Abstract
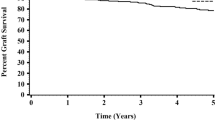
Evaluation of the impact of live unrelated kidney donor (LURD) source on the outcome of renal transplantation is not adequately studied. We aimed to compare the long-term outcome of kidney transplantation from LURDs to that from living related donors (LRDs) among a pediatric recipient population. This study comprised 235 pediatric recipients who received their kidney grafts between 1976 and 2005 at our center. These patients were further subdivided into two groups according to donor source (211 with LRDs) and (24 with LURDs). All patients’ data were assessed with special emphasis on graft and patient survival as well as posttransplant medical complications. Both groups were comparable regarding graft and patient survival at 1, 5, and 10 years. Despite higher incidence of acute vascular rejection among recipients with LURD (12%) vs. LRD (2.8%) (P = 0.03), there was no difference in the incidence of chronic allograft nephropathy. Moreover, the overall incidence of posttransplant complications was comparable among the two groups. In our series, kidney survival was poorer in LURDs compared with LRDs. However, the number of patients with LURD was small, and the difference in results was also small and justifies LURD in exceptional cases when LRD is not possible.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chkhotua AB, Klein T, Shabtai E, Yussim A, Bar-Nathan N, Shaharabani E, Lustig S, Mor E (2003) Kidney transplantation from living-unrelated donors: comparison of outcome with living-related and cadaveric transplants under current immunosuppressive protocols. Urology 62:1002–1006
Salahudeen AK, Woods HF, Pingle A, Nur-El-Huda Suleyman M, Shakuntala K, Nandakumar M, Yahya TM, Daar AS (1990) High mortality among recipients of bought living-unrelated donor kidneys. Lancet 336:725–728
Cameron JS, Hoffenberg R (1999) The ethics of organ transplantation reconsidered: Paid organ donation and the use of executed prisoners as donors. Kidney Int 55:724–732
Sever MS, Kazancioğlu R, Yildiz A, Türkmen A, Ecder T, Kayacan SM, Celik V, Sahin S, Aydin AE, Eldegez U, Ark E (2001) Outcome of living unrelated (commercial) renal transplantation. Kidney Int 60:1477–1483
Levey AS, Hou S, Bush HL Jr (1986) Kidney transplantation from unrelated living donors. Time to reclaim a discarded opportunity. N Engl J Med 314:914–916
Cortesinin R, Berloco P, Famulari A (1988) Long term results in recipients of mismatched related and unrelated living kidneys in the cyclosporine age. Transplant Proc 20:41–42
Matas AJ, Payne WD, Sutherland DE, Humar A, Gruessner RW, Kandaswamy R, Dunn DL, Gillingham KJ, Najarian JS (2001) 2,500 Living donor kidney transplants: a single-center experience. Ann Surg 234:149–164
Foss A, Leivestad T, Brekke IB, Fauchald P, Bentdal O, Lien B, Pfeffer P, Sødal G, Albrechtsen D, Søreide O, Flatmark A (1998) Unrelated living donors in 141 kidney transplantations: a one-center study. Transplantation 66:49–52
Racusen LC, Solez K, Colvin RB, Bonsib SM, Castro MC,Cavallo T, Croker BP, Demetris AJ, Drachenberg CB, Fogo AB, Furness P, Gaber LW, Gibson IW, Glotz D, Goldberg JC, Grande J, Halloran PF, Hansen HE, Hartley B, Hayry PJ, Hill CM, Hoffman EO, Hunsicker LG, Lindblad AS, Marcussen N, Mihatsch MJ, Nadasdy T, Nickerson P, Olsen TS, Papadimitriou JC, Randhawa PS, Rayner DC, Roberts I, Rose S, Rush D, Salinas-Madrigal L, Salomon DR, Sund S, Taskinen E, Trpkov K, Yamaguchi Y (1999) The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney Int 55:713–723
Daar AS, Land W, Yahya TM, Schneewind K, Gutmann T, Jakobsen A (1997) Living-donor renal transplantation: evidence-based justification for an ethical option. Transplant Rev 11:95
Spital A (1998) Unconventional living kidney donors. In: Touraine JL, Traeger J, Bétuel H, Dubernard JM, Revillard JP, Dupuy C (eds) Organ allocation. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, p 297
Evans M (1989) Organ donations should not be restricted to relatives. J Med Ethics 15:17–20
Cecka JM (1999) Results of more than 1000 recent living-unrelated donor transplants in the U.S. Transplant Proc 31:234
Cortesini R, Pretagostini R, Bruzzone P, Alfani D (2002) Living unrelated kidney transplantation. World J Surg 26:238–242
Phadke K, Iyengar A, Karthik S, Kumar A, Olakkengil S (2006) Pediatric renal transplantation: The Bangalore Experience. Indian Pediatr 43:44–48
Sesso R, Josephson MA, Anção MS, Draibe SA, Sigulem D (1998) A retrospective study of kidney transplant recipients from living unrelated donors. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:684–691
Ishikawa N, Tanabe K, Tokumoto T, Shimmura H, Yagisawa T, Nakajima I, Fuchinoue S, Agishi T, Toma H (1999) Long-term results of living unrelated renal transplantation. Transplant Proc 31:2856–2857
Prommool S, Jhangri GS, Cockfield SM, Halloran PF (2000) Time dependency of factors affecting renal allograft survival. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:565–573
Fuller TF, Feng S, Brennan TV, Tomlanovich S, Bostrom A, Freise CE (2004) Increased rejection in living unrelated versus living related kidney transplants does not affect short-term function and survival. Transplantation 78:1030–1035
Al-Uzri A, Sullivan EK, Fine RN, Harmon WE (1998) Living-unrelated renal transplantation in children: a report of the North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS). Pediatr Transplant 2:139–144
Humar A, Durand B, Gillingham K, Payne WD, Sutherland DE, Matas AJ (2000) Living unrelated donors in kidney transplants: better long-term results than with non-HLA-identical living related donors? Transplantation 69:1942–1945
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gheith, O., Sabry, A., El-Baset, S.A. et al. Study of the effect of donor source on graft and patient survival in pediatric renal transplant recipients. Pediatr Nephrol 23, 2075–2079 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0760-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-008-0760-y