating factor associated with increased glomerular permeability to albumin in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med 334:878–883
Zenker M, Aigner T, Wendler O, Tralau T, Müntefering H, Fenski R, Pitz S, Schumacher V, Royer-Pokora B, Wühl E, Cochat P, Bouvier R, Kraus C, Mark K, Madlon H, Dötsch J, Rascher W, Maruniak-Chudek I, Lennert T, Neumann LM, Reis A (2004) Human laminin beta2 deficiency causes congenital nephrosis with mesangial sclerosis and distinct eye abnormalities. Hum Mol Genet 13:2625–2632
Karnovsky MJ, Ainsworth SK (1972) The structural basis of glomerular filtration. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp 2:35–60
Kestilä M, Lenkkeri U, Männikkö M, Lamerdin J, McCready P, Putaala H, Ruotsalainen V, Morita T, Nissinen M, Herva R, Kashtan CE, Peltonen L, Holmberg C, Olsen A, Tryggvason K (1998) Positionally cloned gene for a novel glomerular protein—nephrin—is mutated in congenital nephrotic syndrome. Mol Cell 1:575–582
Wiggins RC (2007) The spectrum of podocytopathies: a unifying view of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int 71:1205–1214
Kriz W (2003) The pathogenesis of ‘classic’ focal segmental glomerulosclerosis—lessons from rat models. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18 [Suppl 6]:vi39–vi44
Sato Y, Wharram BL, Lee SK, Wickman L, Goyal M, Venkatareddy M, Chang JW, Wiggins JE, Lienczewski C, Kretzler M, Wiggins RC (2009) Urine podocyte mRNAs mark progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:1041–1052
Wharram BL, Goyal M, Wiggins JE, Sanden SK, Hussain S, Filipiak WE, Saunders TL, Dysko RC, Kohno K, Holzman LB, Wiggins RC (2005) Podocyte depletion causes glomerulosclerosis: diphtheria toxin-induced podocyte depletion in rats expressing human diphtheria toxin receptor transgene. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2941–2952
Patrakka J, Tryggvason K (2009) New insights into the role of podocytes in proteinuria. Nat Rev Nephrol 5:463–468
Santín S, García-Maset R, Ruíz P, Giménez I, Zamora I, Peña A, Madrid A, Camacho JA, Fraga G, Sánchez-Moreno A, Cobo MA, Bernis C, Ortiz A, de Pablos AL, Pintos G, Justa ML, Hidalgo-Barquero E, Fernández-Llama P, Ballarín J, Ars E, Torra R, FSGS Spanish Study Group (2009) Nephrin mutations cause childhood- and adult-onset focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 76:1268–1276
Boute N, Gribouval O, Roselli S, Benessy F, Lee H, Fuchshuber A, Dahan K, Gubler MC, Niaudet P, Antignac C (2000) NPHS2, encoding the glomerular protein podocin, is mutated in autosomal recessive steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. Nat Genet 24:349–354
Roselli S, Gribouval O, Boute N, Sich M, Benessy F, Attié T, Gubler MC, Antignac C (2002) Podocin localizes in the kidney to the slit diaphragm area. Am J Pathol 160:131–139
Barletta GM, Kovari IA, Verma RK, Kerjaschki D, Holzman LB (2003) Nephrin and Neph1 co-localize at the podocyte foot process intercellular junction and form cis hetero-oligomers. J Biol Chem 278:19266–19271
Simons M, Schwarz K, Kriz W, Miettinen A, Reiser J, Mundel P, Holthöfer H (2001) Involvement of lipid rafts in nephrin phosphorylation and organization of the glomerular slit diaphragm. Am J Pathol 159:1069–1077
Schwarz K, Simons M, Reiser J, Saleem MA, Faul C, Kriz W, Shaw AS, Holzman LB, Mundel P (2001) Podocin, a raft-associated component of the glomerular slit diaphragm, interacts with CD2AP and nephrin. J Clin Invest 108:1621–1629
Harder T (2004) Lipid raft domains and protein networks in T-cell receptor signal transduction. Curr Opin Immunol 16:353–359
Simons K, Toomre D (2000) Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:31–39
Ruf RG, Lichtenberger A, Karle SM, Haas JP, Anacleto FE, Schultheiss M, Zalewski I, Imm A, Ruf EM, Mucha B, Bagga A, Neuhaus T, Fuchshuber A, Bakkaloglu A, Hildebrandt F, Arbeitsgemeinschaft Für Pädiatrische Nephrologie Study Group (2004) Patients with mutations in NPHS2 (podocin) do not respond to standard steroid treatment of nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:722–732
Machuca E, Hummel A, Nevo F, Dantal J, Martinez F, Al-Sabban E, Baudouin V, Abel L, Grünfeld JP, Antignac C (2009) Clinical and epidemiological assessment of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome associated with the NPHS2 R229Q variant. Kidney Int 75:727–735
Roselli S, Heidet L, Sich M, Henger A, Kretzler M, Gubler MC, Antignac C (2004) Early glomerular filtration defect and severe renal disease in podocin-deficient mice. Mol Cell Biol 24:550–560
Mollet G, Ratelade J, Boyer O, Muda AO, Morisset L, Lavin TA, Kitzis D, Dallman MJ, Bugeon L, Hubner N, Gubler MC, Antignac C, Esquivel EL (2009) Podocin inactivation in mature kidneys causes focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:2181–2189
Kaplan JM, Kim SH, North KN, Rennke H, Correia LA, Tong HQ, Mathis BJ, Rodríguez-Pérez JC, Allen PG, Beggs AH, Pollak MR (2000) Mutations in ACTN4, encoding alpha-actinin-4, cause familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 24:251–256
Yao J, Le TC, Kos CH, Henderson JM, Allen PG, Denker BM, Pollak MR (2004) Alpha-actinin-4-mediated FSGS: an inherited kidney disease caused by an aggregated and rapidly degraded cytoskeletal protein. PLoS Biol 2:e167
Michaud JL, Chaisson KM, Parks RJ, Kennedy CR (2006) FSGS-associated alpha-actinin-4 (K256E) impairs cytoskeletal dynamics in podocytes. Kidney Int 70:1054–1061
Winn MP, Conlon PJ, Lynn KL, Farrington MK, Creazzo T, Hawkins AF, Daskalakis N, Kwan SY, Ebersviller S, Burchette JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Howell DN, Vance JM, Rosenberg PB (2005) A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Science 308:1801–1804
Reiser J, Polu KR, Möller CC, Kenlan P, Altintas MM, Wei C, Faul C, Herbert S, Villegas I, Avila-Casado C, McGee M, Sugimoto H, Brown D, Kalluri R, Mundel P, Smith PL, Clapham DE, Pollak MR (2005) TRPC6 is a glomerular slit diaphragm-associated channel required for normal renal function. Nat Genet 37:739–744
Heeringa SF, Möller CC, Du J, Yue L, Hinkes B, Chernin G, Vlangos CN, Hoyer PF, Reiser J, Hildebrandt F (2009) A novel TRPC6 mutation that causes childhood FSGS. PLoS One 4:e7771
Zhu B, Chen N, Wang ZH, Pan XX, Ren H, Zhang W, Wang WM (2009) Identification and functional analysis of a novel TRPC6 mutation associated with late onset familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in Chinese patients. Mutat Res 664:84–90
Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strübing C (2001) The TRP ion channel family. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:387–396
Winn MP (2008) 2007 Young Investigator Award: TRP’ing into a new era for glomerular disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1071–1075
Möller CC, Wei C, Altintas MM, Li J, Greka A, Ohse T, Pippin JW, Rastaldi MP, Wawersik S, Schiavi S, Henger A, Kretzler M, Shankland SJ, Reiser J (2007) Induction of TRPC6 channel in acquired forms of proteinuric kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:29–36
Eckel J, Mukerji N, Lavin P, Ferimazova N, Gbadegesin R, Damodaran T, Bowling B, Wu G, Homstad A, Barisoni L, Bartkowiak B, Winn M (2009) TRPC6 deficiency does not cause glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:314A
Gbadegesin RA, Damodaran T, Homstad A, Bartkowiak B, Bowling B, Wu G, Lavin P, Eckel J, Mukerji N, Winn M (2009) TRPC6 gene dose ameliorates the course of puromycin induced kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:318A
Kim JM, Wu H, Green G, Winkler CA, Kopp JB, Miner JH, Unanue ER, Shaw AS (2003) CD2-associated protein haploinsufficiency is linked to glomerular disease susceptibility. Science 300:1298–1300
Wolf G, Stahl RA (2003) CD2-associated protein and glomerular disease. Lancet 362:1746–1748
Shih NY, Li J, Karpitskii V, Nguyen A, Dustin ML, Kanagawa O, Miner JH, Shaw AS (1999) Congenital nephrotic syndrome in mice lacking CD2-associated protein. Science 286:312–315
Löwik MM, Groenen PJ, Pronk I, Lilien MR, Goldschmeding R, Dijkman HB, Levtchenko EN, Monnens LA, van den Heuvel LP (2007) Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in a patient homozygous for a CD2AP mutation. Kidney Int 72:1198–1203
Gigante M, Pontrelli P, Montemurno E, Roca L, Aucella F, Penza R, Caridi G, Ranieri E, Ghiggeri GM, Gesualdo L (2009) CD2AP mutations are associated with sporadic nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:1858–1864
Niaudet P, Gubler MC (2006) WT1 and glomerular diseases. Pediatr Nephrol 21:1653–1660
Mucha B, Ozaltin F, Hinkes BG, Hasselbacher K, Ruf RG, Schultheiss M, Hangan D, Hoskins BE, Everding AS, Bogdanovic R, Seeman T, Hoppe B, Hildebrandt F, Members of the APN Study Group (2006) Mutations in the Wilms' tumor 1 gene cause isolated steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome and occur in exons 8 and 9. Pediatr Res 59:325–331
Hinkes B, Wiggins RC, Gbadegesin R, Vlangos CN, Seelow D, Nürnberg G, Garg P, Verma R, Chaib H, Hoskins BE, Ashraf S, Becker C, Hennies HC, Goyal M, Wharram BL, Schachter AD, Mudumana S, Drummond I, Kerjaschki D, Waldherr R, Dietrich A, Ozaltin F, Bakkaloglu A, Cleper R, Basel-Vanagaite L, Pohl M, Griebel M, Tsygin AN, Soylu A, Müller D, Sorli CS, Bunney TD, Katan M, Liu J, Attanasio M, O’Toole JF, Hasselbacher K, Mucha B, Otto EA, Airik R, Kispert A, Kelley GG, Smrcka AV, Gudermann T, Holzman LB, Nürnberg P, Hildebrandt F (2006) Positional cloning uncovers mutations in PLCE1 responsible for a nephrotic syndrome variant that may be reversible. Nat Genet 38:1397–1405
Gbadegesin R, Hinkes BG, Hoskins BE, Vlangos CN, Heeringa SF, Liu J, Loirat C, Ozaltin F, Hashmi S, Ulmer F, Cleper R, Ettenger R, Antignac C, Wiggins RC, Zenker M, Hildebrandt F (2008) Mutations in PLCE1 are a major cause of isolated diffuse mesangial sclerosis (IDMS). Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:1291–1297
Gilbert RD, Turner CL, Gibson J, Bass PS, Haq MR, Cross E, Bunyan DJ, Collins AR, Tapper WJ, Needell JC, Dell B, Morton NE, Temple IK, Robinson DO (2009) Mutations in phospholipase C epsilon 1 are not sufficient to cause diffuse mesangial sclerosis. Kidney Int 75:415–419
Boyer O, Benoit G, Gribouval O, Nevo F, Pawtowski A, Bilge I, Bircan Z, Deschênes G, Guay-Woodford LM, Hall M, Macher MA, Soulami K, Stefanidis CJ, Weiss R, Loirat C, Gubler MC, Antignac C (2010) Mutational analysis of the PLCE1 gene in steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome. J Med Genet 47:45–52
Wing MR, Bourdon DM, Harden TK (2003) PLC-epsilon: a shared effector protein in Ras-, Rho-, and G alpha beta gamma-mediated signaling. Mol Interv 3:273–280
Hasselbacher K, Wiggins RC, Matejas V, Hinkes BG, Mucha B, Hoskins BE, Ozaltin F, Nürnberg G, Becker C, Hangan D, Pohl M, Kuwertz-Bröking E, Griebel M, Schumacher V, Royer-Pokora B, Bakkaloglu A, Nürnberg P, Zenker M, Hildebrandt F (2006) Recessive missense mutations in LAMB2 expand the clinical spectrum of LAMB2-associated disorders. Kidney Int 70:1008–1012
Brown EJ, Schlöndorff JS, Becker DJ, Tsukaguchi H, Uscinski AL, Higgs HN, Henderson JM, Pollak MR (2010) Mutations in the formin gene INF2 cause focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 42:72–76
Kopp JB, Smith MW, Nelson GW, Johnson RC, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, Oleksyk T, McKenzie LM, Kajiyama H, Ahuja TS, Berns JS, Briggs W, Cho ME, Dart RA, Kimmel PL, Korbet SM, Michel DM, Mokrzycki MH, Schelling JR, Simon E, Trachtman H, Vlahov D, Winkler CA (2008) MYH9 is a major-effect risk gene for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet 40:1175–1184
Kao WH, Klag MJ, Meoni LA, Reich D, Berthier-Schaad Y, Li M, Coresh J, Patterson N, Tandon A, Powe NR, Fink NE, Sadler JH, Weir MR, Abboud HE, Adler SG, Divers J, Iyengar SK, Freedman BI, Kimmel PL, Knowler WC, Kohn OF, Kramp K, Leehey DJ, Nicholas SB, Pahl MV, Schelling JR, Sedor JR, Thornley-Brown D, Winkler CA, Smith MW, Parekh RS, Family Investigation of Nephropathy and Diabetes Research Group (2008) MYH9 is associated with nondiabetic end-stage renal disease in African Americans. Nat Genet 40:1185–1192
Behar DM, Rosset S, Tzur S, Selig S, Yudkovsky G, Bercovici S, Kopp JB, Winkler CA, Nelson GW, Wasser WG, Skorecki K (2010) African ancestry allelic variation at the MYH9 gene contributes to increased susceptibility to non-diabetic end-stage kidney disease in Hispanic Americans. Hum Mol Genet 19:1816–1827
Franceschini N, Voruganti VS, Haack K, Almasy L, Laston S, Goring HH, Umans JG, Lee ET, Best LG, Fabsitz RR, MacCluer JW, Howard BV, North KE, Cole SA (2010) The association of the MYH9 gene and kidney outcomes in American Indians: the Strong Heart Family Study. Hum Genet 127:295–301
Ghiggeri GM, Caridi G, Magrini U, Sessa A, Savoia A, Seri M, Pecci A, Romagnoli R, Gangarossa S, Noris P, Sartore S, Necchi V, Ravazzolo R, Balduini CL (2003) Genetics, clinical and pathological features of glomerulonephritis associated with mutations of nonmuscle myosin IIA (Fechtner syndrome). Am J Kidney Dis 41:95–104
Dong F, Li S, Pujol-Moix N, Luban NL, Shin SW, Seo JH, Ruiz-Saez A, Demeter J, Langdon S, Kelley MJ (2005) Genotype-phenotype correlation in MYH9-related thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol 130:620–627
Genovese G, Friedman DJ, Ross MD, Lecordier L, Uzureau P, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, Langefeld CD, Oleksyk TK, Uscinski Knob AL, Bernhardy AJ, Hicks PJ, Nelson GW, Vanhollebeke B, Winkler CA, Kopp JB, Pays E, Pollak MR (2010) Association of trypanolytic ApoL1 variants with kidney disease in African Americans. Science 329:841–845
Dreyer SD, Zhou G, Baldini A, Winterpacht A, Zabel B, Cole W, Johnson RL, Lee B (1998) Mutations in LMX1B cause abnormal skeletal patterning and renal dysplasia in nail patella syndrome. Nat Genet 19:47–50
Boerkoel CF, Takashima H, John J, Yan J, Stankiewicz P, Rosenbarker L, André JL, Bogdanovic R, Burguet A, Cockfield S, Cordeiro I, Fründ S, Illies F, Joseph M, Kaitila I, Lama G, Loirat C, McLeod DR, Milford DV, Petty EM, Rodrigo F, Saraiva JM, Schmidt B, Smith GC, Spranger J, Stein A, Thiele H, Tizard J, Weksberg R, Lupski JR, Stockton DW (2002) Mutant chromatin remodeling protein SMARCAL1 causes Schimke immuno-osseous dysplasia. Nat Genet 30:215–220
Berkovic SF, Dibbens LM, Oshlack A, Silver JD, Katerelos M, Vears DF, Lüllmann-Rauch R, Blanz J, Zhang KW, Stankovich J, Kalnins RM, Dowling JP, Andermann E, Andermann F, Faldini E, D’Hooge R, Vadlamudi L, Macdonell RA, Hodgson BL, Bayly MA, Savige J, Mulley JC, Smyth GK, Power DA, Saftig P, Bahlo M (2008) Array-based gene discovery with three unrelated subjects shows SCARB2/LIMP-2 deficiency causes myoclonus epilepsy and glomerulosclerosis. Am J Hum Genet 82:673–684
ISKDC (1978) Nephrotic syndrome in children: prediction of histopathology from clinical and laboratory characteristics at time of diagnosis. A report of the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Kidney Int 13:159–165
Mendoza SA, Tune BM (1992) Treatment of childhood nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 3:889–894
Tune BM, Mendoza SA (1997) Treatment of the idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: regimens and outcomes in children and adults. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:824–832
Xing CY, Saleem MA, Coward RJ, Ni L, Witherden IR, Mathieson PW (2006) Direct effects of dexamethasone on human podocytes. Kidney Int 70:1038–1045
Ransom RF, Lam NG, Hallett MA, Atkinson SJ, Smoyer WE (2005) Glucocorticoids protect and enhance recovery of cultured murine podocytes via actin filament stabilization. Kidney Int 68:2473–2483
Zietse R, Wenting GJ, Kramer P, Schalekamp MA, Weimar W (1992) Effects of cyclosporin A on glomerular barrier function in the nephrotic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 82:641–650
Faul C, Donnelly M, Merscher-Gomez S, Chang YH, Franz S, Delfgaauw J, Chang JM, Choi HY, Campbell KN, Kim K, Reiser J, Mundel P (2008) The actin cytoskeleton of kidney podocytes is a direct target of the antiproteinuric effect of cyclosporine A. Nat Med 14:931–938
Hodson EM, Willis NS, Craig JC (2008) Non-corticosteroid treatment for nephrotic syndrome in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD002290
Mahmoud I, Basuni F, Sabry A, El-Husseini A, Hassan N, Ahmad NS, Elbaz M, Moustafa F, Sobh M (2005) Single-centre experience with cyclosporin in 106 children with idiopathic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:735–742
Cattran DC, Alexopoulos E, Heering P, Hoyer PF, Johnston A, Meyrier A, Ponticelli C, Saito T, Choukroun G, Nachman P, Praga M, Yoshikawa N (2007) Cyclosporin in idiopathic glomerular disease associated with the nephrotic syndrome: workshop recommendations. Kidney Int 72:1429–1447
Xia Z, Liu G, Gao Y, Fan Z, Fu Y, Zhang LF, Ren X, Gao C (2006) FK506 in the treatment of children with nephrotic syndrome of different pathological types. Clin Nephrol 66:85–88
Cattran DC, Appel GB, Hebert LA, Hunsicker LG, Pohl MA, Hoy WE, Maxwell DR, Kunis CL (1999) A randomized trial of cyclosporine in patients with steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. North America Nephrotic Syndrome Study Group. Kidney Int 56:2220–2226
Ziswiler R, Steinmann-Niggli K, Kappeler A, Daniel C, Marti HP (1998) Mycophenolic acid: a new approach to the therapy of experimental mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2055–2066
Hauser IA, Renders L, Radeke HH, Sterzel RB, Goppelt-Struebe M (1999) Mycophenolate mofetil inhibits rat and human mesangial cell proliferation by guanosine depletion. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:58–63
Penny MJ, Boyd RA, Hall BM (1998) Mycophenolate mofetil prevents the induction of active Heymann nephritis: association with Th2 cytokine inhibition. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:2272–2282
Allison AC, Kowalski WJ, Muller CJ, Waters RV, Eugui EM (1993) Mycophenolic acid and brequinar, inhibitors of purine and pyrimidine synthesis, block the glycosylation of adhesion molecules. Transplant Proc 25:67–70
Cattran DC, Wang MM, Appel G, Matalon A, Briggs W (2004) Mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin Nephrol 62:405–411
Montané B, Abitbol C, Chandar J, Strauss J, Zilleruelo G (2003) Novel therapy of focal glomerulosclerosis with mycophenolate and angiotensin blockade. Pediatr Nephrol 18:772–777
Marasà M, Kopp JB (2009) Monoclonal antibodies for podocytopathies: rationale and clinical responses. Nat Rev Nephrol 5:337–348
Guigonis V, Dallocchio A, Baudouin V, Dehennault M, Hachon-Le Camus C, Afanetti M, Groothoff J, Llanas B, Niaudet P, Nivet H, Raynaud N, Taque S, Ronco P, Bouissou F (2008) Rituximab treatment for severe steroid- or cyclosporine-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentric series of 22 cases. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1269–1279
Fernandez-Fresnedo G, Segarra A, González E, Alexandru S, Delgado R, Ramos N, Egido J, Praga M, Trabajo de Enfermedades Glomerulares de la Sociedad Española de Nefrología (GLOSEN) (2009) Rituximab treatment of adult patients with steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1317–1323
Joy MS, Gipson DS, Powell L, MacHardy J, Jennette JC, Vento S, Pan C, Savin V, Eddy A, Fogo AB, Kopp JB, Cattran D, Trachtman H (2010) Phase 1 trial of adalimumab in Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). II. Report of the FONT (Novel Therapies for Resistant FSGS) study group. Am J Kidney Dis 55:50–60
Peyser A, Machardy N, Tarapore F, Machardy J, Powell L, Gipson DS, Savin V, Pan C, Kump T, Vento S, Trachtman H (2010) Follow-up of phase I trial of adalimumab and rosiglitazone in FSGS. III. Report of the FONT study group. BMC Nephrol 11:2
Joy MS, Gipson DS, Dike M, Powell L, Thompson A, Vento S, Eddy A, Fogo AB, Kopp JB, Cattran D, Trachtman H (2009) Phase I trial of rosiglitazone in FSGS. I. Report of the FONT Study Group. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:39–47
Savin VJ, McCarthy ET, Sharma R, Charba D, Sharma M (2008) Galactose binds to focal segmental glomerulosclerosis permeability factor and inhibits its activity. Transl Res 151:288–292
De Smet E, Rioux JP, Ammann H, Déziel C, Quérin S (2009) FSGS permeability factor-associated nephrotic syndrome: remission after oral galactose therapy. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:2938–2940
Lavin P, Gbadegesin R, Damodaran TV, Winn MP (2008) Therapeutic targets in focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:386–392
Garg P, Verma R, Nihalani D, Johnstone DB, Holzman LB (2007) Neph1 cooperates with nephrin to transduce a signal that induces actin polymerization. Mol Cell Biol 27:8698–8712
Galeano B, Klootwijk R, Manoli I, Sun M, Ciccone C, Darvish D, Starost MF, Zerfas PM, Hoffmann VJ, Hoogstraten-Miller S, Krasnewich DM, Gahl WA, Huizing M (2007) Mutation in the key enzyme of sialic acid biosynthesis causes severe glomerular proteinuria and is rescued by N-acetylmannosamine. J Clin Invest 117:1585–1594
Vogelmann SU, Nelson WJ, Myers BD, Lemley KV (2003) Urinary excretion of viable podocytes in health and renal disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F40–F48
Prodromidi EI, Poulsom R, Jeffery R, Roufosse CA, Pollard PJ, Pusey CD, Cook HT (2006) Bone marrow-derived cells contribute to podocyte regeneration and amelioration of renal disease in a mouse model of Alport syndrome. Stem Cells 24:2448–2455
Ronconi E, Sagrinati C, Angelotti ML, Lazzeri E, Mazzinghi B, Ballerini L, Parente E, Becherucci F, Gacci M, Carini M, Maggi E, Serio M, Vannelli GB, Lasagni L, Romagnani S, Romagnani P (2009) Regeneration of glomerular podocytes by human renal progenitors. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:322–332
Appel D, Kershaw DB, Smeets B, Yuan G, Fuss A, Frye B, Elger M, Kriz W, Floege J, Moeller MJ (2009) Recruitment of podocytes from glomerular parietal epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:333–343
Little MH, Bertram JF (2009) Is there such a thing as a renal stem cell? J Am Soc Nephrol 20:2112–2117
Le Berre L, Bruneau S, Naulet J, Renaudin K, Buzelin F, Usal C, Smit H, Condamine T, Soulillou JP, Dantal J (2009) Induction of T regulatory cells attenuates idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:57–67
Acknowledgements
Funding
NIH K08DK082495-01 and grants from the Nephcure foundation to RG. RG is a recipient of a Doris Duke Clinical Scientist Development Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gbadegesin, R., Lavin, P., Foreman, J. et al. Pathogenesis and therapy of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: an update. Pediatr Nephrol 26, 1001–1015 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-010-1692-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-010-1692-x