Abstract
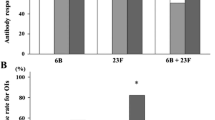
Our objective was to demonstrate that nephrotic children at disease onset and under high-dose prednisone respond to vaccination with 23-valent pneumococcal vaccine (PV). We compared the serological response after PV in 30 children with nephrotic syndrome, directly after initiation of prednisone therapy (60 mg/m2 body surface area) at disease onset (group 1), with the response in 13 patients who received the vaccine while in remission (group 2). Safety was studied, comparing disease course in group 1 with those in patients who did not receive any PV (group 3). In group 1, 23-valent PV antibody (Ab) levels increased tenfold after 1 month and remained increased after 1 year (P < 0.01). Ab response in the short term and in the long term was not different from that of patients in group 2. Serum albumin, age, or immunosuppressive drugs did not influence Ab response. Disease courses in groups 1 and 3 were not different. In conclusion, nephrotic children on high-dose glucocorticoid therapy respond to a 23-valent anti-PV. Children with steroid dependent/resistant forms acquire high Ab levels, even if early relapses delay the tapering of steroids or if immunosuppressive agents are introduced. Patients who relapse during the tapering of steroids already have increased anti-pneumococcal Ab at the time of relapse.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ab:
-
Antibody
- EOD:
-
Every other day
- NS:
-
Nephrotic syndrome
- PV:
-
Pneumococcal vaccine
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
References
van den Berg JG, Weening JJ (2004) Role of the immune system in the pathogenesis of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin Sci (Lond) 107:125–136
Krensky AM, Ingelfinger JR, Grupe WE (1982) Peritonitis in childhood nephrotic syndrome: 1970–1980. Am J Dis Child 136:732–736
Liponski I, Cochat P, Gagnadoux MF, Parchoux B, Niaudet P, David L, Broyer M (1995) Bacterial complications of nephrotic syndrome in children. Presse Med 24:19–22
Hsu K, Pelton S, Karumuri S, Heisey-Grove D, Klein J (2005) Population-based surveillance for childhood invasive pneumococcal disease in the era of conjugate vaccine. Pediatr Infect Dis J 24:17–23
Matsell DG, Roy S 3rd, Bin JA, Wyatt RJ (1990) Nephrosis, peritonitis and complement deficiency. Pediatr Nephrol 4:575
Winkelstein JA (1984) Complement and the host’s defense against the pneumococcus. Crit Rev Microbiol 11:187–208
Ilyas M, Roy S 3rd, Abbasi S, Leggiadro RJ, English BK, Wyatt RJ (1996) Serious infections due to penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in two children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 10:639–641
Whitney CG, Farley MM, Hadler J, Harrison LH, Lexau C, Reingold A, Lefkowitz L, Cieslak PR, Cetron M, Zell ER, Jorgensen JH, Schuchat A (2000) Increasing prevalence of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in the United States. N Engl J Med 343:1917–1924
Abeyagunawardena AS, Goldblatt D, Andrews N, Trompeter RS (2003) Risk of relapse after meningococcal C conjugate vaccine in nephrotic syndrome. Lancet 362:449–450
Guven AG, Akman S, Bahat E, Senyurt M, Yuzbey S, Uguz A, Yegin O (2004) Rapid decline of anti-pneumococcal antibody levels in nephrotic children. Pediatr Nephrol 19:61–65
Spika JS, Halsey NA, Fish AJ, Lum GM, Lauer BA, Schiffman G, Giebink GS (1982) Serum antibody response to pneumococcal vaccine in children with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatrics 69:219–223
Lahood N, Emerson SS, Kumar P, Sorensen RU (1993) Antibody levels and response to pneumococcal vaccine in steroid-dependent asthma. Ann Allergy 70:289–294
Kemper MJ, Meyer-Jark T, Lilova M, Muller-Wiefel DE (2003) Combined T- and B-cell activation in childhood steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol 60:242–247
Wilkes JC, Nelson JD, Worthen HG, Morris M, Hogg RJ (1982) Response to pneumococcal vaccination in children with nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 2:43–46
Hammitt LL, Bruden DL, Butler JC, Baggett HC, Hurlburt DA, Reasonover A, Hennessy TW (2006) Indirect effect of conjugate vaccine on adult carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae: an explanation of trends in invasive pneumococcal disease. J Infect Dis 193:1487–1494
Millar EV, O’Brien KL, Watt JP, Bronsdon MA, Dallas J, Whitney CG, Reid R, Santosham M (2006) Effect of community-wide conjugate pneumococcal vaccine use in infancy on nasopharyngeal carriage through 3 years of age: a cross-sectional study in a high-risk population. Clin Infect Dis 43:8–15
Hanage WP, Huang SS, Lipsitch M, Bishop CJ, Godoy D, Pelton SI, Goldstein R, Huot H, Finkelstein JA (2007) Diversity and antibiotic resistance among nonvaccine serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae carriage isolates in the post-heptavalent conjugate vaccine era. J Infect Dis 195:347–352
Veenhoven RH, Bogaert D, Schilder AG, Rijkers GT, Uiterwaal CS, Kiezebrink HH, van Kempen MJ, Dhooge IJ, Bruin J, Ijzerman EP, de Groot R, Kuis W, Hermans PW, Sanders EA (2004) Nasopharyngeal pneumococcal carriage after combined pneumococcal conjugate and polysaccharide vaccination in children with a history of recurrent acute otitis media. Clin Infect Dis 39:911–919
Millar EV, O’Brien KL, Bronsdon MA, Madore D, Hackell JG, Reid R, Santosham M (2007) Anticapsular serum antibody concentration and protection against pneumococcal colonization among children vaccinated with 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Clin Infect Dis 44:1173–1179
Romero-Steiner S, Musher DM, Cetron MS, Pais LB, Groover JE, Fiore AE, Plikaytis BD, Carlone GM (1999) Reduction in functional antibody activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae in vaccinated elderly individuals highly correlates with decreased IgG antibody avidity. Clin Infect Dis 29:281–288
Cunard R, Kelly CJ (2002) T cells and minimal change disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1409–1411
Sahali D, Pawlak A, Valanciute A, Grimbert P, Lang P, Remy P, Bensman A, Guellaen G (2002) A novel approach to investigation of the pathogenesis of active minimal-change nephrotic syndrome using subtracted cDNA library screening. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1238–1247
Mansour H, Cheval L, Elalouf JM, Aude JC, Alyanakian MA, Mougenot B, Doucet A, Deschenes G (2005) T-cell transcriptome analysis points up a thymic disorder in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 67:2168–2177
Jefferson T, Demicheli V (2002) Polysaccharide pneumococcal vaccines. BMJ 325:292–293
Jackson LA, Benson P, Sneller VP, Butler JC, Thompson RS, Chen RT, Lewis LS, Carlone G, DeStefano F, Holder P, Lezhava T, Williams WW (1999) Safety of revaccination with pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine. JAMA 281:243–248
Vernacchio L, Neufeld EJ, MacDonald K, Kurth S, Murakami S, Hohne C, King M, Molrine D (1998) Combined schedule of 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine followed by 23-valent pneumococcal vaccine in children and young adults with sickle cell disease. J Pediatr 133:275–278
Obaro SK, Huo Z, Banya WA, Henderson DC, Monteil MA, Leach A, Greenwood BM (1997) A glycoprotein pneumococcal conjugate vaccine primes for antibody responses to a pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine in Gambian children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 16:1135–1140
Obaro S, Adegbola R (2002) The pneumococcus: carriage, disease and conjugate vaccines. J Med Microbiol 51:98–104
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Nadjette Mourdi for help with covariance analysis and Marie-José Costantini for secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulinski, T., Leroy, S., Dubrel, M. et al. High serological response to pneumococcal vaccine in nephrotic children at disease onset on high-dose prednisone. Pediatr Nephrol 23, 1107–1113 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0782-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0782-5