Abstract
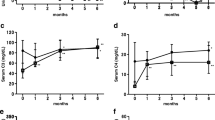
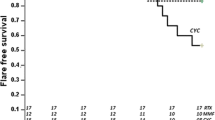
The initial treatment of childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is not standardized. Although corticosteroids are the first-line therapy for SLE, long-term, high-dose steroid therapy is associated with various side effects in children. The Japanese Study Group for Renal Disease in Children (JSRDC) has carried out a multi-center, randomized, controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of corticosteroid and mizoribine (MZB) therapy as an initial treatment for newly diagnosed juvenile SLE. Twenty-eight patients were treated with a combination steroid and MZB (4–5 mg/kg/day) (group S+M) drug therapeutic regimen, while 29 patients were treated with steroid only (group S); both groups were followed up for 1 year. The time to the first flare from treatment initiation was not significantly different between the two groups (Kaplan–Meier method, p = 0.09). During the period when the steroid was given daily (day 0–183), the time to the first flare from treatment initiation was significantly longer in the patients of group S+M than in those of group S (log-rank test, p = 0.02). At the end of the study period, there were no differences in the severity of proteinuria and renal function impairment between the two groups. No patients dropped out of the trial due to adverse events. In conclusion, our combined steroid and MZB drug therapeutic regimen was not shown to be significantly better than the steroid-only therapy as initial treatment for juvenile SLE. Whether MZB administered in a higher dose would be therapeutically advantageous can only be answered by further studies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klein-Gitelman M, Reiff A, Silverman ED (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus in childhood. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 28:561–577
Stichweh D, Arce E, Pascual V (2004) Update on pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 16:577–587
Ausin HA, Balow JE (2000) Treatment of lupus nephritis. Semin Nephrol 20:265–276
Bounpas DT, Austin HA III, Vaughn EM, Klippel JH, Steinberg AD, Yarboro CH, Balow JE (1992) Controlled trial of pulse cyclophosphamide in severe lupus nephritis. Lancet 340:741–745
Bansal VK, Beto JA (1997) Treatment of Lupus Nephritis: A meta-analysis of clinical trial. Am J Kidney Dis 29:193–199
Flanc RS, Roberts MA, Strippoli GF, Chadban SJ, Kerr PG, Atkins RC (2004) Treatment for lupus nephritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD002922
Carneiro JR, Sato EI (1999) Double blind, randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial of methotrexate in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 26:1275–1279
Nwobi O, Abitbol CL, Chandear J, Seeherunvong W, Zilleruelo G (2008) Rituximab therapy for juvenile-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatr Nephrol 23:413–419
Bijl M, Horst G, Bootsma H, Limbug PC, Kallenberg CG (2003) Mycophenolate mofetil prevents a clinical relapse in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus at risk. Ann Rheum Dis 62:534–539
Chan TM, Li FK, Tang CS, Wong RW, Fang GX, Ji YL, Lau CS, Wong AK, Tong MK, Chan KW, Lai KN (2000) Efficacy of Mycophenolate Mofetil in patients with diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med 343:1156–1162
Katsifis GE, Tzioufas AG (2004) Ovarian failure in systemic lupus erythematosus patients treated with pulsed intravenous cyclophosphamide. Lupus 13:673–678
Yokota S (2002) Mizoribine: mode of action and effects in clinical use. Pediatr Int 44:196–198
Aihara Y, Miyamae T, Ito S, Kobayashi S, Imagawa T, Mori M, Ibe M, Mitsuda T, Yokota S (2002) Mizoribin as an effective combined maintenance therapy with prednisolone in child-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatr Int 44:199–204
Tanaka H, Tsugawa K, Suzuki K, Nakahata T, Ito E (2006) Long-term mizoribin intermittent pulse therapy for young patients with flare of lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 21:962–966
Honda M (2002) Nephrotic syndrome and mizoribine in children. Pediatr Int 44:210–216
Goto M, Ikeda M, Hataya H, Ishikura K, Hamasaki Y, Honda M (2006) Beneficial and adverse effects of high-dosage Mizoribin therapy in the management of children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome. Nihon Jinzo Gakkaishi 48:365–370
Nagaoka R, Kaneko K, Ohtomo Y, Yamashiro Y (2002) Mizoribine treatment for childhood IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Int 44:217–223
Yoshioka K, Ohashi Y, Sakai T, Ito H, Yoshikawa N, Nakamura H, Tanizawa T, Wada H, Maki S (2000) A multicenter trial of mizoribine compared with placebo in children with frequently relapsing nephritic syndrome. Kidney Int 58:317–324
Tsuzuki K (2002) Role of mizoribine in renal transplantation. Pediatr Int 44:224–231
Takei S (2002) Mizoribine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr Int 44:205–209
Hiramoto R, Honda M (1997) Initial treatment of 54 pediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosis. In: The 32nd Annual Meeting Japanese Society for Pediatric Nephrology, Tokyo
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the patients and physicians who participated in this trial: H. Tochimaru (Hokkaido), M. Awazu (Tokyo), T. Ogata (Tokyo), J. Miyamoto (Tokyo), K. Ishikura (Tokyo), N. Yata (Tokyo), T. Shijyaku (Kanagawa), A. Saito (Kanagawa), R. Hiramoto (Chiba), C. Nakahara (Ibaragi), K.Tamura (Ibaragi), Y. Kamiyama (Tochighi), T. Miura (Tochigi), Y. Kobayashi (Tochigi), A. Yoshino (Saitama), K. Obata (Saitama), S. Amemiya (Yamanashi), K. Higashida (Yamanashi), K. Iijima (Hyougo), H. Miyamoto (Hyougo), K. Shimomiya (Hyougo), H.Nozu (Hyougo), K.Ohta (Hyougo), Y. Ito (Fukuoka), K. Hatae (Fukuoka), C. Sato (Saga) and A. Furuse (Kumamoto).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1411-7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, Y., Yoshikawa, N., Hattori, S. et al. Combination therapy with steroids and mizoribine in juvenile SLE: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Nephrol 25, 877–882 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1341-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-009-1341-4