Abstract
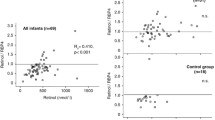
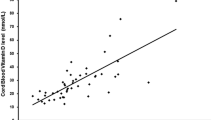
Vitamin A (VA) deficiency in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants is associated with an increased risk for disorders related to kidney and lung maturation and function. VA losses through increased urinary retinol (ROH) excretion might contribute to this deficiency risk. The mechanism accounting for ROH loss in the urine has not yet been clarified. The aim of this study was to assess the excretion of ROH, retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) and transthyretin (TTR) in urine from VLBW infants in comparison with that in term infants in relation to kidney function. Urine specimens were collected from 15 VLBW infants (birth weight < 1,500 g) as well as from 20 term infants during the first 2 days after birth. ROH in urine was detectable in 14 of the 15 VLBW infants at a median concentration of 234 nmol/g creatinine. In the group of term infants, 17 of the 20 excreted ROH, but at an approximately five-times lower concentration (P < 0.001). Excretion of RBP4 and TTR was also much higher in VLBW infants (both P< 0.001). The urinary ROH excretion in VLBW infants may be related to the impaired tubular handling of its carrier proteins RBP4 and TTR. Thus, ROH excretion might contribute to an increased risk of VA deficiency, especially in VLBW infants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chailley-Heu B, Chelly N, Lelievre-Pegorier M, Barlier-Mur AM, Merlet-Benichou C, Bourbon JR (1999) Mild vitamin A deficiency delays fetal lung maturation in the rat. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 21:89–96
Biesalski HK, Nohr D (2003) Importance of vitamin-A for lung function and development. Mol Aspects Med 24:431–440
Baybutt RC, Hu L, Molteni A (2000) Vitamin A deficiency injures lung and liver parenchyma and impairs function of rat type II pneumocytes. J Nutr 130:1159–1165
D’Angio CT, Maniscalco WM (2004) Bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants: pathophysiology and management strategies. Paediatr Drugs 6:303–330
Woodruff CW, Latham CB, Mactier H, Hewett JE (1987) Vitamin A status of preterm infants: correlation between plasma retinol concentration and retinol dose response. Am J Clin Nutr 46:985–988
Tyson JE, Wright LL, Oh W, Kennedy KA, Mele L, Ehrenkranz RA, Stoll BJ, Lemons JA, Stevenson DK, Bauer CR, Korones SB, Fanaroff AA (1999) Vitamin A supplementation for extremely-low-birth-weight infants. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. N Engl J Med 340:1962–1968
Shenai JP, Kennedy KA, Chytil F, Stahlman MT (1987) Clinical trial of vitamin A supplementation in infants susceptible to bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr 111:269–277
Blomhoff R, Green MH, Berg T, Norum KR (1990) Transport and storage of vitamin A. Science 250:399–404
Gerlach TH, Zile MH (1991) Metabolism and secretion of retinol transport complex in acute renal failure. J Lipid Res 32:515–520
Stephensen CB (2001) Vitamin A, infection, and immune function. Annu Rev Nutr 21:167–192
Rosales FJ, Ross AC (1998) A low molar ratio of retinol binding protein to transthyretin indicates vitamin A deficiency during inflammation: studies in rats and a posterior analysis of vitamin A-supplemented children with measles. J Nutr 128:1681–1687
Naylor HM, Newcomer ME (1999) The structure of human retinol-binding protein (RBP) with its carrier protein transthyretin reveals an interaction with the carboxy terminus of RBP. Biochemistry 38:2647–2653
Blaner WS (1989) Retinol-binding protein: the serum transport protein for vitamin A. Endocr Rev 10:308–316
Zanotti G, Berni R (2004) Plasma retinol-binding protein: structure and interactions with retinol, retinoids, and transthyretin. Vitam Horm 69:271–295
Christensen EI, Moskaug JO, Vorum H, Jacobsen C, Gundersen TE, Nykjaer A, Blomhoff R, Willnow TE, Moestrup SK (1999) Evidence for an essential role of megalin in transepithelial transport of retinol. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:685–695
Raila J, Willnow TE, Schweigert FJ (2005) Megalin-mediated reuptake of retinol in the kidneys of mice is essential for vitamin A homeostasis. J Nutr 135:2512–2516
Raila J, Wirth K, Chen F, Buscher U, Dudenhausen JW, Schweigert FJ (2004) Excretion of vitamin A in urine of women during normal pregnancy and pregnancy complications. Ann Nutr Metab 48:357–364
Schweigert FJ, Raila J, Sehouli J, Buscher U (2004) Accumulation of selected carotenoids, alpha-tocopherol and retinol in human ovarian carcinoma ascitic fluid. Ann Nutr Metab 48:241–245
Raila J, Henze A, Spranger J, Mohlig M, Pfeiffer AF, Schweigert FJ (2007) Microalbuminuria is a major determinant of elevated plasma retinol-binding protein 4 in type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney Int 72:505–511
Siegenthaler G, Saurat JH (1987) A slab gel electrophoresis technique for measurement of plasma retinol-binding protein, cellular retinol-binding and retinoic-acid-binding proteins in human skin. Eur J Biochem 166:209–214
Darlow BA, Graham PJ (2002) Vitamin A supplementation for preventing morbidity and mortality in very low birthweight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD000501
Sasanow SR, Spitzer AR, Pereira GR, Heaf L, Watkins JB (1986) Effect of gestational age upon prealbumin and retinol binding protein in preterm and term infants. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 5:111–115
Quadro L, Hamberger L, Gottesman ME, Wang F, Colantuoni V, Blaner WS, Mendelsohn CL (2005) Pathways of vitamin A delivery to the embryo: insights from a new tunable model of embryonic vitamin A deficiency. Endocrinology 146:4479–4490
Schweigert FJ (2001) Inflammation-induced changes in the nutritional biomarkers serum retinol and carotenoids. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 4:477–481
Mitra AK, Alvarez JO, Stephensen CB (1998) Increased urinary retinol loss in children with severe infections. Lancet 351:1033–1034
Stephensen CB, Alvarez JO, Kohatsu J, Hardmeier R, Kennedy JI Jr, Gammon RB Jr (1994) Vitamin A is excreted in the urine during acute infection. Am J Clin Nutr 60:388–392
Bernard A, Vyskocyl A, Mahieu P, Lauwerys R (1988) Effect of renal insufficiency on the concentration of free retinol-binding protein in urine and serum. Clin Chim Acta 171:85–93
Gavrilov V, Yermiahu T, Gorodischer R (2006) Renal pathology and retinol status in multiple myeloma patients. Kidney Int 69:173–177
Hughson M, Farris AB 3rd, Douglas-Denton R, Hoy WE, Bertram JF (2003) Glomerular number and size in autopsy kidneys: the relationship to birth weight. Kidney Int 63:2113–2122
Dunnill MS, Halley W (1973) Some observations on the quantitative anatomy of the kidney. J Pathol 110:113–121
Fouser L, Avner ED (1993) Normal and abnormal nephrogenesis. Am J Kidney Dis 21:64–70
Guignard JP, Torrado A, Da Cunha O, Gautier E (1975) Glomerular filtration rate in the first three weeks of life. J Pediatr 87:268–272
Drukker A, Guignard JP (2002) Renal aspects of the term and preterm infant: a selective update. Curr Opin Pediatr 14:175–182
Hua MJ, Kun HY, Jie CS, Yun NZ, De WQ, Yang Z (1997) Urinary microalbumin and retinol-binding protein assay for verifying children’s nephron development and maturation. Clin Chim Acta 264:127–132
Clark PM, Bryant TN, Hall MA, Lowes JA, Rowe DJ (1989) Neonatal renal function assessment. Arch Dis Child 64:1264–1269
Fell JM, Thakkar H, Newman DJ, Price CP (1997) Measurement of albumin and low molecular weight proteins in the urine of newborn infants using a cotton wool ball collection method. Acta Paediatr 86:518–522
Zugaro A, Pandolfi C, Barbonetti A, Vassallo M, D’Angeli A, Necozione S, Colangeli M, Francavilla S, Francavilla F (2007) Retinol binding protein 4, low birth weight-related insulin resistance and hormonal contraception. Endocrine 32:166–169
American Academy of Pediatrics. Committee on Nutrition (1998) Nutritional needs of preterm infants. In: Kleinman RE (ed) Pediatric nutrition handbook, 4th edn. American Academy of Pediatrics, Elk Grove Village, IL, pp 55–87
Acknowledgment
We are indebted to the medical and nursing staff in the Department of Neonatology, Virchow Hospital, Charité, University Medicine Berlin. We thank A. Hurtienne and E. Pilz for their skillful analytical support. This work was supported by the European Commission (Sixth Framework Program, contract no. LSHM-CT-2006-036534).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagl, B., Loui, A., Raila, J. et al. Urinary vitamin A excretion in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Nephrol 24, 61–66 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0965-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0965-0